Abstract
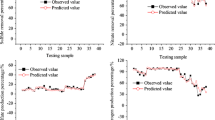
In this study three modeling approaches consisting Modified Stover-Kincannon, multilayer perceptron neural network (MLPANN) and B-Spline quasi interpolation were applied in order to predict effluent of up-flow anaerobic sludge blanket (UASB) reactor and also to find the reaction kinetics. At first run, the average total chemical oxygen demand (TCOD) removal efficiency was 48.3% with hydraulic retention time (HRT) of 26 h and 63.8% with HRT of 37 h, at OLR of 0.77–1.66 kg TCOD/m3 d. At the second run, UASB reactor operated with OLR of 1.94–3.1 kg TCOD/m3 d and achieved the average TCOD removal efficiency of 64.74 and 72.48% with HRT of 26 and 37 h, respectively. The Modified Stover-Kincannon performed well in terms of kinetic determination with a high value of regression coefficient over 0.98. The B-Spline quasi interpolation and MLPANN indicated a great fit for effluent prediction with average R of 0.9984 and 0.9986, and MSE of 157.6050 and 129.7796, respectively; however, they gave no information about reactions occurred in the system.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bustillo-Lecompte CF, MJJoem M. Slaughterhouse wastewater characteristics, treatment, and management in the meat processing industry: a review on trends and advances. J Environ Manag. 2015;161:287–302.
Palatsi J, Viñas M, Guivernau M, Fernandez B, Flotats XJBT. Anaerobic digestion of slaughterhouse waste: main process limitations and microbial community interactions. Bioresour Technol. 2011;102(3):2219–27.
Cao W, Mehrvar M, JCER Design. Slaughterhouse wastewater treatment by combined anaerobic baffled reactor and UV/H2O2 processes. Chem Eng Res Des. 2011;89(7):1136–43.
Chernicharo CAL, CdJRiES, Bio/Technology. Post-treatment options for the anaerobic treatment of domestic wastewater. Rev Environ Sci Biotechnol. 2006;5(1):73–92.
Lettinga G, Van Velsen A, Hobma SD, De Zeeuw W, Klapwijk AJB. Use of the upflow sludge blanket (USB) reactor concept for biological wastewater treatment, especially for anaerobic treatment. Biotechnol Bioeng. 1980;22(4):699–734.
Khan AA, Gaur RZ, Tyagi V, Khursheed A, Lew B, Mehrotra I, et al. Sustainable options of post treatment of UASB effluent treating sewage: a review. Resour Conserv Recycl. 2011;55(12):1232–51.
Gholami M, Nasseri S, Alizadehfard M-R, Mesdaghinia AJWQRJ. Textile dye removal by membrane technology and biological oxidation. Water Qual Res J. 2003;38(2):379–91.
Salimi M, Esrafili A, Gholami M, Jafari AJ, Kalantary RR, Farzadkia M, et al. Contaminants of emerging concern: a review of new approach in AOP technologies. Environ Monit Assess. 2017;189(8):414.
Jin R-C, Zheng PJJ. Kinetics of nitrogen removal in high rate anammox upflow filter. J Hazard Mater. 2009;170(2–3):652–6.
Debik E, Coskun TJBT. Use of the static granular bed reactor (SGBR) with anaerobic sludge to treat poultry slaughterhouse wastewater and kinetic modeling. Bioresour Technol. 2009;100(11):2777–82.
Yetilmezsoy K, Sapci-Zengin ZJSer, assessment r. Stochastic modeling applications for the prediction of COD removal efficiency of UASB reactors treating diluted real cotton textile wastewater. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess. 2009;23(1):13–26.
Yetilmezsoy K. Treatability of poultry manure wastewater using anaerobic sludge bed reactor. Istanbul: Diss. PhD Thesis, Institute of Science, Department of Environmental Engineering, Yildiz Technical University; 2008.
