Abstract
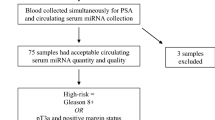
Prostate cancer (PC) is the most frequent cancer in men in the Western world. Currently, serum prostate-specific antigen levels and digital rectal examinations are used to indicate the need for diagnostic prostate biopsy, but lack in specificity and sensitivity. Thus, many men undergo unnecessary biopsy, and better and less invasive tools for PC detection are needed. Furthermore, whereas aggressive PC should be treated immediately to prevent dissemination, indolent PC often does not progress and overtreatment should be avoided. Currently, the best predictors of aggressiveness are Gleason score and T-stage of the primary PC. Better tools to assess PC aggressiveness could aid in treatment decisions. Recently, circulating miRNAs have been suggested as potential new biomarkers for PC with diagnostic and prognostic potential. Here, to identify new serum miRNA biomarker candidates for PC, we performed genome-wide miRNA profiling of serum samples from 13 benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) control patients and 31 PC patients. Furthermore, we carefully reviewed the literature on circulating miRNA biomarkers for PC. Our results confirmed the de-regulation of miR-141 and miR-375, two of the most well-documented candidate miRNA markers for PC. Moreover, we identified several new potential serum miRNA markers for PC and developed three novel and highly specific (100 %) miRNA candidate marker panels able to identify 84 % of all PC patients (miR-562/miR-210/miR-501-3p/miR-375/miR-551b), 80 % of patients with disseminated PC when compared to BPH patients (let-7a*/miR-210/miR-562/miR-616), and 75 % of disseminated PC patients when compared to localized PC patients (miR-375/miR-708/miR-1203/miR-200a), demonstrating high potential of serum miRNAs for diagnosing and staging of PC.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ferlay J, Parkin DM, Steliarova-Foucher E. Estimates of cancer incidence and mortality in Europe in 2008. Eur J Cancer. 2010;46(4):765–81. doi:10.1016/j.ejca.2009.12.014.
Hoogendam A, Buntinx F, de Vet HC. The diagnostic value of digital rectal examination in primary care screening for prostate cancer: a meta-analysis. Family Practice. 1999;16(6):621–6.
Glaser AP, Novakovic K, Helfand BT. The impact of prostate biopsy on urinary symptoms, erectile function, and anxiety. Current Urol Reports. 2012;13(6):447–54. doi:10.1007/s11934-012-0277-6.
Wolters T, van der Kwast TH, Vissers CJ, Bangma CH, Roobol M, Schroder FH, et al. False-negative prostate needle biopsies: frequency, histopathologic features, and follow-up. The Am J Surg Pathol. 2010;34(1):35–43. doi:10.1097/PAS.0b013e3181c3ece9.
Albertsen PC. Treatment of localized prostate cancer: when is active surveillance appropriate? Nature Rev Clin Oncol. 2010;7(7):394–400. doi:10.1038/nrclinonc.2010.63.
Healy NA, Heneghan HM, Miller N, Osborne CK, Schiff R, Kerin MJ. Systemic miRNAs as potential biomarkers for malignancy. Int J Cancer. 2012;131(10):2215–22. doi:10.1002/ijc.27642.
Zhou L, Zhao YP, Liu WJ, Dong J, Chen WY, Zhang TP, et al. Circulating microRNAs in cancer: diagnostic and prognostic significance. Expert Rev of Anticancer Ther. 2012;12(2):283–8. doi:10.1586/era.11.197.
Chen X, Ba Y, Ma L, Cai X, Yin Y, Wang K, et al. Characterization of microRNAs in serum: a novel class of biomarkers for diagnosis of cancer and other diseases. Cell Res. 2008;18(10):997–1006. doi:10.1038/cr.2008.282.
Chen X, Liang H, Zhang J, Zen K, Zhang CY. Secreted microRNAs: a new form of intercellular communication. Trends Cell Biol. 2012;22(3):125–32. doi:10.1016/j.tcb.2011.12.001.
Cocucci E, Racchetti G, Meldolesi J. Shedding microvesicles: artefacts no more. Trends Cell Biol. 2009;19(2):43–51. doi:10.1016/j.tcb.2008.11.003.
