Abstract
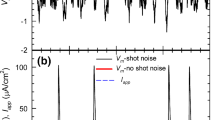
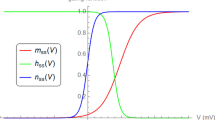
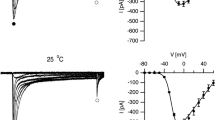
Voltage-gated ion channels in neuronal membranes fluctuate randomly between different conformational states due to thermal agitation. Fluctuations between conducting and nonconducting states give rise to noisy membrane currents and subthreshold voltage fluctuations and may contribute to variability in spike timing. Here we study subthreshold voltage fluctuations due to active voltage-gated Na+ and K+ channels as predicted by two commonly used kinetic schemes: the Mainen et al. (1995) (MJHS) kinetic scheme, which has been used to model dendritic channels in cortical neurons, and the classical Hodgkin-Huxley (1952) (HH) kinetic scheme for the squid giant axon. We compute the magnitudes, amplitude distributions, and power spectral densities of the voltage noise in isopotential membrane patches predicted by these kinetic schemes. For both schemes, noise magnitudes increase rapidly with depolarization from rest. Noise is larger for smaller patch areas but is smaller for increased model temperatures. We contrast the results from Monte Carlo simulations of the stochastic nonlinear kinetic schemes with analytical, closed-form expressions derived using passive and quasi-active linear approximations to the kinetic schemes. For all subthreshold voltage ranges, the quasi-active linearized approximation is accurate within 8% and may thus be used in large-scale simulations of realistic neuronal geometries.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chow C, White J (1996) Spontaneous action potentials due to channel fluctuations. Biophys. J. 71:3013-3021.
Clay JR, DeFelice LJ (1983) Relationship between membrane excitability and single channel open-close kinetics. Biophys. J. 42:151-157.
Colquhoun D, Hawkes AG (1982) On the stochastic properties of bursts of single ion channel openings and of clusters of bursts. Phil. Irans. Roy. Soc. Lond. B 300:1-59.
DeFelice LJ (1981) Introduction to Membrane Noise. Plenum Press, New York.
DeFelice LJ, Isaac A (1992) Chaotic states in a random world. J. Stat. Phys. 70:339-352.
Destexhe A, Pare D (1999) Impact of network activity on the integrative properties of neocortical pyramidal neurons in vivo. J. Neurophysiol. 81:1531-1547.
Fishman HM (1975) Noise measurements in axon membranes. Fed. Proc. 34:1330-1337.
Fishman HM, Poussart DM, Moore LE (1975) Noise measurements in squid axon membrane. J. Membr. Biol. 24:281-304.
Fox RF (1997) Stochastic versions of the Hodgkin-Huxley equations. Biophys. J. 72:2068-2074.
Fox RF, Lu Y (1994) Emergent collective behavior in large numbers of globally coupled independently stochastic ion channels. Phys. Rev. E 49:3421-3431.
Hille B (1992) Ionic Channels of Excitable Membranes. Sinauer, Sunderland, MA.
Hines ML, Carnevale NT (1997) The NEURON simulation environment. Neural Comput. 9:1179-1209.
Hodgkin AL, Huxley AF (1952) A quantitative description of membrane current and its application to conduction and excitation in nerve. J. Physiol. (London) 117:500-544.
HorikawaY(1991) Noise effects on spike propagation in the stochastic Hodgkin-Huxley models. Biol. Cybern. 66:19-25.
Horikawa Y (1993) Simulation study on effects of channel noise on differential conduction at an axon branch. Biophys. J. 65:680-686.
Johnston D, Wu SM (1995) Foundations of Cellular Neurophysiology. MIT Press, Cambridge, MA.
Koch C (1984) Cable theory in neurons with active, linearized membranes. Biol. Cybern. 50:15-33.
Koch C (1999) Biophysics of Computation: Information Processing in Single Neurons. Oxford University Press, New York.
Lecar H, Nossal R (1971a) Theory of threshold fluctuations in nerves. I. Relationships between electrical noise and fluctuations in axon firing. Biophys. J. 11:1048-1067.
Lecar H, Nossal R (1971b) Theory of threshold fluctuations in nerves. II. Analysis of various sources of membrane noise. Biophys. J. 11:1068-1084.
Liebovitch LS, Toth TI (1990) Using fractals to understand the opening and closing of ion channels. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 18:177-194.
Liebovitch LS, Toth TI (1991) A model of ion channel kinetics using deterministic chaotic rather than stochastic processes. J. Theor. Biol. 148:243-267.
Mainen ZF, Joerges J, Huguenard JR, Sejnowski TJ (1995) A model of spike initiation in neocortical pyramidal neurons. Neuron 15:1427-1439.
