Abstract
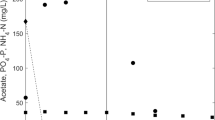
A laboratory-scale granular sequencing batch reactor, fed with acetate, was operated at two different ratios of chemical oxygen demand to phosphorus—15:1 and 100:1. Smaller aerobic granules, but with better settleability, were obtained at the lower ratio. High ratio of phosphorus release to uptake of dissolved organic carbon (0.42 mol/mol) coincided with high percentage of polyphosphate-accumulating organisms (up to 70 % of all bacteria) and implied high metabolic activity of these bacteria. Polyphosphate-accumulating organisms belonged mainly to Accumulibacter and Tetrasphaera (46 and 23 %, respectively). Despite significant abundance, Tetrasphaera-related microorganisms were not detected by oligoprobes Actino-221 and Actino-658, but by broader oligoprobes Tet2-892 and Tet3-654. Low abundance (1 %) of Halomonas phosphatis indicated a minor role of these bacteria in the laboratory-scale reactor fed with synthetic wastewater. When the ratio of chemical oxygen demand to phosphorus was increased to 100:1, deterioration of settling properties was observed, caused by growth of filamentous organisms from Thiothrix/021N group. The higher ratio favoured Competibacter and was selected against all groups of polyphosphate-accumulating organisms. However, a significant percentage (10 %) of polyphosphate-accumulating organisms in the granular sludge with concomitant low ratio of phosphorus release to the uptake of dissolved organic carbon (0.01 mol/mol) suggested shift in the overall population metabolism. Under phosphorus limitation in wastewater, polyphosphate-accumulating organisms no longer synthesized poly-P and behaved as glycogen-accumulating organisms.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahn J, McIlroy S, Schroeder S, Seviour R (2009) Biomass granulation in an aerobic:anaerobic-enhanced biological phosphorus removal process in a sequencing batch reactor with varying pH. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 36:885–893
Barat R, Montoya T, Borrás L, Ferrer J, Seco A (2008) Interactions between calcium precipitation and the polyphosphate accumulating bacteria metabolism. Water Res 42:3415–3424
Bumbac C, Ionescu IA, Tiron O, Badescu VR (2015) Continuous flow aerobic granular sludge reactor for dairy wastewater treatment. Water Sci Technol (in press). doi:10.2166/wst.2015.007
Clescerl LS, Greenberg AE, Eaton AD (eds) (1999) Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 20th edn. American Public Health Association/American Water Works Association/Water Environment Federation, Washington, DC
de Kreuk MK, van Loosdrecht MCM (2004) Selection of slow growing organisms as a means for improving aerobic granular sludge stability. Water Sci Technol 49(11–12):9–17
de Kreuk MK, Kishida N, van Loosdrecht MC (2007) Aerobic granular sludge-state of the art. Water Sci Technol 55(8–9):75–81
Drewnowski J, Makinia J (2014) The role of biodegradable particulate and colloidal organic compounds in biological nutrient removal activated sludge systems. Int J Environ Sci Technol 11:1973–1988
Jenkins D, Wanner J (2014) Activated sludge—100 years and counting. IWA Publishing, London
Kong YH, Beer M, Rees GN, Seviour R (2002) Functional analysis of microbial communities in aerobic-anaerobic sequencing batch reactors fed with different phosphorus/carbon (P/C) ratios. Microbiology 148:2299–2307
Kong YH, Nielsen JL, Nielsen PH (2005) Identity and ecophysiology of uncultured actinobacterial polyphosphate-accumulating organisms in full-scale enhanced biological phosphorus removal plants. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:4076–4085
Lee DJ, Chen YY, Show KY, Whiteley CG, Tay JH (2010) Advances in aerobic granule formation and granule stability in the course of storage and reactor operation. Biotechnol Adv 28:919–934
Lemaire R, Yuan Z, Blackall LL, Crocetti GR (2008) Microbial distribution of Accumulibacter spp and Competibacter spp in aerobic granules from a lab-scale biological nutrient removal system. Environ Microbiol 10:354–363
Li Y, Zou J, Zhang L, Sun J (2014) Aerobic granular sludge for simultaneous accumulation of mineral phosphorus and removal of nitrogen via nitrite in wastewater. Bioresour Technol 154:178–184
Lin YM, Liu Y, Tay JH (2003) Development and characteristics of phosphorus-accumulating microbial granules in sequencing batch reactors. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 62:430–435
