Abstract
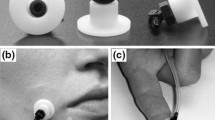
We recorded somatosensory evoked magnetic field (SEF) to investigate the differentiation in the receptive area for the face, lower part of the posterior scalp (mastoid) and shoulder, which occupy an unique area in the homunculus. We analyzed the location of the equivalent current dipole (ECD) of SEF following electrical stimulation of the skin at the face, mastoid and shoulder in 20 normal subjects. Three deflections (1M, 2M and 3M) were obtained within 50 ms of the stimulation in 16 of 20 subjects. The peak latency of the 1M and 2M was not significantly different at any stimulus sites. The amplitude of the 1M was significantly larger following the face than mastoid stimulation (p < 0.05). The 16 subjects were classified according to the locations of the ECD on stimulation of the mastoid: close to that for shoulder stimulation, but significantly (p < 0.05) more superior and medial to that following the face stimulation (Type 1, eleven subjects); close to that for face stimulation, but significantly (P < 0.05) more inferior and lateral to that following the shoulder stimulation (Type 2, five subjects). The site of the receptive area for the posterior scalp shows interindividual variation, possibly due to anatomical differences.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allison, T., McCarthy, G., Wood, C., Darcey, T. M., Spencer, D. D. and Williamson, P. D. Human cortical potentials evoked by stimulation of the median nerve I. Cytoarchtectotic areas generating short-latency activity. J. Neurophysiol., 1989, 62: 694–710.
Baumgartner, C., Sutherling, W.W., Zeitlhofer, J., Lindinger, G., Lind, G. and Deecke, L. Functional anatomy of human hand sensorimotor cortex from spatiotemporal analysis of elec-tro-corticography. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol., 1991a, 78: 56–65.
Baumgartner, C., Doppelbauer, A., Deecke, L., Barth, D.S., Zeitlhofer, J. and Sutherling, W.W. Neuromagnetic inves-tigation of somatotopy of human hand somatosensory cortex. Exp. Brain. Res., 1991b, 87: 641–648.
Baumgartner, C., Sutherling, W.W., Zeitlhofer, J., Lindinger, G., Lind, G. and Deecke, L. Human somatosensory cortical fin-ger representation as studied by combined neuromagnetic and neuroelectric measurements. Neurosci. Lett., 1991c, 134: 103–108.
Baumgartner, C., Sutherling, W.W., Di, S. and Barth, D.S. Spatiotemporal modeling of cerebral evoked magnetic fields to median nerve stimulation. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol., 1991d, 79: 27–35.
Baumgartner, C., Barth, D.S., Levesque, M.F. and Suthering, W.W. Human hand and lip sensorimotor cortex as studied on electrocoticography. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol., 1992, 84: 115–126.
Brenner, D., Lipton, L., Kaufmann, L. and Williamson, S.J. Somatic evoked magnetic fields of the human brain. Science, 1978, 199: 81–83.
Chusid, J.G. Cutaneous innervation. Correlative Neuroanatomy and Functional Neurology. Los Altos: LANGE, 1982: 207–213.
Daube, J.R. and Sandok, B.A. The spinal levels. Medical Neurosciences. Boston: Little Brown, 1978: 296–322.
Findler, G. and Feinsod, M. Sensory evoked response to electri-cal stimulation of trigeminal nerve in humans. J. Neurosurg., 1982, 56: 545–549.
Forss, N., Salmelin, R. and Hari, R. Comparison of somatosensory evoked fields to airpuff and electric stimuli. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol., 1994, 92: 510–517.
Gharib, S., Sutherling, W.W., Nakasato, N., Barth, D.S., Baumgartner, C., Alexopoulos, N., Taylor, S. and Rogers, R.L. MEG and ECoG localization accuracy test. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol., 1995, 94: 109–114.
Godfrey, R.M. and Mitchell, K.W. Somatosensory evoked po-tentials to electrical stimulation of the mental nerve. Br. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg., 1987, 25: 300–307.
