Abstract
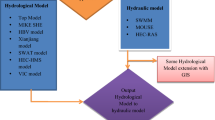
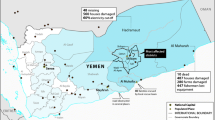
Urban floods are self-invited disasters which are responsible for huge property loss and in some cases loss of lives, self-invited in the sense man’s desire for more and more land, and uncontrolled infrastructure development is altering natural land use, land cover and stream flow paths. Thus, high-intensity rainfall for shorter time period is producing high peak runoff from altered/urbanized catchment. The urban flood events in India have been increasing in past few years, affecting major cities, and the frequency of floods continues to grow in future. It is beyond our capabilities to prevent these events from occurring; therefore, it is very important to develop a strategy to combat such events so that losses in terms of human lives and property can be minimized. This paper explains a framework developed for flood modeling on regional scale combining GIS with a rainfall–runoff model (HEC-HMS) and a hydrologic model (HEC-RAS). Hyderabad city of India is considered as a pilot study area as it is a region of frequent occurrences of severe flash floods. Three major flood events, viz. July 1989, August 2000 and August 2008, that occurred in Hyderabad are selected as cases to examine the modeling framework, and flood inundation maps are prepared representing area at risk and delineate the regions where the flooding is likely to occur. The study represents the importance of 2D modeling of flood problems to develop management strategies to tackle the probable future events by employing flood risk reduction measures.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ministry of Urban Development, GOI, Urban Flooding Standard Operating Procedure (Government of India, New Delhi, 2017)
NDMA (National Disaster Management Authority) GOI, Guidelines on Urban Flooding in India (Government of India, New Delhi, 2016)
WMO (World Meteorological Organization), Integrated Flood Management Concept Paper. WMO-No. 1047 (2009)
A. Zameer, R.M. Rao, K. Reddy, Urban flooding—case study of Hyderabad. Glob. J. Eng. Des. Technol. 2(4), 63–66 (2013)
I. Awakimjan, Urban Flood Modelling Recommendations For Ciudad Del Plata. Bachelor Thesis, University of Twente, Netherland, 2015
A.K. Gupta, S. Nair, Urban floods in Bangalore and Chennai: risk management challenges and lessons for sustainable urban ecology. Curr. Sci. (Bangalore) 100(11), 1638–1645 (2011)
R.K. Prasad, Urban floods—a review. Int. J. Innov. Res. Sci. Eng. Technol. 5(6), 2319–8753 (2014)
F. Rafiq et al., Urban floods in India. Int. J. Sci. Eng. Res. 7(1), 721–734 (2016)
M.R. Knebl et al., Regional scale flood modeling using NEXRAD rainfall, GIS, and HEC-HMS/RAS: a case study for the San Antonio River Basin Summer 2002 storm event. J. Environ. Manag. 75(2005), 325–336 (2005)
E. Tate, Floodplain mapping using HEC-RAS and ArcView GIS. CRWR Online Report 99-1 (1999). http://www.ce.utexas.edu/centers/crwr/reports/online.html
A. Radmehr, S. Araghinejad, Developing strategies for urban flood management of Tehran city using SMCDM and ANN. J. Comput. Civ. Eng. ASCE 28(6), 05014006 (2014)
S. Suriya, B.V. Mudgal, Impact of urbanization on flooding: the Thirusoolam sub watershed—a case study. J. Hydrol. 412–413, 210–219 (2012)
T.J. Chang, C.H. Wang, A.S. Chen, A novel approach to model dynamic flow interactions between storm sewer system and overland surface for different land covers in urban areas. J. Hydrol. 524, 662–679 (2015)
J. Leandro, S.C. Albert, D. Slobodan, A.S. Dragan, Comparison of 1d/1d and 1d/2d coupled sewer/surface hydraulic models for urban flood simulation. J. Hydraul. Eng. 135(6), 495–504 (2009)
