Abstract
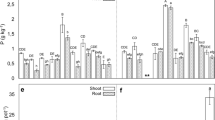
In a runoff irrigation system in Northern Kenya, we studied the nutrient interactions of sole cropped and alley cropped Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench and Acacia saligna (Labill.) H.L. Wendl. The trees were pruned once before the cropping season and the biomass was used as fodder for animals. The nutrient contents in leaf tissue, soil and soil solution were monitored and the uptake of applied tracers (15N, Sr) was followed. The grain yield of alley cropped sorghum was similar to or slightly higher than in monoculture and did not decrease near the tree-crop interface. Foliar N and Ca contents of the crop were higher in the agroforestry combination than in monoculture, corresponding to higher soil N and Ca contents. Soil solution and soil mineral N dynamics indicate an increase of N under the tree row and unused soil N at the topsoil in the alley of the sole cropped trees as well as below 60 cm depth in the crop monoculture. The N use efficiency of the tree+crop combination was higher than the sole cropped trees or crops. Competition was observed for Zn and Mn of both tree and crop whereas for Ca only the tree contents decreased. P, K, Mg and Fe dynamics were not affected by alley cropping at our site. The lower uptake of applied Sr by trees in alley cropping compared to those of the monoculture stand suggested a lower competitiveness of the acacia than sorghum, which did not show lower Sr contents when intercropped. The study showed the usefulness of combining soil and plant analyses together with tracer techniques identifying nutrient competition, nutrient transfer processes and the complementary use of soil nutrients, as the main features of the tree-crop combination.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Carter D C and Miller S 1991 Three years of experience with an on-farm macrocatchment water harvesting system in Botswana. Agric. Water Manage. 19, 191-203.
Cheng W and Coleman D C 1990 Effect of living roots on soil organic matter decomposition. Soil Biol. Biochem. 22, 781-787.
Droppelmann K 1999 Resource capture in a runoff agroforestry system in Northern Kenya. Bayreuther Bodenkundliche Berichte 63, Bayreuth, Germany. 137 pp.
FAO 1990 Soil map of the world, revised legend. FAO, Rome, Italy. 119 p.
Grayston S J, Vaughan D and Jones D 1996 Rhizosphere carbon flow in trees, in comparison with annual plants: the importance of root exudation and its impact onmicrobial activity and nutrient availability. Appl. Soil Ecol. 5, 29-56.
Hagedorn F, Steiner K G, Sekayange L and Zech W 1997 Effect of rainfall pattern on nitrogen mineralization and leaching in a green manure experiment in South Rwanda. Plant Soil 195, 365-375.
Haggar J P, Tanner E V J, Beer J W and Kass D C L 1993 Nitrogen dynamics of tropical agroforestry and annual cropping systems. Soil Biol. Biochem. 25, 1363-1378.
Hartemink A E, Buresh R J, Bashir-Jama and Janssen B H 1996 Soil nitrate and water dynamics in sesbania fallow, weed fallow, and maize. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 60, 568-574.
Klemm W 1989 Bewässerung mit Niederschlagswasser ohne Zwischenspeicherung im Sahel. PhD Dissertation. University of Karlsruhe, Karlsruhe, Germany. 117 p.
Kolberg R L, Rouppet B, Westfall D G and Peterson G A 1997 Evaluation of an in situ soil nitrogen mineralization method in dryland agroecosystems. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 61, 504-508.
Lehmann J and Zech W 1997 Möglichkeiten und Grenzen der Ertragssteigerung in tropischen Alley-cropping Systemen. In Leguminosen zur Verbesserung und nachhaltigen Sicherung der Agrarproduktion. Eds. J C G Ottow and J Sauerborn. pp 165-176. Giessener Beiträge zur Entwicklungsforschung 24.
Lehmann J and Zech W 1998 Fine root turnover of irrigated hedgerow intercropping in Northern Kenya. Plant Soil 198, 19-31.
Lehmann J, von Willert F, Wulf S and Zech W 1997 Influence of runoff irrigation on nitrogen dynamics of Sorghum bicolor (L.) in Northern Kenya. Adv. Geoecol. 31, 1255-1260.
Lehmann J, Droppelmann K and Zech W 1998a Runoff irrigation of crops with contrasting root and shoot development in the semi-arid North of Kenya: water depletion and above-and below-ground biomass production. J. Arid Environ. 38, 479-492.
Lehmann J, Peter I, Steglich C, Gebauer G, Huwe B and Zech W 1998b Below-ground interactions in dryland agroforestry. For. Ecol. Manage. 111, 157-169.
Little T M and Hills F J 1978 Agricultural Experimentation. Wiley and Sons, New York, USA. 350 p.
Lockman R B 1972 Mineral composition of grain sorghum plant samples, Part 3. Suggested nutrient sufficiency limits at various stages of growth. Soil Sci. Plant Analysis 3, 295-303.
Mehlich A 1984 Mehlich 3 soil test extractant: A modification of the Mehlich 2 extractant. Communications Soil Sci. Plant Analysis 15, 1409-1416.
Olson S R and Sommers L E 1982 Phosphorus. In Methods of Soil Analyses: Part 2 Chemical and Microbiological Properties. Eds. A L Page, R H Miller and D R Keeney. pp 403-430. American Society of Agronomy, Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
Palm C A 1995 Contribution of agroforestry trees to nutrient requirements of intercropped plants. Agrofor. Syst. 30, 105-124.
Sanchez P A 1995 Science in Agroforestry. Agrofor. Syst. 30, 5-55.
Schroth G 1995 Tree root characteristics as criteria for species selection and systems design in agroforestry. Agrofor. Syst. 30, 125-143.
Schroth G and Lehmann J 1995 Contrasting effects of roots and mulch from three agroforestry tree species on yields of alley cropped maize. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 54, 89-101.
Schroth G, Olivier R, Balle P, Gnahoua G M, Kanchanakanti N, Jeduc B, Mallet B, Peltier R and Zech W 1995 Alley cropping with Gliricidia sepium on a high base status soil following forest clearing: effects on soil conditions, plant nutrition and crop yields. Agrofor. Syst. 32, 261-276.
Zech W and Drechsel P 1991 Foliar nutrient levels of broad-leaved tropical trees: A tabular review. Plant Soil 131, 29-46.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lehmann, J., Weigl, D., Peter, I. et al. Nutrient interactions of alley cropped Sorghum bicolor and Acacia saligna in a runoff irrigation system in Northern Kenya. Plant and Soil 210, 249–262 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1004698403770
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1004698403770