Abstract
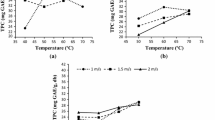
Three distinct drying methods, microwave drying (MWD), convective drying (CVD) and microwave-convective drying (MWCVD) with a grinding process were applied to obtain pumpkin powder. The effects of CVD (60, 70 & 80 °C), MWD (100 & 200 W) and MWCVD (100 W-60 °C, 100 W-70 °C, 100 W-80 °C, 200 W-60 °C, 200 W-70 °C, and 200 W-80 °C) applications on the physicochemical properties (water activity, bulk, tapped & particle densities, porosity, flowability, cohesiveness, swelling capacity, water holding capacity and water solubility index), color values (L*, a*, b*, C, αo and Δe), bioactive compounds (5-Hydroxymethyl-2-furfural (HMF), total phenolic content (TPC) and antioxidant capacity (DPPH and ABTS)) of the eleven pumpkin fruit powders were compared. The MWCVD, namely pumpkin powders dried at 200 W–80 °C resulted in shorter drying times with high‐quality dried pumpkin powders. The bulk, tapped and particle densities of pumpkin powders at 200 W-80 °C by MWCVD were 0.56, 0.66 and 1.74 g/cm3, respectively. These values are indicators of the good porosity (61.82%) of pumpkin powders. In addition, the highest TPC (1277.08 mg GA/100 g dw) and ABTS (126.99 ± 3.31 µmol Trolox/g dw) was observed for microwave-convective dried pumpkin powders at 200 W-80 °C. On the other hand, the lowest HMF level (10.12 ± 1.78 mg/kg dw) was found for the pumpkin poowders dried by MWCVD at 200 W-80 °C. In overall, dried pumpkin powders by a MWCVD method can be employed to acquire a high-quality food material along with an enhanced physicochemical properties, color and bioactive components.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- MWD:
-
Microwave drying
- CVD:
-
Convective drying
- MWCVD:
-
Microwave‐convective drying
- HMF:
-
5-Hydroxymethyl-2-furfural
- TPC:
-
Total phenolic content
References
Abdullah EC, Geldart D (1999) The use of bulk density measurements as flowability indicators. Powder Technol 102:151–165. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0032-5910(98)00208-3
Anderson RA (1982) Water absorption and solubility and amylograph characteristics on roll-cooked small grain products. Cereal Chem 59:265–269
Brand-Williams W, Cuvelier ME, Berset CLWT (1995) Use of a free radical method to evaluate antioxidant activity. LWT-Food Sci Technol 28(1):25–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0023-6438(95)80008-5
Carr RL (1965) Evaluating flow properties of solids. Chem Eng 72(2):163–168
Cemeroğlu B (2010) Food analysis. Association of Food Technology Publications, Ankara, p 657
De Medeiros ACL, Thomazini M, Urbano A, Correia RTP, Favaro-Trindade CS (2014) Structural characterisation and cell viability of a spray dried probiotic yoghurt produced with goats’ milk and Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis (BI-07). Int Dairy J 39(1):71–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.idairyj.2014.05.008
Dewanto V, Wu X, Adom KK, Liu RH (2002) Thermal processing enhances the nutritional value of tomatoes by increasing total antioxidant activity. J Agric Food Chem 50(10):3010–3014. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf0115589
Di Scala K, Vega-Gálvez A, Uribe E, Oyanadel R, Miranda M, Vergara J, Quispe I (2011) Changes of quality characteristics of pepino fruit (Solanum muricatum Ait) during convective drying. Int J Food Sci Technol 46(4):746–753. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2621.2011.02555.x
Escalada MF, Ponce NM, Stortz CA, GerschensonRojas LNAM (2007) Composition and functional properties of enriched fiber products obtained from pumpkin (Cucurbita moschata Duchesne ex Poiret). LWT-Food Sci Technol 40(7):1176–1185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2006.08.006
Fennema O, Hui J, Karel M (2004) Handbook of vegetable preservation and processing. Marcel Dekker, New York
Fernandes FAN, Gallão MI, Rodrigues S (2008) Effect of osmotic dehydration and ultrasound pretreatment on cell structure: Melon dehydration. LWT-Food Sci Technol 41:604–610. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2007.05.007
