Abstract
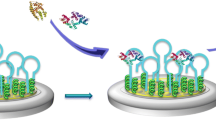
Biosensing technology represents a superior way of identifying a wide range of biomolecules that exist in the human body, food, water, and other environmental sources. In this regard, human health issues are a growing global concern, and the development of effective methods for the detection and differentiation of biomolecules during diagnosis and/or treatment of diseases is essential. However, achieving adequate levels of sensitivity and specificity will be fundamental for the successful clinical application of biosensing technology. Notably, sensitivity and specificity are highly dependent on non-fouling (specificity) of biomolecules on the sensing surfaces, particularly with regard to nanoparticle-tagged biomolecules. Here, the authors have evaluated bio-fouling (i.e., biological non-specificity) by analysing four distinct sensing substrates (gold, silicon, silica and platinum) using anti-mouse immunoglobulin-conjugated gold nanoparticles. As evidenced by scanning electron microscopy and ultraviolet–visible–near-infrared recording spectrophotometry, silica (SiO2) lacked bio-fouling, whereas gold (Au) showed high bio-fouling potential. Indeed, Raman spectroscopic analysis further confirmed these results. Thus, the present findings indicate that SiO2 is an optimal substrate for biosensor development.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nomura K, Gopinath SCB, Lakshmipriya T, Fukuda N, Wang X, Fujimaki M (2013) An angular fluidic channel for prism-free surface-plasmon-assisted fluorescence capturing. Nat Commun 4:2855
Gopinath SCB, Tang TH, Yeng C, Citartan M, Lakshmipriya T (2014) Current aspects in immunosensors. Biosens Bioelectron 57:292–302
Gopinath SCB, Tang TH, Yeng C, Citartan M, Lakshmipriya T (2014) Bacterial sensing: microscope to smart phone. Biosens Bioelectron 60:332–342
Jing M, Bowser MT (2011) A review for measuring aptamer-protein equlibria. Anal Chim Acta 686:9–18
Nagasaki Y (2011) Construction of a densely poly(ethylene glycol)-chain-tethered surface and its performance. Polym J 43:949–958
Horiguchi Y, Miyachi S, Nagasaki Y (2013) High-performance surface acoustic wave immunosensing system on PEG/aptamer hybridized surface. Langmuir 29:7369–7376
Lakshmipriya T, Fujimaki M, Gopinath SCB, Awazu K, Horiguchi Y, Nagasaki Y (2013) High-performance waveguide-mode biosensor for detection of factor IX uses PEG-based blocking agents to suppress non-specific binding and improve sensitivity. Analyst 138:2863–2870
Gopinath SCB, Awazu K, Fujimaki M, Shimizu K, Shima T (2013) Observations of immuno-gold conjugates on influenza viruses using waveguide-mode sensors. PLoS One 8:e69121
Citartan M, Gopinath SCB, Tominaga J, Chen Y, Tang TH (2014) UV–Vis–NIR spectroscopy monitors label-free interaction analyses of molecular recognition elements against erythropoietin on gold-coated polycarbonate towards sensor development. Talanta 126:103–109
Kumar P, Choithani J, Gupta KC (2004) Construction of oligonucleotide on a glass surface using a heterobifunctional reagent, N-(2-trifluoroethanesulfonatoethyl)-N-(methyl)-trithoxysilylpropyl-3-amine (NTMTA). Nucleic Acids Res 32:e80
Baldrich E, Restrepo A, O’Sullivan CK (2004) Effect of linker structure on surface density of aptamer monolayers and their corresponding protein binding efficiency. Anal Chem 76:7053–7063