Manwani A, Koch C (1998) Synaptic transmission: An informationtheoretic pespective. In: Jordan M, Kearns MS, Solla SA, eds. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 10. MIT Press, Cambridge, MA. pp. 201-207.
Manwani A, Koch C (1999a) Detecting and estimating signals in noisy cable structures: I. Neuronal noise sources. Neural Comput. In press.
Manwani A, Koch C (1999b) Detecting and estimating signals in noisy cable structures: II. Information-theoretic analysis. Neural Comput. In press.
Manwani A, Koch C (1999c) Signal detection in noisy weakly active dendrites. In: Kearns MS, Solla SA, Cohn DA, eds. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 11. MIT Press, Cambridge, MA.
Manwani A, Segev I, Yarom Y, Koch C (1998) Neuronal noise sources in membrane patches and linear cables: An analytical and experimental study. Soc. Neurosci. Abstr. 719.4, p. 1813.
Mauro A, Conti F, Dodge F, Schor R (1970) Subthreshold behavior and phenomenological impedance of the squid giant axon. J. Gen. Physiol. 55:497-523.
Papoulis A (1991) Probability, Random Variables, and Stochastic Processes. McGraw-Hill, New York.
Pare DE, Label E, Lang EJ (1997) Differential impact of miniature synaptic potentials on the soma and dendrites of pyramidal neurons in vivo. J. Neurophysiol. 78:1735-1739.
Pare DE, Shink E, Gaudreau H, Destexhe A, Lang EJ (1998) Impact of spontaneous synaptic activity on the resting properties of cat neocortical pyramidal neurons in vivo. J. Neurophysiol. 79:1450-1460.
Press WH, Teukolsky SA, Vetterling WT, Flannery BP (1992) Numerical Recipes in C: The Art of Scientific Computing (2nd ed.). Cambridge University Press, Cambridge.
Rubinstein JT (1995) Threshold fluctuations in an N sodium channel model of the node of Ranvier. Biophys. J. 68:779-785.
Sabah NH, Leibovic KN (1969) Subthreshold oscillatory responses of the Hodgkin-Huxley cable model for the squid giant axon. Biophys. J. 9:1206-1222.
Schneidman E, Freedman B, Segev I (1998) Ion-channel stochasticity may be critical in determining the reliability and precision of spike timing. Neural Comput. 10:1679-1703.
Shadlen MN, Newsome WT (1998) The variable discharge of cortical neurons: Implications for connectivity, computation, and information coding. J. Neurosci. 18:3870-3896.
Skaugen E (1980a) Firing behavior in nerve cell models with a 148 Steinmetz et al. two-state pore system. Acta Physiol. Scand. 109:337-392.
Skaugen E (1980b) Firing behavior in stochastic nerve membrane models with different pore densities. Acta Physiol. Scand. 108:49-60.
Skaugen E, Wallœ L (1979) Firing behavior in a stochastic nerve membrane model based upon the Hodgkin-Huxley equations. Acta Physiol. Scand. 107:343-363.
Stevens CF (1972) Inferences about membrane properties from electrical noise measurements. Biophys. J. 12:1028-1047.
Strassberg AF, DeFelice LJ (1993) Limitations of the Hodgkin-Huxley formalism: Effect of single channel kinetics on transmembrane voltage dynamics. Neural Comput. 5:843-855.
Toib A, Lyakhov V, Marom S (1998) Interaction between duration of activity and rate of recovery from slow inactivation in mammalian brain NaC channels. J. Neurosci. 15:1893-1903.
Traynelis SF, Jaramillo F (1998) Getting the most out of noise in the central nervous system. Trends Neurosci. 21:137-145.
van den Berg RJ, de Goede J, Verveen AA (1975) Conductance fluctuations in Ranvier nodes. Pflug. Arch. 360:17-23.
van den Berg RJ, Rijnsburger WH (1980) Membrane current and noise measurements in voltage-clamped node of Ranvier. J. Membr. Biol. 57:213-221.
Verveen AA, DeFelice LJ (1974) Membrane noise. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 28:189-265.
Wanke E, DeFelice LJ, Conti F (1974) Voltage noise, current noise, and impedance in space clamped squid giant axon. Pflug. Arch. 347:63-74.
White JA, Budde T, Kay AR (1995) A bifurcation analysis of neuronal subthreshold oscillations. Biophys. J. 69:1203-1217.
White JA, Klink R, Alonso A, Kay AR (1998) Noise from voltagegated ion channels may influence neuronal dynamics in the entorhinal cortex. J. Neurophysiol. 80:262-269.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Steinmetz, P.N., Manwani, A., Koch, C. et al. Subthreshold Voltage Noise Due to Channel Fluctuations in Active Neuronal Membranes. J Comput Neurosci 9, 133–148 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008967807741
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008967807741