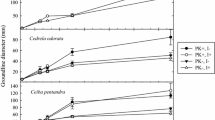
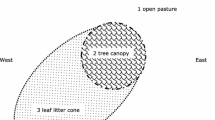
Abstract
Three tree species are traditionally conserved in the traditional slash and burn agricultural system practiced for the production of upland rice (Oryza sativa Linn.) in the Fouta Djallon region of Guinea, i.e. (Parinari excelsa [Sabine], Parkia biglobosa [Jacq.) Benth.], Erythrophleum guinensis [G. Don.]). Sampling a chronosequence of fallow sites indicated that extractable P; exchangeable K, Ca and Mg; cation exchange capacity (CEC) and pH all decreased over the fallow period with patterns that differed with soil depth. Soils under the remnant Parinari excelsa and Parkia biglobosa trees had higher concentrations of organic C; total N; extractable P; exchangeable K, Ca and Mg; total P and Ca; and CEC than did the open microsites. Extractable P; exchangeable K, Ca and Mg; total P and Ca; and CEC were greater under Parinari excelsa than under Erythrophleum guinensis. Intensive measurements of a single mature fallow site showed that the foliar nutrient concentration of the large trees was not an accurate index of which microsite had the greatest accumulation of biomass and nutrients in the aboveground fallow vegetation. The biomass and the total amounts of N, P, K, Ca and Mg in the fallow vegetation were significantly greater for the Parinari excelsa and Parkia biglobosa microsites than for the open microsites. We conclude that although the nutrient status of the soils decreased over the 8-year fallow period, the microsites under the large trees were generally more fertile than the open microsites. However, there were important differences in the effects of the different tree species.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aweto AO (1988) Effects of shifting cultivation on a tropical rain forest soil in southwestern Nigeria. Turrialba 38: 19–22
Aweto AO (1987) Pedological aspects of shifting cultivation in southwestern Nigeria. Resource Management and Optimization 4: 179–197
Aweto AO (1981) Secondary succession and soil fertility restoration in southwestern Nigeria. III. Soil and vegetation interrelationships. J Ecol 69: 957–963
Black GR and Hartge KH (1986) Bulk density. In: Klute A (ed) Methods of Soil Analysis, Part 1: Physical and Mineralogical Methods, 2nd Ed. Agronomy Monograph No. 9, pp 363–375. Soil Science Society of America Inc., Madison, Wisconsin
Bouyoucos GJ (1962) Hydrometer method improved for making particle size analysis of soils. Agronomy Journal 54: 464–465
Boyer J (1982) Les sols ferralitiques. Tome X. Facteurs de fertilité et utilisations des sols. Initiations-documentations techniques no. 52. Office de la Recherche Scientifique et Technique Outre-Mer (ORSTOM). Paris. 384 pp
Bray RL and Kurtz LT (1945) Determination of total, organic and available forms of phosphorus in soils. Soil Science 59: 39–45
Bremner JM and Mulvaney CS (1982) Nitrogen — total. In: Page AL, Miller RH and Keeney DR (eds) Methods of Soil Analysis. Part 2: Chemical and Microbiological Properties. 2nd Ed, pp 595–624. ASA-SSSA. Madison, Wisconsin
Dommergues YR (1987) The role of biological nitrogen fixation in agroforestry. In: Steppler HA and Nair PKR (eds) Agroforestry: A Decade of Development, pp 245–271. International Council for Research in Agroforestry. Nairobi, Kenya
Ewel JJ (1986) Designing agricultural ecosystems for the humid tropics. Annu Rev. Ecol System 17: 245–271
Ewel JJ, Berish C, Brown B, Price N and Raich J (1981) Slash and burn impacts on a Costa Rican wet forest site. Ecology 62: 876–879
Favrichon V (1991) Aménagement intégré de bassin versant. Réflexions à partir du cas des bassins représentatifs pilotes de Bafing et de Balé, Fouta Djallon, République de Guinée. Bois et Forét Tropicale 228: 25–40