Gronewold TMA, Glass S, Quandt E, Famulok M (2005) Monitoring complex formation in the blood coagulation cascade using aptamer-coated SAW sensors. Biosens Bioelectron 20:2044–2052
Odenthal KJ, Gooding J (2007) An introduction to electrochemical DNA biosensors. Analyst 132:603–610
Marquette CA, Blum LJ (2008) Electro-chemiluminescent biosensing. Anal Bioanal Chem 390:155–168
Song S, Wang L, Li J, Zhao J, Fan C (2008) Aptamer-based biosensors. Trends Anal Chem 27:108–117
Varma MM, Nolte DD, Inerowicz HD, Regnier FE (2004) Spinning-disk self-referencing interferometry of antigen-antibody recognition. Opt Lett 29:950–952
Peng L, Varma MM, Cho W, Regnier FE, Nolte DD (2007) Adaptive interferometry of protein on a BioCD. Appl Opt 46:5384–5395
Wang X, Zhao M, Nolte DD (2008) Combined fluorescent and interferometric detection of protein on a BioCD. Appl Opt 47:2779–2789
Rong G, Najmaie A, Sipe JE, Weiss SM (2008) Nanoscale porous silicon waveguide for label-free DNA sensing. Biosens Bioelectron 23:1572–1576
Dhahi ThS, Hashim U, Ahmed NM, Nazma H (2011) Fabrication and characterization of gold nano-gaps for ssDNA immobilization and hybridization deteciton. J New Mat Electrochem Syst 14:191–196
Ali ME, Hashim U, Mustafa S, Man YB, Yusop MH, Bari MF, Islam KhN, Hasan MF (2011) Nanoparticle sensor for label free detection of swine DNA in mixed biological samples. Nanotechnology 22:195503
Ali ME, Hashim U, Mustafa S, Che Man YB, Islam KhN (2012) Gold nanoparticle sensor for the visual detection of pork adulteration in meatball formulation. J Nanomater 2012:103607
Lim Z, Li J, Ng C, Yung LL, Bay B (2011) Gold nanoparticles in cancer therapy. Acta Pharmacol Sin 32:983–990
Iliuk AB, Hu L, Tao WA (2011) Aptamer in bioanalytical applications. Anal Chem 83:4440–4452
Upadhyayula VK (2012) Functionalized gold nanoparticle supported sensory mechanisms applied in detection of chemical and biological threat agents. Anal Chim Acta 715:1–18
Guirgis BS, Sá e Cunha C, Gomes I, Cavadas M, Silva I, Doria G, Blatch GL, Baptista PV, Pereria E, Azzazy HM, Mota MM, Prudencio M, Franco R (2012) Gold nanoparticle-based fluorescence immunoassay for malaria antigen detection. Anal Bioanal Chem 402:1019–1027
Zanoli LM, D′Agata R, Spoto G (2012) Functionalized gold nnaoparticles for the ultrasensitive DNA detection. Anal Bioanal Chem 402:1759–1771
Gopinath SCB, Awazu K, Fujimaki M, Shimizu K, Mizutani W, Tsukagoshi K (2012) Surface functionalization chemistry on highly sensitive silica-based sensor chips. Analyst 137:3520–3527
Liu X, Tykocinski M, Duan Y, Cowan R (2000) Histopathological analysis of cat cochleae following chronic electrical stimulation using high surface electrode (HiQ) platinum electrode. In: 20th annual meeting of Australian Neuroscience Society, vol 11, p 143
Tykocinski M, Liu X, Cowan R (2000) Chronic electrical stimulation of the auditory nerve using high surface area (HiQ) electrodes. In: 4th European congress of oto rhino laryngology head and neck surgery, Berlin, Germany, p 327
Gopinath SCB, Awazu K, Fujimaki M, Shimizu K (2013) Evaluation of Anti-A/Udorn/307/1972 antibody specificity to Influenza viruses using a waveguide mode sensor. PLoS One 8:e81396
Kumaresan R, Umezawa H, Tatsumi N, Ikeda K, Shikata S (2009) Device processing, fabrication and analysis of diamond pseudo-vertical Schottky barrier diodes with low leak current and high blocking voltage. Diam Relat Mater 18:299–302
