Abstract
Purpose. The solubilization of a number of steroids was determined in bile salt simple micelles and a bile salt/phospholipid micellar system to provide a better basis to predict the extent of drug solubilization in vivo.
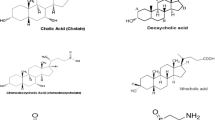
Methods. Excess solid drug was dispersed in taurodeoxycholate or mixed micelle solutions prepared with fixed mole ratios of taurocholate, taurodeoxycholate, taurochenodeoxycholate, glycodeoxycholate, glycocholate, and glycochenodeoxycholate with egg phosphatidylcholine. Drug concentrations were determined from the absorbance following centrifugation. Using NMR spectroscopy, the diffusivities of the simple and mixed micelles were 2 × 10-6 and 8 × 10-7 cm2/s, respectively.
Results. From the change in the concentration of drug in solution with a change in the lipid concentration, the solubilization ratio (SR) was calculated. The SR and aqueous solubility were used to calculate the micelle/aqueous partition coefficients (Km/w). Km/w was correlated with octanol/water partition (Po/w) for the TDC and mixed micelle data sets with correlation lines of logKm/w = 0.74logPo/w + 1.55 (r2 = 0.91) and logKm/w = 0.61 logPo/w + 2.44 (r2 = 0.95), respectively.
Conclusions. With such data, a refined, predictive relationship between the in vitro and the in vivo solubilization with additional information concerning the bile salt/lipid concentration in the human intestine appears possible.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
D. J. Cabral and D. M. Small. Physical Chemistry of bile. In S. G. Schultz, J. G. Forte and B. B. Rauner (eds.), Handbook of Physiology-The Gastrointestinal System III, Section 6, American Physiology Society, Waverly Press, New York, 1989 pp. 621–661.
A. F. Hoffman. The function of bile salts in fat absorption. Biochem. J. 89:57–68 (1962).
T.S. Wiedmann and L. Kamel. Examination of the solubilization of drugs by bile salt micelles. J. Pharm. Sci. (In press) (2002).
D. Horter and J. B. Dressman. Influence of physicochemical properties on dissolution of drugs in the gastrointestinal tract. Adv. Drug Del. Rev. 25:3–14 (1997).
B. L. Pedersen, H. Brondsted, H. Lennernas, F. N. Christensen, A. Mullertz, and H. G. Kristensen. Dissolution of hydrocortisone in human and simulated intestinal fluids. Pharm. Res. 17:183–189 (2000).
B. L. Pedersen, A. Mullertz, H. Brondsted, and H. G. Kristensen. A comparison of the solubility of danazol in human and simulated gastrointestinal fluids. Pharm. Res. 17:891–894 (2000).
M. J. Armstrong and M. C. Carey. Thermodynamic and molecular determinants of sterol solubilities in bile salt micelles. J. Lipid Res. 28:1144–1155 (1987).
V. Bakatselou, R. C. Oppenheim, and J. B. Dressman. Solubilization and wetting effects of bile salts on the dissolution of steroids. Pharm. Res. 8:1461–1469 (1991).
L. J. Naylor, V. Bakatselou, and J. B. Dressman. Comparison of the mechanism of dissolution of hydrocortisone in simple and mixed micelle systems. Pharm. Res. 10:865–870 (1993).
X. Cai, D. J. W. Grant, and T. S. Wiedmann. Analysis of the solubilization of steroids by bile salt micelles. J. Pharm. Sci. 86: 372–377 (1997).
C.-Y. Li, C. L. Zimmerman, and T. S. Wiedmann. Solubilization of retinoids by bile salt/phospholipid aggregates. Pharm. Res. 13: 907–913 (1996).
A. Couper Thermodynamics of Surfactant Solutions. In T. F. Tadros (ed.), Surfactants, Academic Press, Inc., New York, 1984 pp. 19–52.
T. S. Wiedmann, K. Kvanbeck, C-H Han, and V. Roongta. Ionization and solubilization of 4-alkyl benzoic acids and 4-alkyl anilines in sodium taurodeoxycholate solutions. Pharm. Res. 14: 1571–1582 (1997).
J. E. Staggers, O. Hernell, R. J. Stafford, and M. C. Carey. Physical-chemical behavior of dietary and biliary lipids during intestinal digestion and absorption. 1. Phase behavior and aggregation states of model lipid systems patterned after aqueous duodenal contents of healthy adult human beings. Biochemistry 29:2028–2040 (1990).
O. Hernell, J. E. Staggers, and M. C. Carey. Physical-chemical behavior of dietary and biliary lipids during intestinal digestion and absorption. 2. Phase analysis and aggregation states of luminal lipids during duodenal fat digestion in healthy adult human beings. Biochemistry 29:2041–2056 (1990).
P. Stilbs. Fourier transform NMR pulsed-gradient spin-echo (FTPGSE) self-diffusion measurements of solubilization equilibria in SDS solutions. Adv. Coll. Interf. Sci. 87:385–394 (1982).
C. J. O'Connor and R. G. Wallace. Physico-chemical behavior of bile salts. Adv. Coll. Interf. Sci. 22:1–111 (1985).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wiedmann, T.S., Liang, W. & Kamel, L. Solubilization of Drugs by Physiological Mixtures of Bile Salts. Pharm Res 19, 1203–1208 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1019858428449
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1019858428449