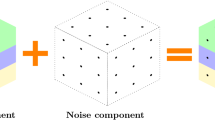
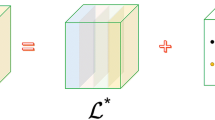
Abstract
Tensor robust principal component analysis has received a substantial amount of attention in various fields. Most existing methods, normally relying on tensor nuclear norm minimization, need to pay an expensive computational cost due to multiple singular value decompositions at each iteration. To overcome the drawback, we propose a scalable and efficient method, named parallel active subspace decomposition, which divides the unfolding along each mode of the tensor into a columnwise orthonormal matrix (active subspace) and another small-size matrix in parallel. Such a transformation leads to a nonconvex optimization problem in which the scale of nuclear norm minimization is generally much smaller than that in the original problem. We solve the optimization problem by an alternating direction method of multipliers and show that the iterates can be convergent within the given stopping criterion and the convergent solution is close to the global optimum solution within the prescribed bound. Experimental results are given to demonstrate that the performance of the proposed model is better than the state-of-the-art methods.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acar, E., Dunlavy, D.M., Kolda, T.G., Mørup, M.: Scalable tensor factorizations with missing data. In: SIAM International Conference on Data Mining, pp. 701–712 (2010)
Boyd, S., Parikh, N., Chu, E., Peleato, B., Eckstein, Jonathan: Distributed optimization and statistical learning via the alternating direction method of multipliers. Found. Trends Mach. Learn. 3(1), 1–122 (2011)
Cabral, R., De La Torre, F., Costeira, J.P., Bernardino, A.: Unifying nuclear norm and bilinear factorization approaches for low-rank matrix decomposition. In: IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 2488–2495 (2013)
Candès, E.J.S., Li, X., Ma, Y., Wright, J.: Robust principal component analysis? J. ACM 58(3), 1–73 (2011)
Cichocki, A., Mandic, D., De Lathauwer, L., Zhou, G.: Tensor decompositions for signal processing applications: from two-way to multiway component analysis. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 32(2), 145–163 (2014)
Filipović, M., Jukić, A.: Tucker factorization with missing data with application to low-\(n\)-rank tensor completion. Multidimens. Syst. Signal Process. 26(3), 1–16 (2013)
Gandy, S., Recht, B., Yamada, I.: Tensor completion and low-n-rank tensor recovery via convex optimization. Inverse Probl. 27(2), 25010–25028(19) (2011)
Goldfarb, D., Qin, Z.: Robust low-rank tensor recovery: models and algorithms. SIAM J. Matrix Anal. Appl. 35(1), 225–253 (2013)
Harshman, R.A.: Foundations of the Parafac procedure: model and conditions for an “explanatory” multi-mode factor analysis. In: UCLA Working Papers (1969)
Håstad, J.: Tensor rank is NP-complete. J. Algorithms 11(4), 451–460 (2006)
Higham, N.: Matrix procrustes problems. Rapport technique, University of Manchester (1995)
Huang, B., Cun, M., Goldfarb, D., Wright, J.: Provable models for robust low-rank tensor completion. Pac. J. Optim. 11(2), 339–364 (2015)
Kolda, T.G., Bader, B.W.: Tensor decompositions and applications. SIAM Rev. 66(4), 294–310 (2005)
Li, X., Lin, S., Yan, S., Dong, X.: Discriminant locally linear embedding with high-order tensor data. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Part B Cybern. 38(2), 342–352 (2008)
Li, Y., Yan, J., Zhou, Y., Yang, J.: Optimum subspace learning and error correction for tensors. In: European Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 790–803 (2010)
Lin, Z., Chen, M., Ma, Y.: The augmented Lagrange multiplier method for exact recovery of corrupted low-rank matrices. Technical Report, University of Illinois, Urbana-Champaign (2009)
Liu, G., Yan, S.: Active subspace: toward scalable low-rank learning. Neural Comput. 24(12), 3371–3394 (2012)
Liu, J., Musialski, P., Wonka, P., Ye, J.: Tensor completion for estimating missing values in visual data. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 35(1), 208–220 (2013)
Mørup, M.: Applications of tensor (multiway array) factorizations and decompositions in data mining. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Data Min. Knowl. Discov. 1(1), 24–40 (2011)
Nocedal, B.J., Wright, S.J.: Numerical Optimization. Springer, Berlin (2006)
Okutomi, M., Yan, S., Sugimoto, S., Liu, G., Zheng, Y.: Practical low-rank matrix approximation under robust \(\ell _1\)-norm. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1410–1417 (2012)
Signoretto, M., Dinh, Q.T., De Lathauwer, L., Suykens, J.A.K.: Learning with tensors: a framework based on convex optimization and spectral regularization. Mach. Learn. 94(3), 303–351 (2014)
Signoretto, M., De Lathauwer, L., Suykens, J.A.K.: Nuclear norms for tensors and their use for convex multilinear estimation (2010)
Sun, J., Papadimitriou, S., Lin, C.Y., Cao, N., Liu, S., Qian, W.: Multivis: content-based social network exploration through multi-way visual analysis. In: SIAM International Conference on Data Mining, pp. 1064–1075 (2009)
Tan, H., Cheng, B., Feng, J., Feng, G., Wang, Wuhong, Zhang, Yu Jin: Low-n-rank tensor recovery based on multi-linear augmented Lagrange multiplier method. Neurocomputing 119(16), 144–152 (2013)
Tao, D., Li, X., Xindong, W., Maybank, S.J.: General tensor discriminant analysis and Gabor features for gait recognition. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 29(10), 1700–1715 (2007)
Tucker, L.R.: Some mathematical notes on three-mode factor analysis. Psychometrika 31(3), 279–311 (1966)
Xu, Y., Hao, R., Yin, W., Su, Z.: Parallel matrix factorization for low-rank tensor completion. Inverse Probl. Imaging 9(2), 601–624 (2015)
Yang, L., Huang, Z.H., Shi, X.: A fixed point iterative method for low n-rank tensor pursuit. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 61(11), 2952–2962 (2013)
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Mr. Qiang Jiang for his help in the preparation of the manuscript when he worked at the Department of Mathematics, Hong Kong Baptist University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Michael K. Ng: Research supported in part by the HKRGC GRF 12306616, 12200317, 12300218 and 12300519, and HKU Grant 104005583.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ng, M.K., Wang, XZ. Parallel Active Subspace Decomposition for Tensor Robust Principal Component Analysis. Commun. Appl. Math. Comput. 3, 221–241 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42967-020-00063-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42967-020-00063-9
Keywords
- Principal component analysis
- Low-rank tensors
- Nuclear norm minimization
- Active subspace decomposition
- Matrix factorization