Abstract
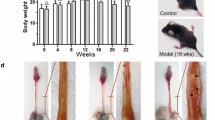
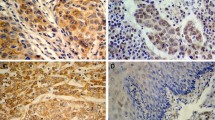
Previous studies have indicated that heat shock protein 27 (HSP27) had high correlation with the development and progression in several tumors. However, the roles of HSP27 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) were uncertain. The aim in this study is to investigate the potential roles of HSP27 in the metastasis of ESCC. The expression of HSP27 in ESCC tissues and four human esophageal cancer cell lines were examined by immunohistochemistry and Western blotting, respectively. Wound healing assays, transwell assays, and in vivo assays were used to identify the differences of metastasis potential between normal and HSP27 overexpressed cells. HSP27 expression was downregulated in cancer tissue compared to the matched normal tissue. And the positive staining was mainly located in the cytoplasm. Statistical analyses showed that the expression of HSP27 in ESCC was significantly correlated with the tumor differentiation (P = 0.023), the patient’s TNM stage (P = 0.013), lymph metastasis (P = 0.020), and distant metastasis (P = 0.017). HSP27 expression was significantly lower in highly metastatic cells than the less ones. The metastatic potentials of EC9706-H and EC109-H cells were higher than EC9706-L and EC109-L cells. In vitro and in vivo assays showed that overexpression of HSP27 in highly metastatic cells dramatically decreased their metastatic capacity. This study indicated that the expression level of HSP27 may be inversely correlated with the metastasis behavior of ESCC, and HSP27 may play an important role in this progression. HSP27 may be a potential molecular target for the therapy and prognosis of patients with ESCC.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011;61:69–90.
Tang S, Gao L, Bi Q, Xu G, Wang S, Zhao G, et al. SDR9C7 promotes lymph node metastases in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. PLoS ONE. 2013;8:e52184.
Sugimachi K, Matsuoka H, Ohno S, Mori M, Kuwano H. Multivariate approach for assessing the prognosis of clinical oesophageal carcinoma. Br J Surg. 1988;75:1115–8.
Nair KS, Naidoo R, Chetty R. Expression of cell adhesion molecules in oesophageal carcinoma and its prognostic value. J Clin Pathol. 2005;58:343–51.
Kuwano H, Kato H, Miyazaki T, Fukuchi M, Masuda N, Nakajima M, et al. Genetic alterations in esophageal cancer. Surg Today. 2005;35:7–18.
Shang L, Wang W, Li X, Liu J, Wen F, Li J. Study on the variation of serum HSP27, HSP70, DKK-1, RFER, RFIR in patients with esophageal carcinoma during perioperative period. China Med Herald. 2012;07:0046–7.
Georgopoulos C, Welch WJ. Role of the major heat shock proteins as molecular chaperones. Ann Rev Cell Biol. 1993;9:601–34.
Malusecka E, Krzyowska-Gruca S, Gawrychowski J, Fiszer-Kierzkowska A, Kolosza Z, Krawczyk Z. Stress proteins Hsp27 and Hsp70i predict survival in non-small cell lung carcinoma. Anticancer Res. 2008;28:501–6.
Lebret T, Watson RW, Molinie V, Molinié V, O’Neill A, Gabriel C, et al. Heat shock proteins HSP27, HSP60, HSP70, and HSP90: expression in bladder carcinoma. Cancer. 2003;98:970–7.
Mehlen P, Mehlen A, Godet J, Arrigo AP. HSP27 as a switch between differentiation and apoptosis in murine embryonic stem cells. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:31657–65.
Straume O, Shimamura T, Lampa MJ, Carretero J, Øyan AM, Jia D, et al. Suppression of heat shock protein 27 induces long-term dormancy in human breast cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012;109:8699–704.
Zhao M, Shen F, Yin YX, Yang YY, Xiang DJ, Chen Q. Increased expression of heat shock protein 27 correlates with peritoneal metastasis in epithelial ovarian cancer. Reprod Sci. 2012;19:748–53.
