Abstract
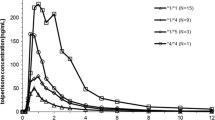
Considering that the genotypes of CYP2C19 and MDR1 C3435T are two major factors attributed to the inter-individual pharmacokinetic variability of lansoprazole (LSZ), the aim of the study was to simultaneously elucidate the effects of CYP2C19 and MDR1 C3435T polymorphisms on the pharmacokinetics difference of LSZ and its metabolites 5′-hydroxy lansoprazole (HLSZ) and lansoprazole sulphone (LSZS) following oral administration of LSZ tablets in healthy Chinese subjects. Plasma concentration of LSZ, HLSZ and LSZS were quantified by a sensitive and specific LC–MS/MS method, while the genotypes of CYP2C19 and MDR1 C3435T for each subject were identified by a direct sequencing method. Statistical analysis was performed in the pharmacokinetic parameters including C max, t 1/2, T max, MRT0–τ, AUC0–2 and AUC0–τ among different genotype groups of CYP2C19 and MDR1 C3435T. Compared to the CYP2C19 EMs, the CYP2C19 PM group showed slower elimination and better oral bioavailability of LSZ, much higher plasma concentrations of LSZS and lower concentrations of HLSZ with statistically significance. Despite a tendency of more favorable absorption and rapid elimination of LSZ in wild genotype, no significant pharmacokinetics difference was observed between the wild genotype of MDR1 C3435T and its mutant types. In conclusion, the pharmacokinetics difference of LSZ in Chinese subjects depends much more on the CYP2C19 polymorphism than on the polymorphism of MDR1 C3435T.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barradell LB, Faulds D, McTavish D (1992) Lansoprazole. A review of its pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic properties and its therapeutic efficacy in acid-related disorders. Drugs 44(2):225–250
Cascorbi I, Gerloff T, Johne A, Meisel C, Hoffmeyer S, Schwab M, Schaeffeler E, Eichelbaum M, Brinkmann U, Roots I et al (2001) Frequency of single nucleotide polymorphisms in the P-glycoprotein drug transporter MDR1 gene in white subjects. Clin Pharmacol Ther 69(3):169–174. doi:10.1067/mcp.2001.114164
De Morais SM, Wilkinson GR, Blaisdell J, Meyer UA, Nakamura K, Goldstein JA et al (1994a) Identification of a new genetic defect responsible for the polymorphism of (S)-mephenytoin metabolism in Japanese. Mol Pharmacol 46(4):594–598
de Morais SM, Wilkinson GR, Blaisdell J, Nakamura K, Meyer UA, Goldstein JA et al (1994b) The major genetic defect responsible for the polymorphism of S-mephenytoin metabolism in humans. J Biol Chem 269(22):15419–15422
Delhotal-Landes B, Cournot A, Vermerie N, Dellatolas F, Benoit M, Flouvat B et al (1991) The effect of food and antacids on lansoprazole absorption and disposition. Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet Spec No 3:315–320
Delhotal-Landes B, Flouvat B, Duchier J, Molinie P, Dellatolas F, Lemaire M et al (1993) Pharmacokinetics of lansoprazole in patients with renal or liver disease of varying severity. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 45(4):367–371
Hoffmeyer S, Burk O, von Richter O, Arnold HP, Brockmoller J, Johne A, Cascorbi I, Gerloff T, Roots I, Eichelbaum M, Brinkmann U et al (2000) Functional polymorphisms of the human multidrug-resistance gene: multiple sequence variations and correlation of one allele with P-glycoprotein expression and activity in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97(7):3473–3478. doi:10.1073/pnas.050585397
Hu YR, Qiao HL, Kan QC (2004) Pharmacokinetics of lansoprazole in Chinese healthy subjects in relation to CYP2C19 genotypes. Acta Pharmacol Sin 25(8):986–990
Hussein Z, Granneman GR, Mukherjee D, Samara E, Hogan DL, Koss MA, Isenberg JI et al (1993) Age-related differences in the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of lansoprazole. Br J Clin Pharmacol 36(5):391–398
Katsuki H, Nakamura C, Arimori K, Fujiyama S, Nakano M et al (1997) Genetic polymorphism of CYP2C19 and lansoprazole pharmacokinetics in Japanese subjects. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 52(5):391–396