Ferrari CC, Germer SPM, Alvim ID, Vissotto FZ, Aguirre JM (2012) Influence of carrier agents on the physicochemical properties of blackberry powder produced by spray drying. Int J Food Sci Technol 47:1237–1245
Fitzpatrick J (2013) Powder properties in food production systems. Handbook of food powders processes and properties. Woodhead Publishing, Cambridge, pp 285–308
Franco TS, Perussello CA, Ellendersen LN, Masson ML (2016) Effects of foam mat drying on physicochemical and microstructural properties of yacon juice powder. LWT-Food Sci Technol 66:503–513. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2015.11.009
Guiné RP, Barroca MJ (2012) Effect of drying treatments on texture and color of vegetables (pumpkin and green pepper). Food Bioprod Process 90(1):58–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fbp.2011.01.003
Hausner HH (1967) Friction conditions in a mass of metal powder. Int J Powder Metall 3:7–13
Hebbar HU, Nandini KE, Lakshmi MC, Subramanian R (2003) Microwave and infrared heat processing of honey and its quality. Food Sci Technol Res 9:49–53. https://doi.org/10.3136/fstr.9.49
İzli N, Yıldız G, Ünal H, Işık E, Uylaşer V (2014) Effect of different drying methods on drying characteristics, colour, total phenolic content and antioxidant capacity of Goldenberry (Physalis peruviana L.). Int J Food Sci 49(1):9–17. https://doi.org/10.1111/ijfs.12266
Kim EHJ, Chen XD, Pearce D (2002) Surface characterization of four industrial spray-dried powders in relation to chemical composition, structure and wetting property. Colloid Surf B 26:197–212. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0927-7765(01)00334-4
Kowalski S, Szadzińska J (2014) Convective-intermittent drying of cherries preceded by ultrasonic assisted osmotic dehydration. Chem Eng Process: Process Intensification 82:65–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cep.2014.05.006
Kroh LW (1994) Caramelisation in food and beverages. Food Chem 51:373–379. https://doi.org/10.1016/0308-8146(94)90188-0
Larrauri JA, Rupérez P, Saura-Calixto F (1997) Effect of drying temperature on the stability of polyphenols and antioxidant activity of red grape pomace peels. J Agric Food Chem 45:1390–1393. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf960282f
Lecumberri E, Mateos R, Izquierdo-Pulido M, Rupérez P, Goya L, Bravo L (2007) Dietary fibre composition, antioxidant capacity and physico-chemical properties of a fibre-rich product from cocoa (Theebroma cacao L.). Food Chem 104:948–954. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2006.12.054
Michalska A, Wojdyło A, Lech K, Łysiak GP, Figiel A (2016) Physicochemical properties of whole fruit plum powders obtained using different drying technologies. Food Chem 207:223–232. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2016.03.075
Monteiro RL, Link JV, Tribuzi G, Carciofi BAM, Laurindo JB (2018) Microwave vacuum drying and multi-flash drying of pumpkin slices. J Food Eng 232:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2018.03.015
Nawirska-Olszańska A, Stepien B, Biesiada A (2017) Effectiveness of the fountain-microwave drying method in some selected pumpkin cultivars. LWT- Food Sci Technol 77:276–281. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2016.11.067
Niro Atomizer S, Copenhagen D (1978) Determination of particle density, content of occluded air and interstitial air. In: Sørensen IH, Krag J, Pisecky J, Westergaard V (eds) Analytical methods for dry milk products, 4th edn. De Forenede Trykkerier A/S, Copenhagen, pp 52–53
Opalic M, Domitran Z, Komes D, Belšcak A, Horžic D, Karlovic D (2009) The effect of ultrasound pre-treatment and air-drying on the quality of dried apples. J Food Sci 27:297–300. https://doi.org/10.17221/606-CJFS
Orsat V, Raghavan V, Meda V (2005) Microwave technology for food processing: an overview. In: Schubert H, Regier M (eds) The microwave processing of foods. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 105–118