Turkdogan-Aydinol FI, Yetilmezsoy K, Comez S, Bayhan HJB, engineering b. Performance evaluation and kinetic modeling of the start-up of a UASB reactor treating municipal wastewater at low temperature. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng. 2011;34(2):153–62.
Chan YJ, Chong MF, Law CLJEt. Performance and kinetic evaluation of an integrated anaerobic–aerobic bioreactor in the treatment of palm oil mill effluent. Environ Technol. 2017;38(8):1005–21.
Wang J, Yan J, Xu WJBej. Treatment of dyeing wastewater by MIC anaerobic reactor. Biochem Eng J. 2015;101:179–84.
Mostafa A, Elsamadony M, El-Dissouky A, Elhusseiny A, Tawfik AJBt. Biological H2 potential harvested from complex gelatinaceous wastewater via attached versus suspended growth culture anaerobes. Bioresour Technol. 2017;231:9–18.
Khataee A, Mirzajani OJD. UV/peroxydisulfate oxidation of CI Basic Blue 3: modeling of key factors by artificial neural network. Desalination. 2010;251(1–3):64–9.
Moral H, Aksoy A, Gokcay CFJC, Engineering C. Modeling of the activated sludge process by using artificial neural networks with automated architecture screening. Comput Chem Eng. 2008;32(10):2471–8.
Raduly B, Gernaey KV, Capodaglio AG, Mikkelsen PS, Henze MJEM, Software. Artificial neural networks for rapid WWTP performance evaluation: methodology and case study. Environ Model Softw. 2007;22(8):1208–16.
Güçlü D, Dursun ŞJB, engineering b. Artificial neural network modelling of a large-scale wastewater treatment plant operation. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng. 2010;33(9):1051–8.
Kordkandi SA, Berardi LJBej. Comparing new perspective of hybrid approach and conventional kinetic modelling techniques of a submerged biofilm reactor performance. Biochem Eng J. 2015;103:170–6.
Vafaei F, Movafeghi A, Khataee A, Zarei M, Lisar SSJE, safety e. Potential of Hydrocotyle vulgaris for phytoremediation of a textile dye: inducing antioxidant response in roots and leaves. Ecotox Environ Safe. 2013;93:128–34.
Aminikhah H, Alavi JJICM. Applying cubic B-Spline quasi-interpolation to solve 1D wave equations in polar coordinates. Computational Mathematics. 2013;2013:1–8.
American Public Health Association & Eaton, Andrew D & Water Environment Federation & American Water Works Association. Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. 21st ed. Washington, D.C.: APHA-AWWA-WEF; 2005.
Jelali M, Kroll A. Hydraulic servo-systems. In: Modelling, identification and control. https://www.springer.com/gp/book/9781852336929.
Ahn J-H, Forster CJPB. A comparison of mesophilic and thermophilic anaerobic upflow filters treating paper–pulp–liquors. Process Biochem. 2002;38(2):256–61.
Kuşçu ÖS, Sponza DTJJohm. Kinetics of para-nitrophenol and chemical oxygen demand removal from synthetic wastewater in an anaerobic migrating blanket reactor. J Hazard Mater. 2009;161(2–3):787–99.
Yu H, Wilson F, Tay J-HJWr. Kinetic analysis of an anaerobic filter treating soybean wastewater. WaterRes. 1998;32(11):3341–52.
Zhu C-G, Kang W-SJAM, Computation. Numerical solution of Burgers–Fisher equation by cubic B-spline quasi-interpolation. Appl Math Comput. 2010;216(9):2679–86.
Aminikhah H, Alavi JJSJ. An efficient B-spline difference method for solving system of nonlinear parabolic PDEs. SeMA Journal. 2018;75(2):335–48.
Calabrò F, Falini A, Sampoli ML, Sestini AJJoC, Mathematics A. Efficient quadrature rules based on spline quasi-interpolation for application to IGA-BEMs. J Comput Appl Math. 2018;338:153–67.
