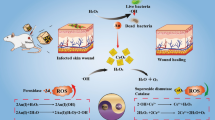
Abstract
Infection and colony formation by microbes has been a negative consequence in wound care. Graphene oxide (GO) has a large surface area and it is biocompatible. Zinc oxide (ZnO) exhibits antimicrobial activity against various infectious microbes. In GO/ZnO nanocomposite, ZnO nanoparticle is homogeneously supported on the GO sheet. It controls the infection in wound area and promotes angiogenesis. The synthesized nanocomposite was characterized using XRD, FTIR, Raman Spectroscopy, UV-DRS, FESEM with EDS, TEM and ICP-OES. Antibacterial activity was studied using the well diffusion method, growth curve, death kinetics, sensitivity coefficient, biofilm inhibition and colony counting method. Reactive oxygen species assay (ROS), lactate dehydrogenase leakage assay (LDH) and DNA fragmentation studies were done to analyze the mechanism of inhibition of nanocomposite against bacteria. A hemolytic study was done to confirm the blood biocompatibility of the nanocomposites. The mechanism of bacterial inhibition is by the production of ROS, loss of membrane integrity, not by DNA fragmentation. The nanocomposites enhanced its antibacterial activity in the presence of visible light compared to dark conditions.



















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Archana S, Kumar KY, Jayanna BK, Olivera S, Anand A, Prashanth MK, Muralidhara HB (2018) Versatile graphene oxide decorated by star shaped zinc oxide nanocomposites with superior adsorption capacity and antimicrobial activity. J Sci Adv Mater Devices 3(2):167–174. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsamd.2018.02.002
Baskar K, Anusuya T, Devanand Venkatasubbu G (2017) Mechanistic investigation on microbial toxicity of nano hydroxyapatite on implant associated pathogens. Mater Sci Eng, C 73:8–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2016.12.060
Beggs CB, Noakes CJ, Sleigh PA, Fletcher LA, Kerr KG (2006) Methodology for determining the susceptibility of airborne microorganisms to irradiation by an upper-room UVGI system. J Aerosol Sci 37(7):885–902. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaerosci.2005.08.002
Bhaisare ML, Wu BS, Wu MC, Khan MS, Tsengb MH, Wu HF (2016) MALDI MS analysis, disk diffusion and optical density measurements for the antimicrobial effect of zinc oxide nanorods integrated in graphene oxide nanostructures. Biomater Sci 4(1):183–194. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5bm00342c
Burlui V, Popa M, Cadinoiu AN, Stadoleanu C, Mihalache G, Zamaru V, Dartu L, Folescu E, Rata DM (2015) Physico-chemical characterization and in vitro hemolysis evaluation of titanium dioxide nanoparticles. Biomaterials 5(2):124–130
Chen D, Wang D, Ge Q, Ping G, Fan M, Qin L, Bai L, Lv C, Shu K (2015) Graphene-wrapped ZnO nanospheres as a photocatalyst for high performance photocatalysis. Thin Solid Films 574:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tsf.2014.11.051
Devanand Venkatasubbu G, Anusuya T (2017) Investigation on curcumin nanocomposite for wound dressing. Int J Biol Macromol 98:366–378. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.02.002
Devanand Venkatasubbu G, Baskar R, Anusuya T, Seshan CA, Chelliah R (2016) Toxicity mechanism of titanium dioxide and zinc oxide nanoparticles against food pathogens. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 148:600–606. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2016.09.042
Devanand Venkatasubbu G, Nagamuthu S, Anusuya T, Kumar J, Chelliah R, Ramakrishnan SR, Antony U, Khan I, Deog-Hwan Oh (2018) TiO2 nanocomposite for the controlled release of drugs against Pathogens causing Wound Infections. Mater Res Express 5(2):024003. https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/aaa936
Fani S, Kamalidehghan B, Lo KM, Hashim NM, Chow KM, Ahmadipour F (2015) Synthesis, structural characterization, and anticancer activity of a monobenzyltin compound against MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Drug Des Dev Ther 9:6191–6201. https://doi.org/10.2147/dddt.s87064
Faria AFD, Moraes ACMD, Marcato PD, Martinez DST, Duran N, Filho AGS, Brandelli A, Alves OL (2014) Eco-friendly decoration of graphene oxide with biogenic silver nanoparticles: antibacterial and antibiofilm activity. J Nanopart Res 16(2):2110. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-013-2110-7
