Abstract
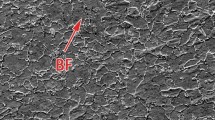
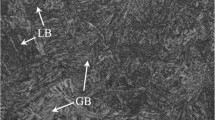
Physical weld simulation for single and two-pass weld of a HY 85 steel has been done using thermo mechanical simulator at constant heat input of 22 kJ/cm. Attempt has been made to investigate the causes behind the deterioration of mechanical properties in the coarse grain heat affected zone (CGHAZ) in single pass and subsequent improvement in the mechanical properties of CGHAZ region in the two-pass weld. HY 85 steel finds wide applications in the making of ship hull. Impact toughness at −50 °C for CGHAZ in the single pass weld has been found to be 49 J. However, impact toughness improves to 122 J in the super critical reheated CGHAZ region for two-pass weld. This improvement in the impact toughness has been observed due to reaustenitization of fine prior austenite grains of average size of 44 µm from 99 µm, refinement of bainitic ferrite lath, and M–A constituents during second pass weld.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kumar S, Nath S K, and Kumar V, Mater Perform Charact ASTM 4 (2015) 365.
Ghosh A, Kundu S, and Chatterjee S, Def Sci J 57 (2007) 627.
Cho G, International Conference Exploiting Advances in Arc Welding Technology, in: Abington Publishing, Cambridge UK, 1998: p 191.
Hu J, Du L X, Wang J J, and Gao C R, Mater Sci Eng A 577 (2013) 161.
Basu B, and Raman R, Weld J 81 (2002) 239s.
Guo A, Misra R D K, Liu J, Chen L, He X, and Jansto S J, Mater Sci Eng A 527 (2010) 6440.
You Y, Shang C, Chen L, and Subramanian S, Mater Des 43 (2013) 485.
Amer A E, Koo M Y, Lee K H, Kim S H, and Hong S H, J Mater Sci 45 (2010) 1248.
Lan L, Qiu C, Zhao D, Gao X, and Du L, Mater Sci Eng A 558 (2012) 592.
Matusuda F, Ikeuchi K, Fukada Y, Horii Y, Okada H, and Shiwaku T, Trans JWRI 24 (1995) 1.
Moeinifar S, Kokabi A H, and Hosseini H R M, Mater Des 32 (2011) 869.
Liu W Y, Wang L, Liu J B, Zhang Y Y, Li P H, and Yuan G L, J Iron Steel Res Int 14 (2007) 220.
Zhang Y Q, Zhang H Q, Li J F, and Liu W M, J Iron Steel Res Int 16 (2009) 73.
Hu J, Du L X, Wang J J, Xie H, Gao C R, and Misra R D K, Mater Sci Eng A 590 (2014) 323.
Kim S, Kang D, Kim T W, Lee J, and Lee C, Mater Sci Eng A 528 (2011) 2331.
Kumar S, Chaudhari G P, Nath S K, and Basu B, Mater Manuf Process 27 (2012) 1382.
Zhang Z, Hauge M, Thaulow C, and Ødegård J, Eng Fract Mech 69 (2002) 353.
Hairer F, Karelova A, Krempaszky C, Werner E, Hebesberger T, and Pichler A, Int. Doctoral Seminar, Smolenice, SK (2008) 50.
Girault E, Jacques P, Harlet P, Mols K, Humbeeck J V, and Aernoudt E, Mater Charact 40 (1998) 111.
Kumar S, Nath S K, and Kumar V, Mater Des 90 (2016) 177.
Yue X, Weld World 59 (2015) 77.
Hu J, Du L X, Xie H, Dong F T, and Misra R D K, Mater Des 60 (2014) 302.
Bhadeshia H K D H, Mater Sci Eng A 273–275 (1999) 58.
da Junior Cruz J A, and Santos D B, J Mater Res Technol 2 (2013) 93.
Kong X, and Qiu C, J Mater Sci Technol 29 (2013) 446.
Wang X L, Wang X M, Shang C J, and Misra R D K, Mater Sci Eng A 649 (2016) 282.
Lan L, Qiu C L, Zhao D W, Gao X H, and Du L X, Mater Sci Technol 27 (2011) 1657.
Bu F Z, Wang X M, Chen L, Yang S W, Shang C J, and Misra R D K, Mater Charact 102 (2015) 146.
Lan L, Qiu C, Zhao D, Gao X, and Du L, J Mater Sci 47 (2012) 4732.
Sakino Y and Kim Y C, Int J Steel Struct 13 (2013) 21.
Moeinifar S, Kokabi A H, and Hosseini H R M, Mater Des (2010) 2948.
Suzuki S, Bessyo K, Toyoda M, Minami F, and Japan Q, J Weld Soc 13 (1995) 293.
Liu W Y, Liu J B, Zhu C M, and Wang H, Adv Mater Res 228–229 (2011) 1196.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the Department of Science and Technology (DST) New Delhi for purchasing Thermo-mechanical simulator Gleeble®3800 in IIT Roorkee from FIST grant (SR/FST/ETI-216/2007 Dated 06.02.2008).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, S., Nath, S.K. Effect of Weld Thermal Cycles on Microstructures and Mechanical Properties in Simulated Heat Affected Zone of a HY 85 Steel. Trans Indian Inst Met 70, 239–250 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-016-0880-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-016-0880-1