Abstract
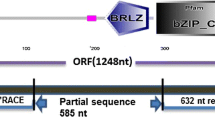
The seed storage proteins of Coix, sorghum and maize are codified by homologous genes which are coordinately expressed in the endosperm in a temporal-specific fashion. Opaque2 (O2), a bZIP protein originally isolated from maize, has been described as a transcription activator of α- and β-prolamin genes. The isolation and characterization of cDNA and genomic clones encoding the Opaque2 homologue from Coix are reported here. The coding region of the Coix O2 gene is interrupted by five introns and codifies a polypeptide of 408 amino acids. Comparison of the deduced amino acid sequence with two different sequences of maize O2 protein showed that the Coix O2 protein is similar to the maize O2 isolated from W22 maize inbred line. The Coix O2 protein has the same binding specificity and expression pattern of the maize O2. The O2 proteins together with OHP1, OsBZIPPA, SPA, CPRF2 and RITA1 were assigned to one of the five bZIP plant families in an updated classification of plant bZIP according to bZIP domain similarity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aeschbacher RA, Schrott M, Potrykus I, Saul MW: Isolation and molecular characterization of PosF21, an Arabidopsis thaliana gene which shows characteristics of a b-ZIP class transcription factor. Plant J 1: 303–316 (1991).
Aguan K, Sugawara K, Suzuki N, Kusano T: Isolation of genes for low-temperature-induced proteins in rice by simple subtractive method. Plant Cell Physiol 32: 1285–1289 (1991).
Aguan K, Sugawara K, Suzuki N, Kusano T: Low-temperature-dependent expression of a rice gene encoding a protein with a leucine-zipper motif. Mol Gen Genet 240: 1–8 (1993).
Albani D, Hammond-Kosack MCU, Smith C, Conlan S, Colot V, Holdsworth M, Bevan MW: The wheat transcriptional activator SPA: a seed-specific bZIP protein that recognizes the GCN4-like motif in the bifactorial endosperm box of prolamin genes. Plant Cell 9: 171–184 (1996).
Brochetto-Braga MR, Leite A, Arruda P: Partial purification and characterization of lysine-ketoglutarate reductase in normal and opaque-2 maize endosperm. Plant Physiol 98: 1139–1147 (1992).
Bucher P: Weight matrix descriptions of four eukaryotic polymerase II promoter elements derived from 502 unrelated promoter sequences. J Mol Biol 212: 563–578 (1990).
Ciceri P, Gianazza E, Lazzari B, Lippoli G, Genga A, Hoschek G, Schmidt RJ, Viotti A: Phosphorylation of Opaque2 changes diurnally and impacts its DNA binding activity. Plant Cell 9: 97–108 (1997).
Clayton WD: Notes on tribe Andropogoneae (Gramineae). Kew Bull 35: 813–818 (1983).
Cord Neto G, Yunes JA, da Silva MJ, Vettore AL, Arruda P, Leite A: The involvement of Opaque 2 in β-prolamin gene regulation in maize and Coix suggests a more general role for this transcriptional activator. Plant Mol Biol 27: 1015–1029 (1995).
Dalby A, Davies I: Ribonuclease activity in developing seeds of normal and Opaque 2 maize. Science 155: 1573–1575 (1967).
Felsenstein J: PHYLIP (Phylogeny Interference Package) version 3._5c. Distributed by the author. Department of Genetics, University of Washington, Seattle, WA (1993).
Feltkamp D, Masterson R, Starke J, Rosahl S: Analysis of the involvement of ocs-like bZIP-binding elements in the differential strength of the bidirectional mas1′2′ promoter. Plant Physiol 105: 259–268 (1994).
Foster R, Izawa T, Chua N-H: Plant bZIP proteins gather at ACGT elements. FASEB J 8: 192–200 (1994).
Gallusci P, Varott S, Matsuoko M, Maddaloni M, Thompson RD: Regulation of cytosolic pyruvate,orthophosphate dikinase expression in developing maize endosperm. Plant Mol Biol 31: 45–55 (1996).
Giroux MJ, Boyer C, Fleix G, Hannah C: Coordinated transcriptional regulation of storage product genes in the maize endosperm. Plant Physiol 106: 713–722 (1994).
Hartings H, Maddaloni M, Lazzaroni N, Di Fonzo N, Motto M, Salamini F, Thompson R: The O2 gene which regulates zein deposition in maize endosperm encodes a protein with structural homologies to transcriptional activators. EMBO J 8: 2795–2801 (1989).
Hodges R, Sodak J, Smillie L, Jurasek L: Tropomyosin: amino acid sequence and coiled-coil structure. Cold Spring Harbor Symp Quant Biol 37: 299–310 (1972).
