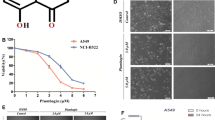
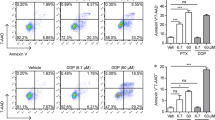
Abstract
Capsaicin is a major pungent ingredient found in hot pepper, has long been reported to control of obesity and anti-carcinogenic activities. Capsaicin induced apoptosis in a various cancer cells, however the precise molecular mechanisms have been poorly understood. In present study, the effect of capsaicin in cell viability the U87MG human glioma cells and its molecular mechanisms of cell death were investigated. Capsaicin induced reduction of cell viability in doseand time-dependent manners. Apoptosis was determined based on the increase of positive TUNEL stained cells. The mechanisms of apoptosis were related with mitochondrial pathway (Bcl-2/Bax), activation of MAPK pathway. These data suggest that capsaicin could be a novel chemotherapeutic agent of human malignant gliomas.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Stavric, B. Role of chemopreventers in human diet. Clin Biochem 27:319–332 (1994).
Ferguson, L. R. Antimutagens as cancer chemopreventive agents in the diet. Mutat Res 307:395–410 (1994).
Cordell, G. A. & Araujo, O. E. Capsaicin: identification, nomenclature, and pharmacotherapy. Ann Pharmacother 27:330–336 (1993).
Surh, Y. J., Lee, E. & Lee, J. M. Chemoprotective properties of some pungent ingredients present in red pepper and ginger. Mutat Res 402:259–267 (1998).
Tsou, M. F. et al. Involvement of Bax, Bcl-2, Ca2+ and caspase-3 in capsaicin-induced apoptosis of human leukemia HL-60 cells. Anticancer Res 26:1965–1971 (2006).
Lo, Y. C. et al. Capsaicin-induced cell death in a human gastric adenocarcinoma cell line. World J Gastroenterol 11:6254–6257 (2005).
Chou, C. C. et al. Capsaicin-induced apoptosis in human breast cancer MCF-7 cells through caspase-independent pathway. Oncol Rep 21:665–671 (2009).
Holland, E. C. Glioblastoma multiforme: the terminator. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 97:6242–6244 (2000).
Cheema, F. A., Badr, A. & Iqbal, J. Glioblastoma multiforme presenting as treatment-resistant depression. J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci 22:123.E26 (2010).
Kanu, O. O. et al. Glioblastoma multiforme: a review of therapeutic targets. Expert Opin Ther Targets 13:701–718 (2009).
Hewitson, T. D. & Darby, I. A. In situ localization of apoptosis using TUNEL. Methods Mol Biol 611:161–170 (2010).
Wieder, R. TUNEL assay as a measure of chemotherapy-induced apoptosis. Methods Mol Med 111:43–54 (2005).
Negoescu, A., Guillermet, C., Lorimier, P., Brambilla, E. & Labat-Moleur, F. Importance of DNA fragmentation in apoptosis with regard to TUNEL specificity. Biomed Pharmacother 52:252–258 (1998).
Lee, S. et al. MAPK signaling is involved in camptothecin-induced cell death. Mol Cells 14:348–354 (2002).
Ren, D., Yang, H. & Zhang, S. Cell death mediated by MAPK is associated with hydrogen peroxide production in Arabidopsis. J Biol Chem 277:559–565 (2002).
Oh, H. L., Seok, J. Y., Kwon, C. H., Kang, S. K. & Kim, Y. K. Role of MAPK in ceramide-induced cell death in primary cultured astrocytes from mouse embryonic brain. Neurotoxicology 27:31–38 (2006).
Cohen, G. M. Caspases: the executioners of apoptosis. Biochem J 326(Pt 1):1–16 (1997).
Riedl, S. J. & Shi, Y. Molecular mechanisms of caspase regulation during apoptosis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 5:897–907 (2004).
Parvez, T. Present trend in the primary treatment of aggressive malignant glioma: glioblastoma multiforme. Technol Cancer Res Treat 7:241–248 (2008).
Legler, J. M. et al. RESPONSE: Re: brain and other central nervous system cancers: recent trends in incidence and mortality. J Natl Cancer Inst 91:2050A–22051 (1999).
Paoletti, P. Therapeutic strategy for central nervous system tumors: present status, criticism and potential. J Neurosurg Sci 28:51–60 (1984).
Stupp, R. et al. Changing paradigms-an update on the multidisciplinary management of malignant glioma. Oncologist 11:165–180 (2006).
Kala, M., Srámek, V., Houdek, M., Vaverka, M. & Zmrzlík, P. Treatment of glioblastoma multiforme. Cas Lek Cesk 132:653–656 (1993).
Jendrossek, V., Belka, C. & Bamberg, M. Novel chemotherapeutic agents for the treatment of glioblastoma multiforme. Expert Opin Investig Drugs 12:1899–1924 (2003).