Aminikhah H, Alavi JJC. B-spline collocation and quasi-interpolation methods for boundary layer flow and convection heat transfer over a flat plate. Calcolo. 2017;54(1):299–317.
Zhang J, Zheng J, Gao QJAM, Computation. Numerical solution of the Degasperis–Procesi equation by the cubic B-spline quasi-interpolation method. Appl Math Comput. 2018;324:218–27.
Zhu C-G, Wang R-HJAM, Computation. Numerical solution of Burgers’ equation by cubic B-spline quasi-interpolation. Appl Math Comput. 2009;208(1):260–72.
Del Nery V, De Nardi I, Damianovic MHRZ, Pozzi E, Amorim A, Zaiat MJR, conservation et al. Long-term operating performance of a poultry slaughterhouse wastewater treatment plant. Resour Conserv Recy. 2007;50(1):102–14.
Martínez J, Borzacconi L, Mallo M, Galisteo M, Vinas MJWs, Technology. Treatment of slaughterhouse wastewater. Water Sci Technol. 1995;32(12):99–104.
Borja R, Banks CJ, Wang Z, Mancha AJBt. Anaerobic digestion of slaughterhouse wastewater using a combination sludge blanket and filter arrangement in a single reactor. Bioresour Technol. 1998;65(1–2):125–33.
Caixeta CE, Cammarota MC, Xavier AMJBT. Slaughterhouse wastewater treatment: evaluation of a new three-phase separation system in a UASB reactor. Bioresour Technol. 2002;81(1):61–9.
Borja R, Banks CJ, Wang ZJBt. Effect of organic loading rate on anaerobic treatment of slaughterhouse wastewater in a fluidised-bed reactor. Bioresour Technol. 1995;52(2):157–62.
Tritt WJBt. The anaerobic treatment of slaughterhouse wastewater in fixed-bed reactors. Bioresour Technol. 1992;41(3):201–7.
Ruiz I, Veiga MC, De Santiago P, Blazquez RJBT. Treatment of slaughterhouse wastewater in a UASB reactor and an anaerobic filter. Bioresour Technol. 1997;60(3):251–8.
KJBt Y. Integration of kinetic modeling and desirability function approach for multi-objective optimization of UASB reactor treating poultry manure wastewater. Bioresour Technol. 2012;118:89–101.
Işik M, Sponza DTJPB. Substrate removal kinetics in an upflow anaerobic sludge blanket reactor decolorising simulated textile wastewater. Process Biochem. 2005;40(3–4):1189–98.
Sponza DT, AJJoem U. Kinetic of carbonaceous substrate in an upflow anaerobic sludge sludge blanket (UASB) reactor treating 2, 4 dichlorophenol (2, 4 DCP). J Environ Manag. 2008;86(1):121–31.
Büyükkamaci N, Filibeli AJPB. Determination of kinetic constants of an anaerobic hybrid reactor. Process Biochem. 2002;38(1):73–9.
Sandhya S, Sarayu K, KJBt S. Determination of kinetic constants of hybrid textile wastewater treatment system. Bioresour Technol. 2008;99(13):5793–7.
Acknowledgements
We would like to acknowledge Sepidroud slaughterhouse factory for its cooperation in providing slaughterhouse wastewater sample.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Highlights
• Performance of up-flow anaerobic sludge blanket reactor.
• Effect of HRT on removal efficiency.
• Multi-layer perceptron and B-Spline quasi interpolation were used in order to predict the effluent of UASB reactor.
• Kinetic modeling of UASB reactor by modified Stover-Kincannon.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Besharati Fard, M., Mirbagheri, S.A., Pendashteh, A. et al. Biological treatment of slaughterhouse wastewater: kinetic modeling and prediction of effluent. J Environ Health Sci Engineer 17, 731–741 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40201-019-00389-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40201-019-00389-4