Abstract
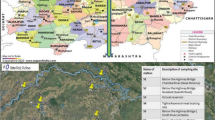
Wei River is the major source of water for the urban residents, industrial production and agricultural activities in the central Shaanxi plain of China. Water quality of the Wei River was determined by collecting water samples from 25 locations along the Baoji Xi’an reach and analyzing for pH, EC, BOD5, DO, COD, F, Se, As, and Hg. Fuzzy synthetic evaluation with the entropy method for weight determination was used to assess the water quality of the river. Results indicate that the water quality of 23 sampling sites fall into the fifth grade (bad level), whereas two sampling sites are in the fourth grade (poor level). The comparison of this method with the typical fuzzy synthetic evaluation shows that it is effective in water quality assessment. The assessment results indicate that the Wei River is heavily polluted at most of the sampling locations, with mercury as the major pollutant. Strict enforcement of the regulations for domestic and industrial wastewater discharges is vital to avoid damage to the water environment and to protect human and ecological health.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chang NB, Chen HW, Ning SK (2001) Identification of river water quality using the fuzzy synthetic evaluation approach. J Environ Manag 63:293–305. doi:10.1006/jema.2001.0483
Charkhabi AH, Sakizadeh M (2006) Assessment of spatial variation of water quality parameters in the most polluted branch of the Anzali Wetland, Northern Iran. Polish J Environ Stud 15(3):395–403
Chinese Environmental Protection Agency (2002a) Technical specifications requirements for monitoring of surface water and waste water (HJ/T91-2002). China Environment Press, Beijing (in Chinese)
Chinese Environmental Protection Agency (2002b) National surface water environmental quality standards of China (GB3838-2002). China Standards Press, Beijing (in Chinese)
Croke BEW, Ticehurst JL, Letcher RA, Norton JP, Newham LTH, Jakeman AJ (2007) Integrated assessment of water resources: Australian experiences. Water Resour Manag 21:351–373. doi:10.1007/s11269-006-9057-8
Cude CO (2001) Water quality index: a tool for evaluating water quality management effectiveness. J Am Water Resour Assoc 37:125–137. doi:10.1111/j.1752-1688.2001.tb05480.x
Dahiya S, Singh B, Gaur S, Garg VK, Kushwaha HS (2007) Analysis of groundwater quality using fuzzy synthetic evaluation. J Hazard Mater 147:938–946. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.01.119
Fisher B (2003) Fuzzy environmental decision-making: applications to air pollution. Atmos Environ 37:1865–1877. doi:10.1016/S1352-2310(03)00028-1
Haiyan W (2002) Assessment and prediction of overall environmental quality of Zhuzhou city, Hunan province, China. J Environ Manag 66:329–340
Icaga Y (2007) Fuzzy evaluation of water quality classification. Ecol Indic 7:710–718. doi:10.1016/j.ecolind.2006.08.002
Nasiri F, Maqsood I, Huang G, Fuller N (2007) Water quality index: a fuzzy river-pollution decision support expert system. J Water Resour Plan Manag 133(2):95–105. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9496(2007)133:2(95)
Onkal-Engin G, Demir I, Hiz H (2004) Assessment of urban air quality in Istanbul using fuzzy synthetic evaluation. Atmos Environ 38:3809–3815. doi:10.1016/j.atmosenv.2004.03.058
Shen G, Lu Y, Wang M, Sun Y (2005) Status and fuzzy comprehensive assessment of combined heavy metal and organo-chlorine pesticide pollution in the Taihu Lake region of China. J Environ Manag 76:355–362. doi:10.1016/j.jenvman.2005.02.011
Singh B, Dahiya S, Jain S, Garg VK, Kushwaha HS (2008) Use of fuzzy synthetic evolution for assessment of groundwater quality for drinking usage: a case study of Southern Haryana, India. Environ Geol 54:249–255. doi:10.1007/s00254-007-0812-9
Sudheer KP, Chaubey I, Garg V (2006) Lake water quality assessment from landsat thematic mapper data using neural network: an approach to optimal band combination selection. J Am Water Resour Assoc 42:1683–1695. doi:10.1111/j.1752-1688.2006.tb06029.x
Wang HM, Lu WX, Xin G, Wang HX (2007) Application of grey clustering methods for surface water quality evaluation. Water Sav Irriga 5:20–22 (in Chinese)
Yang XY (2002) The issue and actions of water resource exploitation and usage in irrigation area of Wei River valley. Shaanxi Water Resour 4:24–25 (in Chinese)
Yang HJ, Shen ZM, Zhang JP, Wang WH (2007) Water quality characteristics along the course of the Huangpu River (China). J Environ Sci 19:1193–1198. doi:10.1016/S1001-0742(07)60195-8
Zou ZH, Yun Y, Sun JN (2006) Entropy method for determination of weight of evaluating indicators in fuzzy synthetic evaluation for water quality assessment. J Environ Sci 18:1020–1023. doi:10.1016/S1001-0742(06)60032-6
Acknowledgments
The research was supported by the Program for New Century Excellent Talents in University under Grant NCET-05-0861, and the Provincial Natural Sciences Foundation of Shaanxi Province under Grant 2006D14.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, X., Li, L.Y., Lei, K. et al. Water quality assessment of Wei River, China using fuzzy synthetic evaluation. Environ Earth Sci 60, 1693–1699 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-009-0303-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-009-0303-2