Jung, M. Y., Kwon, S. K. & Moon, A. Chemopreventive allylthiopyridazine derivatives induce apoptosis in SK-Hep-1 hepatocarcinoma cells through a caspase-3-dependent mechanism. Eur J Cancer 37:2104–2110 (2001).
Takahata, K., Chen, X., Monobe, K. & Tada, M. Growth inhibition of capsaicin on HeLa cells is not mediated by intracellular calcium mobilization. Life Sci 64:PL165–171 (1999).
Zhang, J., Nagasaki, M., Tanaka, Y. & Morikawa, S. Capsaicin inhibits growth of adult T-cell leukemia cells. Leuk Res 27:275–283 (2003).
Coultas, L. & Strasser, A. The role of the Bcl-2 protein family in cancer. Semin Cancer Biol 13:115–123 (2003).
Dejean, L. M. et al. Oligomeric Bax is a component of the putative cytochrome c release channel MAC, mitochondrial apoptosis-induced channel. Mol Biol Cell 16:2424–2432 (2005).
Saito, M., Korsmeyer, S. J. & Schlesinger, P.H. BAX-dependent transport of cytochrome c reconstituted in pure liposomes. Nat Cell Biol 2:553–555 (2000).
Gross, A., McDonnell, J. M. & Korsmeyer, S. J. BCL-2 family members and the mitochondria in apoptosis. Genes Dev 13:1899–1911 (1999).
Youle, R. J. & Strasser, A. The BCL-2 protein family: opposing activities that mediate cell death. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 9:47–59 (2008).
Rohwer, F. & Azam, F. Detection of DNA damage in prokaryotes by terminal deoxyribonucleotide transferase-mediated dUTP nick end labeling. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:1001–1006 (2000).
Nagata, S. DNA degradation in development and programmed cell death. Annu Rev Immunol 23:853–875 (2005).
Yue, T. L., Ohlstein, E. H. & Ruffolo, R. R. Apoptosis: a potential target for discovering novel therapies for cardiovascular diseases. Curr Opin Chem Biol 3:474–480 (1999).
Kerr, J. F., Wyllie, A. H. & Currie, A. R. Apoptosis: a basic biological phenomenon with wide-ranging implications in tissue kinetics. Br J Cancer 26:239–257 (1972).
Hickman, J. A. Apoptosis induced by anticancer drugs. Cancer Metastasis Rev 11:121–139 (1992).
Kim, J. A., Kang, Y. S. & Lee, Y. S. A phospholipase C-dependent intracellular Ca2+ release pathway mediates the capsaicin-induced apoptosis in HepG2 human hepatoma cells. Arch Pharm Res 28:73–80 (2005).
Schaeffer, H. J. & Weber, M. J. Mitogen-activated protein kinases: specific messages from ubiquitous messengers. Mol Cell Biol 19:2435–2444 (1999).
Roux, P. P. & Blenis, J. ERK and p38 MAPK-activated protein kinases: a family of protein kinases with diverse biological functions. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 68:320–344 (2004).
Kolch, W. Meaningful relationships: the regulation of the Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK pathway by protein interactions. Biochem J 351Pt 2:289–305 (2000).
Seger, R. & Krebs, E. G. The MAPK signaling cascade. FASEB J 9:726–735 (1995).
Zohrabian, V. M., Forzani, B., Chau, Z., Murali, R. & Jhanwar-Uniyal, M. Rho/ROCK and MAPK signaling pathways are involved in glioblastoma cell migration and proliferation. Anticancer Res 29:119–123 (2009).
Kang, H. J. et al. Roles of JNK-1 and p38 in selective induction of apoptosis by capsaicin in ras-transformed human breast epithelial cells. Int J Cancer 103:475–482 (2003).
Kwon, C. H., Park, J. Y., Kim, T. H., Woo, J. S. & Kim, Y. K. Ciglitazone induces apoptosis via activation of p38 MAPK and AIF nuclear translocation mediated by reactive oxygen species and Ca (2+) in opossum kidney cells. Toxicology 257:1–9 (2009).
Zhang, R., Humphreys, I., Sahu, R. P., Shi, Y. & Srivastava, S. K. In vitro and in vivo induction of apoptosis by capsaicin in pancreatic cancer cells is mediated through ROS generation and mitochondrial death pathway. Apoptosis 13:1465–1478 (2008).
Denizot, F. & Lang, R. Rapid colorimetric assay for cell growth and survival. Modifications to the tetrazolium dye procedure giving improved sensitivity and reliability. J Immunol Methods 89:271–277 (1986).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jeon, J.H., Choi, Y.J., Han, I.H. et al. Capsaicin-induced apoptosis in the human glioblastoma U87MG cells via p-38 MAPK and Bcl-2/Bax signaling pathway. Mol. Cell. Toxicol. 8, 69–76 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13273-012-0009-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13273-012-0009-5