Abstract
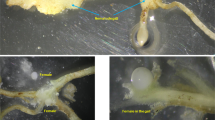
The nematodes which belong to the family Longidoridae are obligatory plant parasites and are considered as economically significant pests since they cause severe crop losses around the world. Conventional identification of nematodes using morphological features is a time-consuming and challenging task. To overcome the challenges in conventional identification methods, rapid and reliable identification methods need to be established which will not only enable proper identification but also provide effective management program for nematodes which devastate the root system. In the present study, we have observed the nematode infection in a unique brinjal variety (Solanum melongena L. var. Mattu Gulla) grown in Mattu Village, Udupi District of Karnataka, India and identified the nematodes on the basis of molecular characterization using D3 expansion region of 28S rRNA gene sequence. Cephalobus cubaensis was found from the roots of Mattu Gulla for the first time. Our study will facilitate further screening and characterization of the root-knot and root-lesion nematode infections in both nursery as well as post-transplantation seedlings of Mattu Gulla in the field conditions.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Banna L, Ploeg AT, Williamson VM, Kaloshian I (2004) Discrimination of six Pratylenchus species using PCR and species-specific primers. J Nematol 36:142–146
Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman DJ (1990) Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol 215:403–410
Banu JG, Sankari Meena K, Selvi C, Manickam S (2017) Molecular marker-assisted selection for nematode resistance in crop plants. J Entomol Zool Stud 5:1307–1311
Barrière A, Félix MA (2006) Isolation of C. elegans and related nematodes. In: The C. elegans Research Community (ed) WormBook, pp 1–19. https://doi.org/10.1895/wormbook.1.115.2, http://www.wormbook.org. Accessed 3 Oct 2018
Bernhard EC (1992) Soil nematode biodiversity. Biol Fertil Soils 14:99–103
Bhadury P, Austen MC, Bilton DT, Lambshead JD, Rogers AD, Smerdon GR (2005) Combined morphological and molecular analysis of individual nematodes through short-term preservation in formalin. Mole Ecol Notes 5:965–968
Bhat RV, Madhyastha MN (2007) Preserving the heritage of Mattu Gulla—a variety of brinjal unique to Udupi District. Curr Sci 93:905–907
Brussaard L, Kuyper TW, Goede RGM (2001) On the relationships between nematodes, mycorrhizal fungi and plants: functional composition of species and plant performance. Plant Soil 232:155–165
Carrasco-Ballesteros SP, Castillo P, Adams BJ, Perez-Artes E (2007) Identification of Pratylenchus thornei, the cereal legume root-lesion nematode, based on SCAR-PCR and satellite DNA. Eur J Plant Pathol 118:115–125
Cook R, Yeates GW (1993) Nematode pests of grassland and forage crops. In: Evans K, Trudgill DL, Webster JM (eds) Plant parasitic nematodes in temperate agriculture. CABI Publishing, Wallingford, pp 305–350
Decraemer W, Hunt DJ (2006) Structure and classification. In: Perry RN, Moens M (eds) Plant nematology. CAB International, Wallingford, pp 3–32
Desaeger JR, Rao MR, Bridge J (2004) Nematodes and other soilborne pathogens in agroforestry. In: van Noordwijk M, Cadisch G, Ong CK (eds) Below-ground interactions in tropical agroecosystems: concepts and models with multiple plant components. CABI, Wallingford, pp 263–283
Ferris H, Bongers T, De Goede RGM (2001) A framework for soil food web diagnostics: extension of the nematode faunal analysis concept. Appl Soil Ecol 18:13–29
Ganguly AK, Dutta TK (2012) Plant parasitic nematodes: an emerging problem under changing climate and agricultural practices. J Mycol Plant Pathol 43:541
Gazaway W, Mullen JM, Sikora EJ (1995) Collecting soil and root samples for nematode analysis. Circ ANR 114:1–2
Geographical Indications Journal (2011) Government of India, G.I. Application-199, 40, pp 20–24 (http://ipindia.nic.in/girindia/journal/Journal_40.pdf. Accessed 10 Mar 2012
Handop ZA, Carta LK, Skantar AM (2008) Taxonomy, morphology and phylogenetics of coffee-associated root-lesion nematodes, Pratylenchus spp. In: Souza RM (ed) Plant-Parasitic Nematodes of Coffee. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 29–50
Holterman M, Rybarczyk K, van den Elsen S, van Megen H, Mooyman P, Santiago RP, Bongers T, Bakker J, Helder J (2008) A ribosomal DNA-based framework for the detection and quantification of stress-sensitive nematode families in terrestrial habitats. Mol Ecol Resour 8:23–34
Inserra RN, Troccoli A, Gozel U, Bernard EC, Dunn D, Duncan LW (2007) Pratylenchus hippeastri n. sp. (Nematoda: pratylenchidae) from amaryllis in Florida with notes on P. scribneri and P. hexincisus. Nematol 9:25–42
Jain RK (1992) Nematode pests of vegetable crops. In: Bhatti DS, Walia RK (eds) Nematode pests of crops. CBS Publishers & Distributors, New Delhi, pp 77–97