Hari, R., Reinikainen, K., Kaukoranta, E., Hamalainen, M., Ilmoniemi, R., Penttinen, A., Salminen, J. and Teszner, D. Somatosensory evoked cerebral magnetic fields from SI and SII in man. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol., 1984, 57: 254–263.
Hari, R., Hamalainen, M., Knuutila, J., Sams, M. and Vilkman, V. Functional organization of the human first and second somatosensory cortices: neuromagnetic study. Eur. J. Neurosci., 1993, 5: 724–734.
Hari, R., Nagamine, R., Nishitani, N., Mikuni, N., Sato, T., Tarkiainen, A. and Shibasaki, H. Time-varying activation of different cytoarchitectonic areas of the human SI cortex after tibial nerve stimulation. Neuroimage, 1996, 4: 111–118.
Hoshiyama, M., Kakigi, R., Koyama, S., Kitamura, Y., Shimojo, M. and Watanabe, S. Somatosensory evoked magnetic fields after mechanical stimulation of the scalp in humans. Neurosci. Lett., 1995, 195: 29–32.
Hoshiyama, M., Kakigi, R., Koyama, S., Kitamura, Y., Shimojo, M. and Watanabe, S. Somatosensory evoked magnetic fields following stimulation of the lip in humans. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol., 1996, 100: 96–104.
Huttunen, J., Kaukoranta, E. and Hari, R. Cerebral magnetic re-sponses to stimulation of tibial and sural nerves. J. Neurol. Sci., 1987, 79: 43–54.
Itomi, K., Kakigi, R., Hoshiyama, M. and Maeda, K. Dermatome versus homunculus; detailed topography of the primary somatosensory cortex following trunk stimulation. Clin. Neurophysiol., 2000, 111: 405–412.
Kakigi, R. Somatosensory evoked magnetic fields following median nerve stimulation. Neurosci. Res., 1994, 20: 165–174.
Kakigi, R., Koyama, S., Hoshiyama, M., Shimojo, M., Kitamura, Y. and Watanabe, S. Topography of somatosensory evoked magnetic fields following posterior tibial nerve stimulation. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol., 1995, 95: 127–134.
Katifi, H.A. and Sedwick, E.M. Somatosensory evoked poten-tials from posterior tibial nerve and lumbosacral derma-tomes. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol., 1986, 65: 249–259.
Kaukoranta, E., Hari, R., Hamalainen, M. and Huttunen, J. Cerebral magnetic fields evoked by peroneal nerve stimulation. Somatosens. Res., 1986, 3: 309–321.
Leahy, R.M., Mosher, J.C., Spencer, M.E., Huang, M.X. and Lewine, J.D. A study of dipole localization accuracy for MEG and EEG using a human skull phantom. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol., 1998, 107: 159–173.
Maloney, S.R., Bell, W.L., Shoaf, S.C., Blair, E.P., Good, D.C. and Quinlivan, L. Measurement of lingual and palatine somatosensory evoked potentials. Clin. Neurophysiol., 2000, 111: 291–296.
McCarthy, G., Allison, T. and Spencer, D.D. Localization of the face area of human sensorimotor cortex by intracranial recording of somatosensory evoked potentials. J. Neurosurg., 1993, 79: 874–884.
Minassian, B.A., Otsubo, H., Shelly, W., Ellioff, I., Rutka, J.T. and Snead, O.C. Magnetoencephalographic localization in pediatric epilepsy surgery: comparison with invasive intracranial electroencephalography. Ann. Neurol., 1999, 46: 627–633.
Mogilner, A., Nomura, M., Robary, U., Jagow, R., Lado, F., Rusinek, H. and Llinas, R. Neuromagnetic studies of the lip area of primary somatosensory cortex in humans: evi-dence of an oscillotopic organization. Exp. Brain Res., 1994, 99: 137–147.
Nakamura, A., Yamada, T., Goto, A., Kato, T., Ito, K., Abe, Y., Kachi, T. and Kakigi, R. Somatosensory homunculus drawn by MEG. Neuroimage, 1998, 7: 377–386.
Narici, L., Mondena, I., Opsomer, R. J., Pizzella, V., Romani, G.L., Torrioli, G., Traversa, R. and Rossini, P.M. Neuromagnetic somatosensory homunculus: a non-invasive approach in humans. Neurosci. Lett., 1991, 121: 51–54.
