Abstract
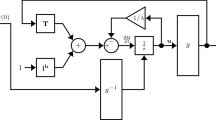
When solving an optimization problem with a Hopfield network, a solution is obtained after the network is relaxed to an equilibrium state. The relaxation process is an important step in achieving a solution. In this paper, a new procedure for the relaxation process is proposed. In the new procedure, the amplified signal received by a neuron from other neurons is treated as the target value for its activation (output) value. The activation of a neuron is updated directly based on the difference between its current activation and the received target value, without using the updating of the input value as an intermediate step. A relaxation rate is applied to control the updating scale for a smooth relaxation process. The new procedure is evaluated and compared with the original procedure in the Hopfield network through simulations based on 200 randomly generated instances of the 10-city traveling salesman problem. The new procedure reduces the error rate by 34.6% and increases the percentage of valid tours by 194.6% as compared with the original procedure.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hopfield, J. J. and Tank, D. W.: Neural computations of decisions in optimization problems. Biological Cybernetics 52 (1985), 141–152.
Wilson, G. V. and Pawley, G. S.: On the stability of the traveling salesman problem algorithm of Hopfield and Tank. Biological Cybernetics 58 (1988), 63–70.
Brandt, R. D., Wang, Y., Laub, A. J. and Mitra, S. K.: Alternative networks for solving the traveling salesman problem and the list-matching problem. Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Neural Networks, San Diego, CA. II: (1988) 333-340.
Aiyer, S. V. B., Niranjan, M. and Fallside, F.: A theoretical investigation into the performance of the Hopfield model. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks 1(2) (1990), 204–215.
Protzel, P. W., Palumbo, D. L. and Arras, M. K.: Performance and fault-tolerance of neural networks for optimization, IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks 4 (1993), 600–614.
Li, S. Z.: (1996), Improving convergence and solution quality of Hopfield-type neural networks with augmented Lagrange multipliers. IEEE Transactions On Neural Networks 7(6) (1996), 1507–1516.
Catania, V., Cavalieri, S. and Russo, M.: Tuning Hopfield neural network by a fuzzy approach. Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Neural Networks (1996), 1067–1072.
Cooper, B. S.: Higher order neural networks-can they help us optimise? in Proceedings of the Sixth Australian Conference on Neural Networks (ACNN'95) (1995), 29–32.
Van den Bout, D. E. and Miller, T. K.: (1989), Improving the performance of the Hopfield-Tank neural network through normalization and annealing. Biological Cybernetics 62 (1989), 129–139.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zeng, X., Martinez, T. A New Relaxation Procedure in the Hopfield Network for Solving Optimization Problems. Neural Processing Letters 10, 211–222 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1018780424422
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1018780424422