Thery C, Zitvogel L, Amigorena S. Exosomes: composition, biogenesis and function. Nature Rev Immunol. 2002;2(8):569–79. doi:10.1038/nri855.
Ratajczak J, Wysoczynski M, Hayek F, Janowska-Wieczorek A, Ratajczak MZ. Membrane-derived microvesicles: important and underappreciated mediators of cell-to-cell communication. Leukemia. 2006;20(9):1487–95. doi:10.1038/sj.leu.2404296.
Simons M, Raposo G. Exosomes—vesicular carriers for intercellular communication. Current Opinion in Cell Biol. 2009;21(4):575–81. doi:10.1016/j.ceb.2009.03.007.
Vickers KC, Palmisano BT, Shoucri BM, Shamburek RD, Remaley AT. MicroRNAs are transported in plasma and delivered to recipient cells by high-density lipoproteins. Nat Cell Biol. 2011;13(4):423–33. doi:10.1038/ncb2210.
Arroyo JD, Chevillet JR, Kroh EM, Ruf IK, Pritchard CC, Gibson DF, et al. Argonaute2 complexes carry a population of circulating microRNAs independent of vesicles in human plasma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011;108(12):5003–8. doi:10.1073/pnas.1019055108.
Turchinovich A, Weiz L, Langheinz A, Burwinkel B. Characterization of extracellular circulating microRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011;39(16):7223–33. doi:10.1093/nar/gkr254.
Ma R, Jiang T, Kang X. Circulating microRNAs in cancer: origin, function and application. J Exp Clin Cancer Res: CR. 2012;31:38. doi:10.1186/1756-9966-31-38.
Mitchell PS, Parkin RK, Kroh EM, Fritz BR, Wyman SK, Pogosova-Agadjanyan EL, et al. Circulating microRNAs as stable blood-based markers for cancer detection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008;105(30):10513–8. doi:10.1073/pnas.0804549105.
Kelly BD, Miller N, Healy NA, Walsh K, Kerin MJ. A review of expression profiling of circulating microRNAs in men with prostate cancer. BJU Int. 2013;111(1):17–21. doi:10.1111/j.1464-410X.2012.11244.x.
Selth LA, Tilley WD, Butler LM. Circulating microRNAs: macro-utility as markers of prostate cancer? Endocrine-related cancer. 2012;19(4):R99–R113. doi:10.1530/ERC-12-0010.
Andersen CL, Jensen JL, Orntoft TF. Normalization of real-time quantitative reverse transcription-PCR data: a model-based variance estimation approach to identify genes suited for normalization, applied to bladder and colon cancer data sets. Cancer Res. 2004;64(15):5245–50. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-0496.
Taylor BS, Schultz N, Hieronymus H, Gopalan A, Xiao Y, Carver BS, et al. Integrative genomic profiling of human prostate cancer. Cancer Cell. 2010;18(1):11–22. doi:10.1016/j.ccr.2010.05.026.
Bryant RJ, Pawlowski T, Catto JW, Marsden G, Vessella RL, Rhees B, et al. Changes in circulating microRNA levels associated with prostate cancer. British J Cancer. 2012;106(4):768–74. doi:10.1038/bjc.2011.595.
Brase JC, Johannes M, Schlomm T, Falth M, Haese A, Steuber T, et al. Circulating miRNAs are correlated with tumor progression in prostate cancer. Int J Cancer. 2011;128(3):608–16. doi:10.1002/ijc.25376.
Nguyen HC, Xie W, Yang M, Hsieh CL, Drouin S, Lee GS, et al. Expression differences of circulating microRNAs in metastatic castration resistant prostate cancer and low-risk, localized prostate cancer. Prostate. 2012. doi:10.1002/pros.22572.
Lodes MJ, Caraballo M, Suciu D, Munro S, Kumar A, Anderson B. Detection of cancer with serum miRNAs on an oligonucleotide microarray. PLoS One. 2009;4(7):e6229. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0006229.
Moltzahn F, Olshen AB, Baehner L, Peek A, Fong L, Stoppler H, et al. Microfluidic-based multiplex qRT-PCR identifies diagnostic and prognostic microRNA signatures in the sera of prostate cancer patients. Cancer Res. 2011;71(2):550–60. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-1229.
