Abstract
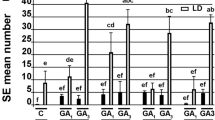
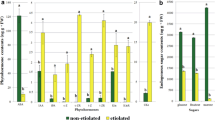
The influence of exogenous gibberellic acid (GA3) andpaclobutrazol, an inhibitor of gibberellin biosynthesis, on growth of callusandsomatic embryogenesis in petiole-derived tissue cultures of Medicagosativa L. has been investigated. GA3 (0.5–500μM) or paclobutrazol(5–100 μM) were added to either an induction (with 2,4 Dand kinetin) or a differentiation medium (without plant growth regulators).Gibberellin A3, applied during the induction as well as thedifferentiation stage, reduced the weight of callus and increased the number ofsomatic embryos in Medicago sativa L. tissue cultures.Somatic embryo production was increased more by the presence of exogenousGA3 in the differentiation than induction medium. The inclusion ofpaclobutrazol in the induction or differentiation medium caused the inhibitionof callus growth and embryo production. Callus growth was much less affectedthan embryogenesis. These results indicate that gibberellins are beneficial forboth embryoinduction and formation. The level of endogenous gibberellins is presumablysufficient for callus induction and growth. However, it seems not optimal forthe induction and particularly for the differentiation of embryos.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ammirato P.V. 1977. Hormonal control of somatic embryo development from cultured cells of caraway. Interactions of abscisic acid, zeatin and gibberellic acid. Plant Physiol. 59: 579–586.
Das A.B., Rout G.R. and Das P. 1995. In vitro somatic embryogenesis from callus culture of the timber yielding tree Hardwickia binata Roxb. Plant Cell Rep. 15: 147–149.
Fujimura T. and Komamine A. 1975. Effects of various growth regulators on the embryogenesis in a carrot cell suspension culture. Plant Sci. Lett. 5: 359–369.
Gomes da Cunha A.C. and Ferreira M.F. 1996. Somatic embryogenesis, organogenesis and callus growth kinetics of flax. Plant Cell Tiss. Org. Cult. 47: 1–8.
Hita O., Lafarga C. and Guerra H. 1997. Somatic embryogenesis from chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) immature cotyledons: the effect of zeatin, gibberellic acid and indole-3-butyric acid. Acta. Physiol. Plant 19: 333–338.
Hutchinson M.J., KrishnaRaj S. and Saxena P.K. 1997. Inhibitory effect of GA3 on the development of thidiazuron-induced somatic embryogenesis in geranium (Pelargonium x hortorum Bailey) hypocotyl cultures. Plant Cell Rep. 16: 435–438.
Komamine A., Kawahara R., Matsumoto M., Sunabori S., Toya T., Fujiwara A. et al. 1992. Mechanisms of somatic embryogenesis in cell cultures: physiology, biochemistry and molecular biology. In Vitro Cell Dev. Biol. 28P: 11–14.
Li B. and Wolyn D.J. 1995. The effects of ancymidol, abscisic acid, uniconazole and paclobutrazol on somatic embryogenesis of asparagus. Plant Cell Rep. 14: 529–533.
Li B. and Wolyn D.J. 1997. Interactions of ancymidol with sucrose and α-naphtalene-acetic acid in promoting asparagus (Asparagus officinalis L.) somatic embryogenesis. Plant Cell Rep. 16: 879–883.
Meijer E.G.M. and Brown D.C.W. 1987. A novel system for rapid high frequency somatic embryogenesis in Medicago sativa. Physiol. Plant 69: 591–596.
Mikuła A., Wilbik W. and Rybczyński J.J. 1998. Wplyw regulatoròw wzrostu na somatyczna embriogeneze Gentiana sp w kulturach in vitro. II Ogòlnopolska Konferencja “Zastosowanie kultur in vitro w fizjologii roslin”: 141–154.
Noma M., Huber J. and Pharis R.P. 1979. Occurrence of 1(10) gibberellin A1 counterpart, GA1, GA4 and GA7 in somatic cell embryo cultures of carrot and anise. Agric. Biol. Chem. 43: 1793–1794.
Noma M., Huber J., Ernst D. and Pharis R.P. 1982. Quantitation of gibberellins and the metabolism of [3H] gibberellin A, during somatic embryogenesis in carrot and anise cell cultures. Planta 155: 369–376.
Rademacher W., Fristch H. and Graebe J.E. et al. 1987. Tetcyclasis and triazole-type plant growth retardants; Their influence on the biosynthesis of gibberellins and other metabolic processes. Pestic Sci. 21: 241–252.
Schenk R.U. and Hildebrandt A.C. 1972. Medium and techniques for induction and growth of monocotyledonous and dicotyledonous plant cell cultures. Can. J. Bot. 50: 199–204.
Shimizu K., Nagaike H., Yabuya T. and Adachi T. 1997. Plant regeneration from suspension culture of Iris germanica. Plant Cell Tiss. Org. Cult. 50: 27–31.
Tisserat B. and Murashige T. 1977. Repression of asexual embryogenesis in vitro by some plant growth regulators. In Vitro 13: 799–805.
Williams E.G. and Maheswaran G. 1986. Somatic embryogenesis: factors influencing co-ordinated behaviour of cells as an embryogenic group. Ann. Bot. 7: 443–462.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ruduś, I., Kępczyńska, E. & Kępczyński, J. Regulation of Medicago sativa L. somatic embryogenesis by gibberellins. Plant Growth Regulation 36, 91–95 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1014751125297
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1014751125297