Fu PP, Xia Q, Hwang HM, Ray PC, Yu H (2014) Mechanisms of nanotoxicity: generation of reactive oxygen species. J Food Drug Anal 22(1):64–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfda.2014.01.005
Hosseini SA, Babaei S (2017) Graphene oxide/zinc oxide (GO/ZnO) nanocomposite as a superior photocatalyst for degradation of methylene blue (MB)-process modeling by response surface methodology (RSM). J Braz Chem Soc 28:299–307. https://doi.org/10.5935/0103-5053.20160176
Huang K, Li YH, Lin S, Liang C, Wang H, Ye CX, Wang YJ, Zhang R, Fan DY, Yang HJ, Wang YG, Lei M (2014a) A facile route to reduced graphene oxide–zinc oxide nanorod composites with enhanced photocatalytic activity. Powder Technol 257:113–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2014.02.047
Huang Y, Wang T, Zhao X, Wang X, Zhou L, Yang Y, Liao F, Ju Y (2014b) Poly(lactic acid)/graphene oxide–ZnO nanocomposite films with good mechanical, dynamic mechanical, anti-UV and antibacterial properties. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 90(9):1677–1684. https://doi.org/10.1002/jctb.4476
Jayabal P, Gayathri S, Sasirekha V, Mayandi J, Ramakrishnan V (2014) Preparation and characterization of ZnO/Graphene nanocomposite for improved photovoltaic performance. J Nanoparticle Res 16(11):12640. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-014-2640-7
Jayanti DN, Nugraheni AY, Kurniasari Baqiya MA, Darminto B (2017) Photoluminescence of reduced graphene oxide prepared from old coconut shell with carbonization process at varying temperatures. IOP Conf Series Mater Sci Eng 196:012005. https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899x/196/1/012005
Kaushik M, Niranjan R, Thangam R, Madhan B, Pandiyarasan V, Ramachandran C, Deog-Hwan Oh, Devanand Venkatasubbu G (2019) Investigation on the antimicrobial activity and wound healing potential of ZnO nanoparticles. Appl Surf Sci 479:1169–1177. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.02.189
Kavitha T, Gopalan AI, Lee KP, Park SY (2012) Glucose sensing, photocatalytic and antibacterial properties of graphene–ZnO nanoparticle hybrids. Carbon 50(8):2994–3000. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2012.02.082
Khand MS, Abdelhamida HN, Hui-Fen Wu (2015) Near infrared (NIR) laser mediated surface activation of graphene oxide nanoflakes for efficient antibacterial, antifungal and wound healing treatment. Colloid Surf B Biointerfaces 127:281–291. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2014.12.049
Liu Y, He L, Mustapha A, Li H, Hu ZQ, Lin M (2009) Antibacterial activities of zinc oxide nanoparticles against Escherichia coli O157:H7. J Appl Microbio 107:1193–1201. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2672.2009.04303.x
Liu S, Cao S, Guo J, Luo L, Zhou Y, Lin C, Shi J, Fan C, Lv M, Wang L (2018) Graphene oxide-silver nanocomposites modulate the biofilm formation and extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) production. Nanoscale 10:19603–19611. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8nr04064h
Manikandan E, Kavitha G, Kennedy J (2014) Epitaxial zinc oxide, graphene oxide composite thin-films by laser technique for micro-Raman and enhanced field emission study. Ceram Int 40(10):16065–16070. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2014.07.129
Moraes ACMD, Lima BA, Faria AFD, Brocchi M, Alves OL (2015) Graphene oxide-silver nanocomposite as a promising biocidal agent against methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Int J Nanomed 10:6847–6861. https://doi.org/10.2147/ijn.s90660
Mu H, Tang JJ, Liu Q, Sun C, Wang T, Duan J (2016) Potent antibacterial nanoparticles against biofilm and intracellular bacteria. Sci Rep 6(1):18877. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep18877
Padmanabhan A, Kaushik M, Niranjan R, Richards JS, Ebright B, Devanand Venkatasubbu G (2019) Zinc oxide nanoparticles induce oxidative and proteotoxic stress in ovarian cancer cells and trigger apoptosis independent of p53-mutation status. Appl Sur Sci 487:807–818. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.05.099
Paula R, Gayenb RN, Biswasc S, Bhatd SV, Bhunia R (2016) Enhanced UV detection by transparent graphene oxide/ZnO composite thin films. RSC Adv 6(66):61661–61672. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6ra05039e