Zhang HL, Yang LF, Zhu Y, Yao XD, Zhang SL, Dai B, et al. Serum miRNA-21: elevated levels in patients with metastatic hormone-refractory prostate cancer and potential predictive factor for the efficacy of docetaxel-based chemotherapy. Prostate. 2011;71(3):326–31. doi:10.1002/pros.21246.
Yaman Agaoglu F, Kovancilar M, Dizdar Y, Darendeliler E, Holdenrieder S, Dalay N, et al. Investigation of miR-21, miR-141, and miR-221 in blood circulation of patients with prostate cancer. Tumour Biol : J Int Soc for Oncodevelopmental Biol and Med. 2011;32(3):583–8. doi:10.1007/s13277-011-0154-9.
Selth LA, Townley S, Gillis JL, Ochnik AM, Murti K, Macfarlane RJ, et al. Discovery of circulating microRNAs associated with human prostate cancer using a mouse model of disease. Int J Cancer. 2012;131(3):652–61. doi:10.1002/ijc.26405.
Mahn R, Heukamp LC, Rogenhofer S, von Ruecker A, Muller SC, Ellinger J. Circulating microRNAs (miRNA) in serum of patients with prostate cancer. Urology. 2011;77(5):1265 e9-16. doi:10.1016/j.urology.2011.01.020.
Heneghan HM, Miller N, Kelly R, Newell J, Kerin MJ. Systemic miRNA-195 differentiates breast cancer from other malignancies and is a potential biomarker for detecting noninvasive and early stage disease. The oncologist. 2010;15(7):673–82. doi:10.1634/theoncologist.2010-0103.
Zheng C, Yinghao S, Li J. MiR-221 expression affects invasion potential of human prostate carcinoma cell lines by targeting DVL2. Med Oncol. 2012;29(2):815–22. doi:10.1007/s12032-011-9934-8.
Shen J, Hruby GW, McKiernan JM, Gurvich I, Lipsky MJ, Benson MC, et al. Dysregulation of circulating microRNAs and prediction of aggressive prostate cancer. Prostate. 2012;72(13):1469–77. doi:10.1002/pros.22499.
Chen ZH, Zhang GL, Li HR, Luo JD, Li ZX, Chen GM, et al. A panel of five circulating microRNAs as potential biomarkers for prostate cancer. Prostate. 2012;72(13):1443–52. doi:10.1002/pros.22495.
Jung K. A review of expression profiling of circulating microRNAs in men with prostate cancer. BJU Int. 2013;111(1):3–4. doi:10.1111/j.1464-410X.2012.11257.x.
Olmos D, Brewer D, Clark J, Danila DC, Parker C, Attard G, et al. Prognostic value of blood mRNA expression signatures in castration-resistant prostate cancer: a prospective, two-stage study. The lancet Oncol. 2012;13(11):1114–24. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(12)70372-8.
Ross RW, Galsky MD, Scher HI, Magidson J, Wassmann K, Lee GS, et al. A whole-blood RNA transcript-based prognostic model in men with castration-resistant prostate cancer: a prospective study. The lancet Oncol. 2012;13(11):1105–13. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(12)70263-2.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Birgitte Trolle, Conni Sørensen, Nadia Gadeberg Knudsen, Karin Fredborg, and Susanne Skou for excellent technical assistance. The Danish Cancer Biobank is acknowledged for biological material. This study was supported by the Danish Agency for Science, Technology and Innovation, the Lundbeck Foundation, the John and Birthe Meyer Foundation, the Danish Cancer Society, and the Danish Council for Strategic Research.
Conflicts of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
All procedures followed were in accordance with the ethical standards of the responsible committee on human experimentation (institutional and national) and with the Helsinki Declaration of 1975, as revised in 2000. Informed consent was obtained from all patients for being included in the study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 753 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Haldrup, C., Kosaka, N., Ochiya, T. et al. Profiling of circulating microRNAs for prostate cancer biomarker discovery. Drug Deliv. and Transl. Res. 4, 19–30 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13346-013-0169-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13346-013-0169-4