Hong JC, Cheong YH, Nagao RT, Bahk JD, Key JL, Cho MJ: Isolation of two soybean G-box binding factors which interact with a G-box sequence of an auxin-responsive gene. Plant J 8: 199–211 (1995).
Hurst HC: Transcription factors 1: bZIP proteins. Protein Pro-file 1: 125–134 (1994).
Isawa T, Foster R, Nakajima M, Shimamoto K, Chua N-H: The rice bZIP transcriptional activator RITA-1 is highly expressed during seed development. Plant Cell 6: 1277–1287 (1994).
Izawa T, Foster R, Chua N-H: Plant bZIP protein DNA binding specificity. J Mol Biol 230: 1131 (1993).
Johnson PF: Identification of C/EBP basic region residues involved in DNA sequence recognition and half-site spacing preference. Mol Cell Biol 13: 6919–6930 (1993).
Katagiri F, Seipel K, Chua N-H: Identification of a novel dimer stabilization region in a plant bZIP transcription activator. Mol Cell Biol 12: 4809–4816 (1992).
Klimczak LJ, Schindler U, Cashmore AR: DNA binding activity of the Arabidopsis G-bos binding factor GBF1 is stimulated by phosphorylation by casein kinase II from broccoli. Plant Cell 4: 87–98 (1992).
Kodrzyck R, Boston RS, Larkins BA: The opaque-2 mutation of maize differentially reduces zein gene transcription. Plant Cell 1: 105–114 (1989).
Kusano T, Berberich T, Harada M, Suzuki N, Sugawara K: A maize DNA-binding factor with a bZIP motif is induced by low temperature. Mol Gen Genet 248: 507–517 (1995).
Leite A, Ottoboni LMM, Targon MLPN, Silva MJ, Turcinelli SR, Arruda P: Phylogenetic relationship of zeins and coixins as determined by immunological cross-reactivity and Southern blot analysis. Plant Mol Biol 14: 743–751 (1990).
Lohmer S, Maddaloni M, Motto M, Di Fonzo N, Hartings H, Salamini F, Thompson RD: The maize regulatory locus opaque-2 encodes a DNA-binding protein which activates the transcription of the b-32 gene. EMBO J 10: 617–624 (1991).
Lupas A: Prediction and analysis of coiled-coil structures. Meth Enzymol 266: 513–525 (1996).
Meier I, Guissem W: Novel conserved sequence motifs in plant G-box binding proteins and implications for interactive domains. Nucl Acids Res 22: 470–478 (1994).
Meshi T, Iwabuchi M: Plant transcription factors. Plant Cell Physiol 36: 1405–1420 (1995).
Miao Z-H, Liu X, Lam E: TGA3 is a distinct member of the TGA family of bZIP transcription factors in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Mol Biol 25: 1–11 (1994).
Mikami K, Sakamoto A, Iwabuchi: The HBP-1 family of wheat basic/leucine zipper proteins interacts with overlapping cisacting hexamer motifs of plant histone genes. J Mol Biol 13: 9974–9985 (1994).
Motto M, Maddaloni M, Ponziani G, Brembilla M, Marotta R, Di Fonzo N, Soave C, Thompson R, Salamini F: Molecular cloning of the o2-m5 allele of Zea mays using transposon marking. Mol Gen Genet 212: 488–504 (1988).
Murashige T, Skoog F: A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue culture. Physiol Plant 15: 473–507 (1962).
Nakagawa H, Ohmiya K, Hattori T: A rice bZIP protein, designated OSBZ8 is rapidly induced by abscisic acid. Plant J 9: 217–227 (1996).
O'Shea EK, Klemm JD, Kim PS, Alber T: X-ray structure of the GCN4 leucine zipper, a two-stranded, parallel coiled coil. Science 254: 539–544 (1991).
Ottoboni LMM, Leite A, Yunes JA, Targon MLPN, Souza Filho GA, Arruda P: Sequence analysis of 22 KDa-like α-coixin genes and their comparison with homologous zein and kafirin genes reveals highly conserved protein structure and regulatory elements. Plant Mol Biol 21: 765–778 (1993).
Pater S, Katgiri F, Kijne J, Chua N-H: bZIP proteins bind to a palindromic sequence without an ACGT core located in a seedspecific element of the pea lectin promoter. Plant J 6: 133–140 (1994).
Pinna LA: Casein kinase 2: an ‘eminence grise’ in cellular regulation? Biochim Biophys Acta 1054: 267–284 (1990).
Pirovano L, Lanzini S, Hartings H, Lazzaroni N, Rossi V, Joshi R, Thompson RD, Salamini F, Motto M: Structural and functional analysis of an opaque-2-related gene from sorghum. Plant Mol Biol 24: 515–523 (1994).
Prescott A, Martin C: Rapid method for quantitative assessment of levels of specific mRNAs. Plant Mol Biol Rep 4: 219–224 (1987).