Rada-Mendoza M, Luz Sanz M, Olano A, Villamiel M (2004) Formation of hydroxymethylfurfural and furosine during the storage of jams and fruit-based infant foods. Food Chem 85:605–609. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2003.07.002
Re R, Pellegrini N, Proteggente A, Pannala A, Yang M, Rice-Evans C (1999) Antioxidant activity applying an improved ABTS radical cation decolorization assay. Free Radic Biol Med 26(9–10):1231–1237. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0891-5849(98)00315-3
Sacilik K, Elicin AK (2006) The thin layer drying characteristics of organic apple slices. J Food Eng 73:281–289. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2005.03.024
Seremet L, Botez E, Nistor OV, Andronoiu DG, Mocanu GD (2016) Effect of different drying methods on moisture ratio and rehydration of pumpkin slices. Food Chem 195:104–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2015.03.125
Serpen A, Gökmen V, Fogliano V (2012) Total antioxidant capacities of raw and cooked meats. Meat Sci 90(1):60–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.meatsci.2011.05.027
Singleton VL, Orthofer R, Lamuela-Raventos RM (1999) Analysis of total phenols and other oxidation substrates and antioxidants by means of Folin-Ciocalteau reagent. Methods Enzymol 299:152–178. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0076-6879(99)99017-1
Sultana B, Anwar F, Ashraf M, Saari N (2012) Effect of drying techniques on the total phenolic contents and antioxidant activity of selected fruits. J Med Plants Res 6:161–167. https://doi.org/10.5897/JMPR11.916
Szulc K, Lenart A (2012) Water vapour adsorption propetries of aggwlomerated baby food powders. J Food Eng 109:135–141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2011.09.023
Vadivambal R, Jayas DS (2007) Changes in quality of microwave-treated agricultural products—a review. Biosyst Eng 98:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biosystemseng.2007.06.006
Yıldız G, İzli G (2020) Microwave and convective drying methods on food drying. IKSAD International Publishing House, Ankara, Turkey
Yildiz G, Izli G (2019) Influence of microwave and microwave-convective drying on the drying kinetics and quality characteristics of pomelo. J Food Process Preserv 43(6):e13812. https://doi.org/10.1111/jfpp.13812
Yıldız G, İzli N, Ünal H, Uylaşer V (2015) Physical and chemical characteristics of goldenberry fruit (Physalis peruviana L.). J Food Sci Technol 52(4):2320–2327. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-014-1280-3
Zanoelo EF, Cardozo-Filho L, Cardozo-Junior EL (2006) Superheated steamdrying of mate leaves and effect of drying conditions on the phenol content. J Food Process Eng 29(3):253–268. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1745-4530.2006.00064.x
Zhang Z, Song H, Peng Z, Luo Q, Ming J, Zhao G (2012) Characterization of stipe and cap powders of mushroom (Lentinus edodes) prepared by different grinding methods. J Food Eng 109:406–413. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2011.11.007
Acknowledgements
We are thankful to the Bursa Technical University Experiment Station for affording lab space and equipment for the necessary experiments.
Funding
This research received no specific grant from any funding agency in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Gl: Conceptualization, methodology, data curation, writing, GY: writing—review and editing, SEB: methodology.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There is no conflict of interest to report for the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
İzli, G., Yildiz, G. & Berk, S.E. Quality retention in pumpkin powder dried by combined microwave-convective drying. J Food Sci Technol 59, 1558–1569 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-021-05167-5
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-021-05167-5