Pereira MF, Silva-Neta AR, Farias AFF, Souza AG, Fonseca MG, Pontes LFBL, Santos IMG (2017) Pure and Al-doped ZnO obtained by the modified Pechini method applied in ethanolic transesterification of cotton seed oil. Ceramica 63:82–89. https://doi.org/10.1590/0366-69132017633652066
Prakash J, Venkatesan M, Bharath G, Anwer S, Pandiyarasan V, Prema D, Venkataprasanna KS, Devanand Venkatasubbu G (2019) Investigations on the in vivo toxicity analysis of reduced graphene oxide/TiO2 nanocomposite in zebrafish embryo and larvae (Danio rerio). Appl Surf Sci 481:1360–1369. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.03.287
Pulingam T, Thong KL, Ali MdE, Appaturi JN, Dinshaw IJ, Ong ZY, Leo BF (2019) Graphene oxide exhibits differential mechanistic action towards gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. Colloid Surf B Biointerfaces 181:6–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2019.05.023
Raghupathi KR, Koodali RT, Manna AC (2011) Size-dependent bacterial growth inhibition and mechanism of antibacterial activity of zinc oxide nanoparticles. Langmuir 27(7):4020–4028. https://doi.org/10.1021/la104825u
Rajaura RS, Sharma V, Ronin RS, Gupta DK, Srivastava S, Agrawal K, Vijay YK (2017) Synthesis, characterization and enhanced antimicrobial activity of reduced graphene oxide–zinc oxide nanocomposite. Mater Res Express 4(2):025401. https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/aa5bff
Sawai J, Shiga H, Kojima H (2001) Kinetic analysis of death of bacteria in CaO powder slurry. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 47(1):23–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0964-8305(00)00115-3
Seil JT, Webster TJ (2012) Antimicrobial applications of nanotechnology: methods and literature. Int J Nanomed 7:2767–2781. https://doi.org/10.2147/ijn.s24805
Shareena TD, McShan D, Dasmahapatra AK, Tchounwou PB (2018) A review on graphene-based nanomaterials in biomedical applications and risks in environment and health. Nano-Micro Lett 10(3):53. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40820-018-0206-4
Szunerits S, Boukherroub R (2016) Antibacterial activity of graphene-based materials. J Mater Chem B 4(43):6892–6912. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6tb01647b
Tahira K, Ahmada A, Li B, Nazirb S, Khana AU, Nasirc T, Khand ZUH, Nazb R, Raza M (2016) Visible light photo catalytic inactivation of bacteria and photo degradation of methylene blue with Ag/TiO2 nanocomposite prepared by a novel method. J Photochem Photobiol B Biol 162:189–198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2016.06.039
Tien HN, Luan VH, Hoa LT, Khoa NT, Hahn SH, Chung JS, Shin EW, Hur SH (2013) One-pot synthesis of a reduced graphene oxide–zinc oxide sphere composite and its use as a visible light photocatalyst. Chem Eng J 229:126–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2013.05.110
Wu X, Tan S, Xing Y, Pu Q, Wu M, Zhao JX (2017) Graphene Oxide as an Efficient Antimicrobial Nanomaterial for Eradicating Multi-Drug Resistant Bacteria in Vitro and in Vivo. Colloid Surf B Biointerfaces 157:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2017.05.024
Xie Y, He Y, Irwin PL, Jin T, Shi X (2011) Antibacterial Activity and Mechanism of Action of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles against Campylobacter jejuni. Appl Environ Microbiol 77(7):2325–2331. https://doi.org/10.1128/aem.02149-10
Zhong L, Yun K (2015) Graphene oxide-modified ZnO particles: synthesis, characterization, and antibacterial properties. Int J Nanomed 10:79–92. https://doi.org/10.2147/ijn.s88319
Acknowledgement
The authors D. Prema and G. Devanand Venkatasubbu would like to thank the Department of Physics and Nanotechnology, SRM Institute of Science and Technology for providing the necessary lab facilities. The authors would like to acknowledge SRM Institute of Science and Technology for providing Micro Raman facilities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Prema, D., Prakash, J., Vignesh, S. et al. Mechanism of inhibition of graphene oxide/zinc oxide nanocomposite against wound infection causing pathogens. Appl Nanosci 10, 827–849 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-019-01152-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-019-01152-9