Kauffman JB, Cummings DL and Ward DE (1994) Relationships of fire, biomass and nutrient dynamics along a vegetation gradient in the Brazilian cerrado. J Ecol 82: 519–531
Kauffman JB, Sanford RL, Cummings DL, Salcedo IH and Sampaio EVSB (1993) Biomass and nutrient dynamics associated with slash fires in neotropical dry forests. Ecology 74: 140–151
Juo ASR and Kang T (1989) Nutrient effects of modification of shifting cultivation in West Africa. In: Proctor J (ed) Mineral Nutrients in Tropical Forest and Savanna Ecosystems, Special Public. No. 9, pp 289–300. British Ecological Society. Oxford
Lal R (1989a) Potential of agroforestry as a sustainable alternative to shifting cultivation: concluding remarks. Agrofor Syst 8: 239–242
Lal R (1989b) Agroforestry systems and soil surface management of a tropical alfisol. III. Changes in soil chemical properties. Agrofor Syst 8: 113–132
Lal R (1987) Managing the soil of sub-Saharan Africa. Science 236: 1069–1076
MacDicken KG (1991) Impacts of Leucaena leucocephala as a fallow improvement crop in shifting cultivation on the island of Mindoro, Philippines. For Ecol Manage 45: 185–192
Mulongoy K (1986) Nitrogen cycling in alley cropping systems. International Institute for Tropical Agriculture Research Briefs No. 7, pp 3–5. Ibadan, Nigeria
Nair PKR (1991) State-of-the-art of agroforestry systems. For Ecol Manage 45: 5–29
Nakano K and Syahbuddin N (1989) Nutrient dynamics in forest fallows in southeast Asia. In: Proctor J (ed) Mineral Nutrients in Tropical Forest and Savanna Ecosystems, Special Public. No. 9, pp 325–335. British Ecological Society, Oxford
Nye PH and Greenland DJ (1960) The soil under shifting cultivation. Technical Communication No. 51. Commonwealth Bur Soils. Harpenden, United Kingdom, 144 pp
Ong CK, Corlett, RP and Black CR (1991) Above and below ground interactions in agroforestry systems. For Ecol Manage 45: 45–57
Parkinson JA and Allen SE (1975) A wet oxidation procedure suitable for the determination of nitrogen and mineral nutrients in biological material. Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis 6: 1–11
Raintree JB and Warner K (1986.) Agroforestry pathways for intensification of shifting cultivation. Agrofor Syst 4: 39–54
Stuanes AO, Ogner G and Open M (1984) Ammonium nitrate as extractant for soil exchangeable cations, exchangeable acidity and aluminum. Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis 15: 773–778
Tsutsumi T, Yoda K, Sahunalu P, Dhanmanonda P and Prachaiyo B (1983) Shifting cultivation: an experiment at Nam Phrom, northeast Thailand, and its implications for upland farming in the monsoon tropics. In: Agroecological Studies on Shifting Cultivation and Its Transformation Process to Sustained Upland Farming, pp 13–62. Ministry of Education, Science and Culture, Japan
Whitmore TC (1989) Tropical forest nutrients, where do we stand? A tour de horizon. In: Proctor J (ed) Mineral Nutrients in Tropical Forest and Savanna Ecosystems, Special Public. No. 9, pp 1–13. British Ecological Society, Oxford
Yeomans JC and Bremner JM (1988) A rapid and precise method for routine determination of organic carbon in soil. Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis 19: 1467–1476
Young A (1989) Agroforestry for Soil Conservation. International Council for Research in Agroforestry, Nairobi, 276 pp
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sirois, MC., Margolis, H.A. & Camiré, C. Influence of remnant trees on nutrients and fallow biomass in slash and burn agroecosystems in Guinea . Agroforestry Systems 40, 227–246 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006093329468
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006093329468