Nihashi, T., Kakigi, R., Kawakami, O., Hoshiyama, M., Itomi, K., Nakanishi, H., Kajita, Y., Inao, S. and Yoshida, J. Representation of the ear in human primary somatosensory cortex. Neuroimage, 2001, 13: 295–304.
Penfield, W. and Boldrey, E. Somatic motor and sensory repre-sentation in the cerebral cortex of man as studied by electrical stimulation. Brain, 1937, 60: 389–443.
Penfild, W. and Rasmussen, T. The cerebral cortex in man, New York: Macmillan, 1950.
Poletti, C.E. C2 and C3 dermatomes in man. Cephalalgia, 1991, 11: 155–159.
Sarvas, J. Basic mathematical and electromagnetic concepts of the biomagnetic inverse problem. Phys. Med. Biol., 1987, 32: 11–22.
Schnitzler, A., Volkmann, J., Frieling, T., Witte, O.W. and Freund, H.J. Different cortical organization of visceral somatic sensation in humans. Eur. J. Neurosci., 1999, 11: 305–315.
Shimojo, M., Kakigi, R., Hoshiyama, M., Koyama, S., Kitamura, Y. and Watanabe, S. Differentiation of receptive fields in the sensory cortex following stimulation of various nerves of the lower limb in humans: a magnetoencephalographic study. J. Neurosurg., 1996, 85: 255–262.
Slimp, J.C., Rubner, D.E., Snowden, M.L. and Stolov, W.C. Dermatomal somatosensory evoked potentials: cervical, thoracic, and lumbosacral levels. Electroencephalogr. clin. Neurophysiol., 1992, 84: 55–70.
Suk, J., Ribary, U., Cappell, J., Yamamoto, T. and Llinas, R. Anatomical localization revealed by MEG recordings of the human somatosensory system. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol., 1991, 78: 185–196.
Sutherling, W.W., Crandall, P.H., Darcey, T.M., Becker, D.P., Levesque, M.F. and Barth, D.S. The magnetic and electric fields agree with intracranial localizations of somatosensory cortex. Neurology, 1988, 38: 1705–1714.
Wood, C.C., Cohen, D., Cuffin, B.N., Yarita, M. and Allison, T. Electrical sources in human somatosensory cortex: identification by combined magnetic and potential recordings. Science, 1985, 227: 1051–1053.
Wood, C.C., Spencer, D.D., Allison, T., McCarthy, G., William-son, P.D. and Goff, W.R. Localization of human sensorimotor cortex during surgery by cortical surface re-cording of somatosensory evoked potentials. J. Neurosurg., 1988, 68: 99–111.
Woolsey, C.N., Erickson, T.C. and Gilson, W.E. Localization in somatic sensory and motor areas of human cerebral cortex as determined by direct recording of evoked potentials and electrical stimulation. J. Neurosurg., 1979, 51: 476–506.
Xiang, J., Kakigi, R., Hoshiyama, M., Kaneoke, Y., Naka, D., Takeshima, Y. and Koyama, S. Somatosensory evoked magnetic fields and potentials following passive finger toe movement in humans. Electroencephalogr. clin. Neurophysiol., 1997a, 104: 393–401.
Xiang, J., Hoshiyama, M., Koyama, S., Kaneoke, Y., Suzuki, H., Watanabe, S., Naka, D. and Kakigi, R. Somatosensory evoked magnetic fields following passive finger move-ment. Brain Res. Cogn. Brain Res., 1997b, 6: 73–82.
Yang, T.T., Gallen, C.C., Schwartz, B. and Bloom, F.E. Noninvasive somatosensory homunculus mapping in hu-mans by using a large-array biomagnetometer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci., 1993, 90: 3098–3102.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Itomi, K., Kakigi, R., Hoshiyama, M. et al. A Unique Area of the Homonculus: The Topography of the Primary Somatosensory Cortex in Humans Following Posterior Scalp and Shoulder Stimulation. Brain Topogr 14, 15–23 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1012511621766
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1012511621766