Pysh LD, Aukerman MJ, Schmidt, RJ: OHP1: a maize basic domain/leucine zipper protein that interacts with Opaque2. Plant Cell 5: 227–236 (1993).
Quandt K, Frech K, Karas H, Wingender E, Werner T: MatInd and MatInspector: new fast and versatile tools for detection of concensus matches in nucleotide sequence data. Nucl Acids Res 23: 4878–4884 (1995).
Rechsteiner M, Rogers SW: PEST sequences and regulation by proteolysis. Trends Biochem Sci 21: 267–271 (1996).
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T: Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual, 2nd ed. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor, NY (1989).
Schindler U, Beckmann H, Cashmore AR: TGA1 and G-box binding factors: two distinct classes of Arabdopsis leucine zipper proteins compete for the G-box-like element TGACGTGG. Plant Cell 4: 1309–1319 (1992).
Schindler U, Menkens AE, Beckmann H, Ecker JR, Cashmore AR: Heterodimerization between light-regulated and ubiquitously expressed Arabdopsis GBF bZIP proteins. EMBO J 11: 1261–1273 (1992).
Schmidt RJ, Burr FA, Burr B: Transposon tagging and molecular analysis of the maize regulatory locus opaque-2. Science 238: 960–963 (1987).
Schmidt RJ, Burr FA, Aukerman MJ, Burr B: Maize regulatory gene opaque-2 encodes a protein with a ‘leucine zipper’ motif that binds to zein DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87: 46–50 (1990).
Schmidt RJ, Ketudat M, Aukerman MJ, Hoschek G: Opaque-2 is a transcriptional activator that recognizes a specific target site in 22-kD zein genes. Plant Cell 4: 689–700 (1992).
Schmidt RJ: Opaque-2 and zein gene expression. In: Verma DPS (ed) Control of Plant Gene Expression, pp. 337–355. CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL (1993).
Siegel LI, Bresnick E: Northern hybridization analysis of RNA using diethylpyrocarbonate-treated nonfatmilk. Anal Biochem 159: 82–87 (1986).
Singh K, Dennis ES, Ellis JG, Llewellyn DJ, Tokuhisa JG, Wahleithner JA, Peacock J: OCSBF-1, a maize ocs enhancer binding factor: isolation and expression during development. Plant Cell 2: 891–903 (1990).
Staden R: An interactive graphics program for comparing and aligning nucleic acid and amino acid sequences. Nucl Acids Res 10: 2951–2961 (1982).
Suckow M, Schwamborn K, Kisters-Woike B, Wilcken-Bergmann B, Müller-Hill B: Replacement of invariant bZIP residues within the basic region of the yeast transcriptional activator GCN4 can change its DNA binding specificity. Nucl Acids Res 21: 4395–4404 (1994).
Suckow M, Wilckern-Bergmann B, Müller-Hill B: Identification of three residues in the basic regions of the bZIP protein GCN4, C/EBP and TAF-1 that are involved in specific DNA binding. EMBO J 12: 1193–1200 (1993).
Targon MLN, Ottoboni LMM, Leite A, Ludevid D, Puigdoménech P, Arruda P: Synthesis and deposition of coixin in seeds of Coix lacryma-jobi. Plant Sci 83: 169–180 (1992).
Thompson JD, Higgins DG, Gibson, TJ: CLUSTAL W: improving of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, positions-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucl Acids Res 22: 4673–4680 (1994).
Torres-Schumann S, Ringli C, Heierli D, Amrhein N, Keller B: In vitro binding of the tomato bZIP transcriptional activator VSF-1 to a regulatory element that controls xylen-specific gene expression. Plant J 9: 283–296 (1996).
Weisshaar B, Armstrong GA, Block A, da Costa e Silva O, Hahlbrock K: Light-inducible and constitutively DNA-binding proteins recognizing a plant promoter element with functional revelance in light responsiveness. EMBO J 10: 1777–1786 (1991).
Wilson CM, Alexander DE: Ribonuclease activity in normal and opaque2 mutant endosperm of maize. Science 155: 1575–1576 (1967).
Yunes JA, Cord Neto G, Leite A, Ottoboni LM, Arruda P: The role of the opaque2 transcriptional factor in the regulation of protein accumulation and amino acid metabolism in maize seeds. An Acad Bras Ci 66: 227–238 (1994).
Yunes JA, Cord Neto G, Silva JM, Leite A, Ottoboni LMM, Arruda P: The transcriptional activator Opaque2 recognize two different target sequences in the 22-kD-like α-prolamin genes. Plant Cell 6: 237–250 (1994).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vettore, A.L., Yunes, J.A., Cord Neto, G. et al. The molecular and functional characterization of an Opaque2 homologue gene from Coix and a new classification of plant bZIP proteins. Plant Mol Biol 36, 249–263 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005995806897
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005995806897