Kodaira C, Sugimoto M, Nishino M, Yamade M, Shirai N, Uchida S, Ikuma M, Yamada S, Watanabe H, Hishida A, Furuta T et al (2009) Effect of MDR1 C3435T polymorphism on lansoprazole in healthy Japanese subjects. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 65(6):593–600. doi:10.1007/s00228-009-0625-8
Miura M, Inoue K, Satoh S, Itoh Y, Kagaya H, Tada H, Tanaka Y, Habuchi T, Suzuki T et al (2007) Influence of cytochrome P450 (CYP) 3A5 polymorphisms on the pharmacokinetics of lansoprazole enantiomers in CYP2C19 extensive metaboliser renal transplant recipients. Clin Drug Investig 27(4):251–258
Pauli-Magnus C, Rekersbrink S, Klotz U, Fromm MF et al (2001) Interaction of omeprazole, lansoprazole and pantoprazole with P-glycoprotein. Naunyn Schmiedeberg’s Arch Pharmacol 364(6):551–557
Pichard L, Curi-Pedrosa R, Bonfils C, Jacqz-Aigrain E, Domergue J, Joyeux H, Cosme J, Guengerich FP, Maurel P et al (1995) Oxidative metabolism of lansoprazole by human liver cytochromes P450. Mol Pharmacol 47(2):410–418
Siegmund W, Ludwig K, Giessmann T, Dazert P, Schroeder E, Sperker B, Warzok R, Kroemer HK, Cascorbi I et al (2002) The effects of the human MDR1 genotype on the expression of duodenal P-glycoprotein and disposition of the probe drug talinolol. Clin Pharmacol Ther 72(5):572–583. doi:10.1067/mcp.2002.127739
Song M, Gao X, Hang T, Wen A et al (2008) Simultaneous determination of lansoprazole and its metabolites 5′-hydroxy lansoprazole and lansoprazole sulphone in human plasma by LC-MS/MS: application to a pharmacokinetic study in healthy volunteers. J Pharm Biomed Anal 48(4):1181–1186. doi:10.1016/j.jpba.2008.08.034
Teh LK, Lee WL, Amir J, Salleh MZ, Ismail R et al (2007) Single step PCR for detection of allelic variation of MDR1 gene (P-glycoprotein) among three ethnic groups in Malaysia. J Clin Pharm Ther 32(3):313–319. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2710.2007.00822.x
US Department of Health and Human Services FaDA (2001) Guidance for Industry, Bioanalytical Method
Wu GL, Zhou HL, Shentu JZ, He QJ, Yang B et al (2008) Determination of lansoprazole in human plasma by rapid resolution liquid chromatography-electrospray tandem mass spectrometry: application to a bioequivalence study on Chinese volunteers. J Pharm Biomed Anal 48(5):1485–1489. doi:10.1016/j.jpba.2008.09.046
Xu HR, Chen WL, Li XN, Chu NN et al (2010) The effect of CYP2C19 activity on pharmacokinetics of lansoprazole and its active metabolites in healthy subjects. Pharm Biol 48(8):947–952. doi:10.3109/13880200903300220
Zalloum I, Hakooz N, Arafat T (2012) Genetic polymorphism of CYP2C19 in a Jordanian population: influence of allele frequencies of CYP2C19*1 and CYP2C19*2 on the pharmacokinetic profile of lansoprazole. Mol Biol Rep 39(4):4195–4200. doi:10.1007/s11033-011-1204-5
Zhang D, Wang X, Yang M, Wang G, Liu H et al (2011) Effects of CYP2C19 polymorphism on the pharmacokinetics of lansoprazole and its main metabolites in healthy Chinese subjects. Xenobiotica Fate Foreign Compd Biol Syst 41(6):511–517. doi:10.3109/00498254.2011.559556
Zhang D, Yang M, Liu M, Zhang Y, Wang X, Xiao X, Liu H et al (2012) Pharmacokinetics of lansoprazole and its main metabolites after single intravenous doses in healthy Chinese subjects. Xenobiotica Fate Foreign Compd Biol Syst 42(11):1156–1162. doi:10.3109/00498254.2012.687119
Acknowledgments
This research was financially supported by A Project Funded by the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions, 2010, PAPD (TCM combined with western medicine); Leading Talents of scientific research in TCM of Jiangsu Province (No. LJ200906); The National Science and Technology Major Project ‘Creation of Major New Drugs’ (2012ZX09303009-002) from China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
C. Li and J. Zhang contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, CY., Zhang, J., Chu, JH. et al. A correlative study of polymorphisms of CYP2C19 and MDR1 C3435T with the pharmacokinetic profiles of lansoprazole and its main metabolites following single oral administration in healthy adult Chinese subjects. Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet 39, 121–128 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13318-013-0148-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13318-013-0148-7