Jones KL, Todd TC, Herman MA (2006) Development of taxon-specific markers for high-throughput screening of microbial-feeding nematodes. Mol Ecol Notes 6:712–714
Jones JT, Haegeman A, Danchin EG, Gaur HS, Helder J, Jones MG, Kikuchi T, Manzanilla-López R, Palomares-Rius JE, Wesemael WM, Perry RN (2013) Top 10 plant-parasitic nematodes in molecular plant pathology. Mol Plant Pathol 14:946–961
Keiko GA, Mitani S (2000) Characterization of mutations induced by ethyl ethanesulfonate, UV, and Trimethylpsoralen in the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 269:64–69
Kerrigan J, Rogers JD (2013) Biology, ecology and ultrastructure of Ascobotryozyma and Botryozyma, unique commensal nematode-associated yeasts. Mycologia 105:34–51
Khan MR (2015) Nematode diseases of crops in India. In: Awasthi LP (ed) Recent advances in the diagnosis and management of plant diseases. Springer, New Delhi, pp 183–224
Khan MR, Jain RK, Singh RV, Pramanik A (2010) Economically important plant parasitic nematodes distribution-atlas. Directorate of information and publications of agriculture. Indian Council of Agricultural Research, Krishi Anusandhan Bhavan, New Delhi, pp 1–145
Kornobis FW, Susulovska S, Susulovsky A, Subbotin SA (2015) Morphological and molecular characterization of Paralongidorus rex Andrássy, 1986 (Nematoda: Longidoridae) from Poland and Ukrain. Eur J Plant Pathol 141:385
Luc M (1987) A reappraisal of Tylenchina (Nemata). 7. The family Pratylenchidae Thorne, 1949. Revue de Nématologie 10:203–218
Madani M, Subbotin SA, Moens M (2005) Quantitative detection of the potato cyst nematode, Globodera pallida, and the beet cyst nematode, Heterodera schachtii, using real-time PCR with SYBR green I dye. Mol Cell Probes 19:81–86
Munera GE, Bert W, Decraeme W (2009) Morphological and molecular characterisation of Pratylenchus araucensis n. sp. (Pratylenchidae), a root-lesion nematode associated with Musa plants in Colombia. Nematol 11:799–813
Neher DA (2001) Role of nematodes in soil health and their use as indicators. J Nematol 33:161–168
Reddy PP, Singh DB, Ramkishun (1979) Effect of rootknot nematodes on the susceptibility of Pusa purple cluster brinjal to bacterial wilt. Curr Sci 48:915–916
Ruehle JL (1973) Nematodes and forest trees—types of damage to tree roots. Annu Rev Phytopathol 11:99–118
Sasser JN, Freckman DW (1987) A world perspective on nematology: the role of the society. In: Veech JA, Dickson DW (eds) Vistas on nematology. Society of Nematologists, Maryland, pp 7–14
Sato E, Min YY, Shirakashi T, Wada S, Toyota K (2007) Detection of the root-lesion nematode, Pratylenchus penetrans (Cobb), in a nematode community using real-time PCR. Jpn J Nematol 37:87–92
Sohlenius B (1980) Abundance, biomass and contribution to energy flow by soil nematodes in terrestrial ecosystems. Oikos 34:186–194
Stiernagle T (1999) Maintenance of C. elegans. In: Hope IA (ed) C. elegans: a practical approach. Oxford University Press, Oxford, pp 51–67
Subbotin SA, Waeyenberge L, Molokanova IA, Moens M (1999) Identification of Heterodera avenae group species by morphometrics and rDNA-RFLPs. Nematol 1:195–207
Subbotin SA, Ragsdale EJ, Mullens T, Roberts P, Mundo-Ocampo M, Baldwin JG (2008) A phylogenetic framework for root lesion nematodes of the genus Pratylenchus (Nematoda): evidence from 18S and D2D3 expansion segments of 28S ribosomal RNA genes and morphological characters. Mol Phylogenet Evol 48:491–505
Uehara T, Mizukubo T, Kushida A, Momota Y (1998) Identification of Pratylenchus penetrans (Cobb) by PCR using ITS-based species specific primer. Jpn J Nematol 28:1–7
Waeyenberge L, Ryss A, Moens M, Pinochet J, Vrain TC (2000) Molecular characterization of 18 Pratylenchus species using rDNA restriction fragment length polymorphism. Nematol 2:135–142
Yeates GW (2003) Nematodes as soil indicators: functional and biodiversity aspects. Biol Fertil Soil 37:199–210
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Manipal Academy of Higher Education (MAHE), Manipal, Karnataka, India and TIFAC-CORE and FIST, DST, New Delhi and K-FIST, VGST, Govt. of Karnataka for the facilities. We are indebted to Prof. K. Satyamoorthy, Director, Manipal School of Life Sciences, MAHE for encouragement, support and critical comments. We would like to thank Mrs. Shashikala Tantry for her experimental assistance and Mr. Kiran K.R. for the format of article; Shri Mohan Rao and Lakshmana Rao, Members of Mattu Gulla Growers Association, Mattu Village, Udupi District, Karnataka, India for their help in collection of plant samples.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Muthusamy, A., Singh, R., Paul, B. et al. Occurrence and molecular identification of nematodes associated with brinjal (Solanum melongena L.) var. Mattu Gulla. Indian Phytopathology 72, 453–459 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42360-019-00153-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42360-019-00153-6