C. Zoppou, Review of urban storm water models. Environ. Model Softw. 16, 195–231 (2001)
V.G. Mitchell et al., State of the art review of integrated urban water Models, in NOVATECH 2007, Sixth International Conference on Sustainable Techniques and Strategies in Urban Water Management, 25–28 JUNE 2007, Lyon, Rhone-Alpes, France (2007)
V.A. Rangari, A.K. Patel, N.V. Umamahesh, Review of urban stormwater models, in HYDRO 2015, 20th International Conference on Hydraulics, IIT Roorkee, India (2015)
F. Hashemyan, M.R. Khaleghi, M. Kamyar, Combination of HEC-HMS and HEC-RAS models in GIS in order to simulate flood (Case study: Khoshke Rudan river in Fars province, Iran). Res. J. Recent Sci. 4(8), 122–127 (2015)
E. Ranaee, M. Mahmoodian, S.R. Quchani, The combination of HEC-Geo-HMS, HECHMS and MIKE11 software utilize in a two branches river flood routing modeling, in Second International Conference on Environmental and Computer Science, IEEE, pp. 317–321 (2009)
F.A. Maniyar, J.P. Bhatt, Literature study on hydraulic modelling of floodplain mapping. Int. J. Res. Eng. Technol. eISSN: 2319-1163 (2015)
N.A. Adnan, P.M. Atkinson, Remote sensing of river bathymetry for use in hydraulic model prediction of flood inundation, in IEEE 8th International Colloquium on Signal Processing and Its Applications, pp. 159–163 (2012)
D. Jinkang, Q. Li, R. Hanyi, Z. Tianhui, Z. Dapeng, X. Youpeng, C.Y. Xu, Assessing the effects of urbanization on annual runoff and flood events using an integrated hydrological modeling system for Qinhuai river basin. China J. Hydrol. 464–465, 127–139 (2012)
Real time forecasting of Adyar and Cooum rivers to monitor the cyclonic impact, NRSC report (2016). NRSC-RSA-WRG-FF&HMD—May 2016-TR 853
M.S. Horritt, P.D. Bates, Evaluation of 1D and 2D numerical models for predicting river flood inundation. J. Hydrol. 268, 87–99 (2002)
S. Dhalla, 2D Modeling of Urban Flood Vulnerable Areas, in A.D. Latornell Conservation Symposium, November 22, 2013 (2013)
S.R. Ahrens, D.R. Maidment, Flood Forecasting for the Buffalo Bayou Using CRWR-PrePro and HEC-HMS (CRWR Report 99-6) (Center for Research in Water Resources, Austin, 1999)
HEC GeoHMS reference manual; USACE, version 4.2. (US Army Corps of Engineers, CPD-77, 2009)
HEC-HMS reference manual; USACE, version 4.2. (US Army Corps of Engineers, CPD-74-A, 2016)
G. Schumann et al., Comparison of remotely sensed water stages from LiDAR, topographic contours and SRTM. ISPRS J. Photogramm Rem Sens 63, 283–296 (2008)
J. Lastra et al., Flood hazard delineation combining geomorphological and hydrological methods: an example in the Northern Iberian Peninsula. Nat. Hazards 45, 277–293 (2008)
HEC-RAS, reference manual; USACE, version 5.0. (US Army Corps of Engineers, CPD-68, 2016)
Acknowledgements
This work is undertaken as a part of Information Technology Research Academy-Water, Media Lab Asia project entitled “Integrated Urban Flood Management in India: Technology Driven Solution.” We also thank Greater Hyderabad Municipal Corporation for sharing technical data. The Landsat satellite images are downloaded from the United States Geological Survey.
Funding
Funding was provided by ITRA, Digital India Corporation, Government of India (Grant No. ITRA/15(68)/water/IUFM/01).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rangari, V.A., Sridhar, V., Umamahesh, N.V. et al. Floodplain Mapping and Management of Urban Catchment Using HEC-RAS: A Case Study of Hyderabad City. J. Inst. Eng. India Ser. A 100, 49–63 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40030-018-0345-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40030-018-0345-0