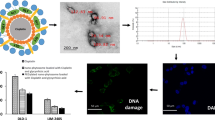
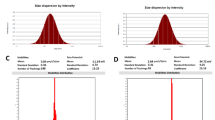
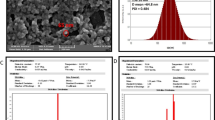
Abstract
A new cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor (code: PCX-3) was synthesized as a sodium salt form of celecoxib, a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID), and tested for its anticancer activity using human colon adenocarcinoma cells (HT-29) in vitro. Anti-proliferative effect of HT-29 cells by PCX-3 in DPPC/Chol liposomes was more effective than the free PCX-3 by 2-folds (IC30 = 125 μM vs. 227.5 μM). The same liposomal formulation of PCX-3 also showed a 2-fold increased effect than the free one both in DNA fragmentation and caspase activity of HT-29 cells at 19-743 μM and 37–371 μM ranges, respectively, suggesting apoptosis-based anti-proliferative effect. Down regulation of prostaglandin E2 level of HT-29 cells by the treatment of liposomal PCX-3 was more profound than its free form at 0.001–0.002 μM range. These data suggest that the liposomal formulation of this newly synthesized PCX-3 could be re-visited as a new anticancer or chemo-preventive agent in the future.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arico S, Pattingre S, Bauvy C, Gane P, Barbat A, Codogno P, Ogier-Denis E (2002) Celecoxib induces apoptosis by inhibiting 3-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase-1 activity in the human colon cancer HT-29 cell line. J Biol Chem 277:27613–27621
Bligh EG, Dyer WJ (1959) A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol 37:911–917
DuBois RN, Radhika A, Reddy BS, Entingh AJ (1996) Increased cyclooxygenase-2 levels in carcinogen-induced rat colonic tumors. Gastroenterology 110:1259–1262
Dubois RN, Abramson SB, Crofford L, Gupta RA, Simon LS, Van De Putte LB, Lipsky PE (1998) Cyclooxygenase in biology and disease. FASEB J 12:1063–1073
Elder DJ, Paraskeva C (1999) Induced apoptosis in the prevention of colorectal cancer by non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Apoptosis 4:365–372
Elder DJ, Halton DE, Hague A, Paraskeva C (1997) Induction of apoptotic cell death in human colorectal carcinoma cell lines by a cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2)-selective nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug: independence from COX-2 protein expression. Clin Cancer Res 3:1679–1683
Everts B, Wahrborg P, Hedner T (2000) COX-2-Specific inhibitors—the emergence of a new class of analgesic and anti-inflammatory drugs. Clin Rheumatol 19:331–343
Hara A, Yoshimi N, Niwa M, Ino N, Mori H (1997) Apoptosis induced by NS-398, a selective cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor, in human colorectal cancer cell lines. Jpn J Cancer Res 88:600–604
Jackson LM, Hawkey CJ (2000) COX-2 selective nonsteroidal anti-Inflammatory drugs: do they really offer any advantages? Drugs 59:1207–1216
Jacoby RF, Seibert K, Cole CE, Kelloff G, Lubet RA (2000) The cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor celecoxib is a potent preventive and therapeutic agent in the min mouse model of adenomatous polyposis. Cancer Res 60:5040–5044
Kargman SL, O’Neill GP, Vickers PJ, Evans JF, Mancini JA, Jothy S (1995) Expression of prostaglandin G/H synthase-1 and -2 protein in human colon cancer. Cancer Res 55:2556–2559
Laneuville O, Breuer DK, Dewitt DL, Hla T, Funk CD, Smith WL (1994) Differential inhibition of human prostaglandin endoperoxide H synthases-1 and -2 by nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 271:927–934
Needleman P, Isakson PC (1997) The discovery and function of COX-2. J Rheumatol Suppl 49:6–8
Oshima M, Dinchuk JE, Kargman SL, Oshima H, Hancock B, Kwong E, Trzaskos JM, Evans JF, Taketo MM (1996) Suppression of intestinal polyposis in Apc delta716 knockout mice by inhibition of cyclooxygenase 2 (COX-2). Cell 87:803–809
Piazza GA, Rahm AL, Krutzsch M, Sperl G, Paranka NS, Gross PH, Brendel K, Burt RW, Alberts DS, Pamukcu R et al (1995) Antineoplastic drugs sulindac sulfide and sulfone inhibit cell growth by inducing apoptosis. Cancer Res 55:3110–3116
Picot D, Loll PJ, Garavito RM (1994) The X-ray crystal structure of the membrane protein prostaglandin H2 synthase-1. Nature 367:243–249
Pidgeon C, McNeely S, Schmidt T, Johnson JE (1987) Multilayered vesicles prepared by reverse-phase evaporation: liposome structure and optimum solute entrapment. Biochemistry 26:17–29
Sano H, Kawahito Y, Wilder RL, Hashiramoto A, Mukai S, Asai K, Kimura S, Kato H, Kondo M, Hla T (1995) Expression of cyclooxygenase-1 and -2 in human colorectal cancer. Cancer Res 55:3785–3789
Seedher N, Bhatia S (2003) Solubility enhancement of Cox-2 inhibitors using various solvent systems. AAPS PharmSciTech 4:E33
Sheehan KM, Sheahan K, O’Donoghue DP, MacSweeney F, Conroy RM, Fitzgerald DJ, Murray FE (1999) The relationship between cyclooxygenase-2 expression and colorectal cancer. JAMA 282:1254–1257
Sheng GG, Shao J, Sheng H, Hooton EB, Isakson PC, Morrow JD, Coffey RJ Jr, DuBois RN, Beauchamp RD (1997) A selective cyclooxygenase 2 inhibitor suppresses the growth of H-ras-transformed rat intestinal epithelial cells. Gastroenterology 113:1883–1891
Shiff SJ, Rigas B (1997) Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and colorectal cancer: evolving concepts of their chemopreventive actions. Gastroenterology 113:1992–1998
Shiff SJ, Koutsos MI, Qiao L, Rigas B (1996) Nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs inhibit the proliferation of colon adenocarcinoma cells: effects on cell cycle and apoptosis. Exp Cell Res 222:179–188
Smith ML, Hawcroft G, Hull MA (2000) The effect of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs on human colorectal cancer cells: evidence of different mechanisms of action. Eur J Cancer 36:664–674
Szoka F Jr, Papahadjopoulos D (1978) Procedure for preparation of liposomes with large internal aqueous space and high capture by reverse-phase evaporation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 75:4194–4198
Vane JR, Botting RM (1998) Mechanism of action of antiinflammatory drugs. Int J Tissue React 20:3–15
Williams CS, Smalley W, DuBois RN (1997) Aspirin use and potential mechanisms for colorectal cancer prevention. J Clin Invest 100:1325–1329
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The first two authors, Bee Kim and Dae Hwan Shin, equally contributed to this paper as co-first authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, B., Shin, D.H., Kim, H.D. et al. Antitumor effect of a newly synthesized celecoxib derivative encapsulated in liposome. Journal of Pharmaceutical Investigation 43, 101–106 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40005-013-0057-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40005-013-0057-4