Yu Z, Zhi J, Peng X, Zhong X, Xu A. Clinical significance of HSP27 expression in colorectal cancer. Mol Med Rep. 2010;3:953–8.
Norton JA, Weinberger PM, Merkley MA, Khichi SS, Jackson LL, Dynan WS. Multi-spectral imaging analysis of HSPB1 expression in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Laryngoscope. 2010;120:S171.
Huang Q, Ye J, Chen W, Wang L, Lin W, Lin J, et al. Heat shock protein 27 is over-expressed in tumor tissues and increased in sera of patients with gastric adenocarcinoma. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2010;48:263–9.
Gibert B, Eckel B, Gonin V, Goldschneider D, Fombonne J, Deux B, et al. Targeting heat shock protein 27 (HspB1) interferes with bone metastasis and tumour formation in vivo. Br J Cancer. 2012;107:63–70.
Nakajima M, Kuwano H, Miyazaki T, Masuda N, Kato H. Significant correlation between expression of heat shock proteins 27, 70 and lymphocyte infiltration in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 2002;178:99–106.
Kawanishi K, Shiozaki H, Doki Y, Sakita I, Inoue M, Yano M, et al. Prognostic significance of heat shock proteins 27 and 70 in patients with squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus. Cancer. 1999;85:1649–57.
Gong T, Xue Z, Tang S, Zheng X, Xu G, Gao L, et al. Nuclear expression of twist promotes lymphatic metastasis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Biol Ther. 2012;13:606–13.
Xu G, Tang S, Yang J, Chen K, Kang J, Zhao G, et al. BMP7 expression in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and its potential role in modulating metastasis. Dig Dis Sci. 2013;58:1871–9.
Qian H, Lu N, Xue L, Liang X, Zhang X, Fu M, et al. Reduced MTA1 expression by RNAi inhibits in vitro invasion and migration of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cell line. Clin Exp Metastasis. 2005;22:653–62.
Song Y, Zhao C, Dong L, Fu M, Xue L, Huang Z, et al. Overexpression of cyclin B1 in human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells induces tumor cell invasive growth and metastasis. Carcinogenesis. 2008;29:307–15.
Parcellier A, Schmitt E, Brunet M, Hammann A, Solary E, Garrido C. Small heat shock proteins HSP27 and alphaB-crystallin: cytoprotective and oncogenic functions. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2005;7:404–13.
Guo K, Kang NX, Li Y, Sun L, Gan L, Cui FJ, et al. Regulation of HSP27 on NF–kappaB pathway activation may be involved in metastatic hepatocellular carcinoma cells apoptosis. BMC Cancer. 2009;9:100.
Bhargavan B, Fatma N, Chhunchha B, Singh V, Kubo E, Singh DP. LEDGF gene silencing impairs the tumorigenicity of prostate cancer DU145 cells by abating the expression of Hsp27 and activation of the Akt/ERK signaling pathway. Cell Death Dis. 2012;3:e316.
Zhao L, Li ZG, Ding YQ. Expression of HSP27 in colorectal carcinoma and its relationship with lymphatic metastasis. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Bao. 2008;28:41–4.
Chen JH, Chen LM, Xu LY, Wu MY, Shen ZY. Expression and significance of heat shock proteins in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Zhonghua Zhong Liu ZaZhi. 2006;28:758–61.
Lambot MA, Peny MO, Fayt I, Haot J, Noël JC. Overexpression of 27-kDa heat shock protein relates to poor histological differentiation in human oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Histopathology. 2000;36:326–30.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundations of China (NO. 30900674, 81272516, 30973428, 81090273, 81090270) and the Clinical New Techniques Project of Xijing Hospital (No. XJGX13LZ02).
Conflict of interest
None
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
L. Xue, L. Yang, and Zhi-an Jin contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xue, L., Yang, L., Jin, Za. et al. Increased expression of HSP27 inhibits invasion and metastasis in human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Tumor Biol. 35, 6999–7007 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-014-1946-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-014-1946-5