Liu Y, Liu Q-S (2006) Causes and control of filamentous growth in aerobic granular sludge sequencing batch reactors. Biotechnol Adv 24:115–127
Loy A, Horn M, Wagner M (2003) ProbeBase: an online resource for rRNA-targeted oligonucleotide probes. Nucleic Acids Res 31:514–516
Lu H, Oehmen A, Virdis B, Keller J, Yuan ZG (2006) Obtaining highly enriched cultures of Candidatus Accumulibacter phosphatis through alternating carbon sources. Water Res 40:3838–3848
Muszyński A, Łebkowska M, Tabernacka A, Miłobędzka A (2013) From macro to lab-scale: changes in bacterial community led to deterioration of EBPR in lab reactor. Cent Eur J Biol 8(2):130–142
Nguyen HT, Le VQ, Hansen AA, Nielsen JL, Nielsen PH (2011) High diversity and abundance of putative polyphosphate-accumulating Tetrasphaera-related bacteria in activated sludge systems. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 76:256–267
Nguyen HT, Nielsen JL, Nielsen PH (2012) ‘Candidatus Halomonas phosphatis’, a novel polyphosphate-accumulating organism in full-scale enhanced biological phosphorus removal plants. Environ Microbiol 14:2826–2837
Nielsen PH, Daims H, Lemmer H (2009) Fish handbook for biological wastewater treatment. IWA Publishing, London
Nittami T, McIlroy S, Seviour EM, Schroeder S, Seviour RJ (2009) Candidatus Monilibacter spp, common bulking filaments in activated sludge, are members of Cluster III Defluviicoccus. Syst Appl Microbiol 32:480–489
Oehmen A, Lemos PC, Carvalho G, Yuan Z, Keller J, Blackall LL, Reis MAM (2007) Advances in enhanced biological phosphorus removal: from micro to macro scale. Water Res 41:2271–2300
Seviour RJ, Nielsen PH (2010) Microbial ecology of activated sludge. IWA Publishing, London
Wang R, Peng Y, Cheng Z, Ren N (2014) Understanding the role of extracellular polymeric substances in an enhanced biological phosphorus removal granular sludge system. Bioresour Technol 169:307–312
Weber S, Ludwig W, Schleifer KH, Fried J (2007) Microbial composition and structure of aerobic granular sewage biofilms. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:6233–6240
Wei D, Shi L, Yan T, Zhang G, Wang Y, Du B (2014) Aerobic granules formation and simultaneous nitrogen and phosphorus removal treating high strength ammonia wastewater in sequencing batch reactor. Bioresour Technol 171:211–216
Weissbrodt DG, Lochmatter S, Ebrahimi S, Rossi P, Maillard J, Holliger C (2012) Bacterial selection during the formation of early-stage aerobic granules in wastewater treatment systems operated under wash-out dynamics. Front Microbiol 3:332
Weissbrodt DG, Schneiter GS, Fürbringer JM, Holliger C (2013) Identification of trigger factors selecting for polyphosphate- and glycogen-accumulating organisms in aerobic granular sludge sequencing batch reactors. Water Res 47:7006–7018
Winkler MK, Bassin JP, Kleerebezem R, de Bruin LM, van den Brand TP, van Loosdrecht MC (2011) Selective sludge removal in a segregated aerobic granular biomass system as a strategy to control PAO-GAO competition at high temperatures. Water Res 45:3291–3299
Yan C, Zheng Z (2014) Performance of mixed LED light wavelengths on biogas upgrade and biogas fluid removal by microalga Chlorella sp. Appl Energy 113:1008–1014
Yan C, Zhang L, Luo X, Zheng Z (2013) Effects of various LED light wavelengths and intensities on the performance of purifying synthetic domestic sewage by microalgae at different influent C/N ratios. Ecol Eng 51:24–32
Zhou Y, Pijuan M, Zeng RJ, Lu H, Yuan Z (2008) Could polyphosphate-accumulating organisms (PAOs) be glycogen-accumulating organisms (GAOs)? Water Res 42:2361–2368
Zhu L, Dai X, Xu X, Lv M, Cao D (2014) Microbial community analysis for aerobic granular sludge reactor treating high-level 4-chloroaniline wastewater. Int J Environ Sci Technol 11:1845–1854
Zilles JL, Hung CH, Noguera DR (2002) Presence of Rhodocyclus in a full-scale wastewater treatment plant and their participation in enhanced biological phosphorus removal. Water Sci Technol 46(1–2):123–128
Acknowledgments
The authors recognize the excellent technical assistance of E. Łukomska, D. Rosińska, J. Klimkiewicz and Ł. Juraszek.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Muszyński, A., Miłobędzka, A. The effects of carbon/phosphorus ratio on polyphosphate- and glycogen-accumulating organisms in aerobic granular sludge. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 12, 3053–3060 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-015-0828-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-015-0828-8