Gopinath SCB, Kumaresan R, Awazu K, Fujimaki M, Mizuhata M, Tominaga J, Kumar PKR (2010) Evaluation of nucleic acid duplex formation on gold over layers on biosensor fabricated using Czochralski-grown silicon crystal silicon substrate. Anal Bioanal Chem 398:751–758
Lakshmipriya T, Fujimaki M, Gopinath SCB, Awazu K (2013) Detection of influenza viruses by aptamers in surface plasmon fluorescence spectroscopy. Langmuir 29:15107–15115
Gopinath SCB, Lakshmipriya T, Awazu K (2014) Colorimetric detection of controlled assembly and disassembly of aptamers on unmodified gold nanoparticles. Biosens Bioelectron 51:115–123
Tinguely J, Sow I, Leiner C, Grand J, Hohenau A, Felidj N (2011) Gold nanoparticles for plasmonic biosensing: the role of metal crystallinity and nanoscale roughness. BioNanoScience 1:128–135
Bosker WTE, Iakovlev PA, Norde W, Cohen Stuart MA (2005) BSA adsorption on bimodal peo brushes. J Colloid Interface Sci 286:496–503
Michel R, Pasche S, Textor M, Castner DG (2005) Influence of peg architecture on protein adsorption and conformation. Langmuir 21:12327–12332
Blattler TM, Pasche S, Textor M, Griesser HJ (2006) High salt stability and protein resistance of poly(-l-lysine)-g-poly(ethylene glycol) copolymers covalently immobilized via aldehyde plasma polymer interlayers on inorganic and polymeric substrates. Langmuir 22:5760–5769
Szleifer I (1997) Polymers and proteins: interactions at interfaces. Curr Opin Solid State Mater Sci 2:337–344
Chen A, Kozak D, Battersby BJ, Trau M (2010) Particle-by-particle quantification of protein adsorption onto poly(ethylene glycol) grafted surfaces. Biofouling J Bioadhesion Biofilm Res 24:267–273
Gopinath SCB, Awazu K, Fujimaki M, Sugimoto K, Ohki Y, Komatsubara T, Tominaga J, Gupta KC, Kumar PKR (2008) Influence of nonometric holes on the sensitivity of waveguide plasmon: a label-free nano-sensor to analyze RNA-aptamer ligand interactions. Anal Chem 80:6602–6609
Gopinath SCB, Awazu K, Fons P, Tominaga J, Kumar PKR (2009) A sensitive multilayered structure suitable for biosensing on the BioDVD platform. Anal Chem 81:4963–4970
Fujimaki M, Nomura K, Sato K, Kato T, Gopinath SCB, Wang X, Awazu K, Ohki Y (2010) Detection of coloured nanomaterials using evanescent field-based waveguide sensors. Opt Exp 18:15732–15740
Gopinath SCB, Anbu P, Lakshmipriya T, Hilda A (2013) Strategies to characterize fungal lipases. BioMed Res Int 2013:154549. doi:10.1155/2013/154549
Acknowledgments
T.H. Tang was supported by a USM Research University Grant 1001/CIPPT/813043. This study was supported by University of Malaya High Impact Research MoHE Grant UM.C/625/1/HIR/MOE/DENT/09 and UM.C/625/1/HIR/MOHE/MED/16/5. R. Kumaresan was supported by NIMS Special Research Grant. T. Lakshmipriya acknowledges the post-doctoral fellowship from Universiti Sains Malaysia.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Subash C. B. Gopinath and Ramanujam Kumaresan have contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gopinath, S.C.B., Kumaresan, R., Nishimura, T. et al. Investigation on Optimally Performing Sensor Substrates through Bio-fouling of Immunoglobulin-Conjugated Gold Nanoparticles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci., India, Sect. B Biol. Sci. 87, 807–814 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40011-015-0659-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40011-015-0659-x