Abstract
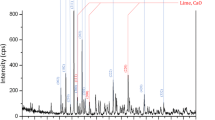
Calcium orthophosphates (CaP) and hydroxyapatite (HA) were intensively studied in order to design and develop a new generation of bioactive and osteoconductive bone prostheses. The main drawback now in the CaP and HA thin films processing persists in their poor mechanical characteristics, namely hardness, tensile and cohesive strength, and adherence to the metallic substrate. We report here a critical comparison between the microstructure and mechanical properties of HA and CaP thin films grown by two methods. The films were grown by KrF* pulsed laser deposition (PLD) or KrF* pulsed laser deposition assisted by in situ ultraviolet radiation emitted by a low pressure Hg lamp (UV-assisted PLD). The PLD films were deposited at room temperature, in vacuum on Ti–5Al–2.5Fe alloy substrate previously coated with a TiN buffer layer. After deposition the films were annealed in ambient air at 500–600 °C. The UV-assisted PLD films were grown in (10−2–10−1 Pa) oxygen directly on Ti–5Al–2.5Fe substrates heated at 500–600 °C. The films grown by classical PLD are crystalline and stoichiometric. The films grown by UV-assisted PLD were crystalline and exhibit the best mechanical characteristics with values of hardness and Young modulus of 6–7 and 150–170 GPa, respectively, which are unusually high for the calcium phosphate ceramics. To the difference of PLD films, in the case of UV-assisted PLD, the GIXRD spectra show the decomposition of HA in Ca2P2O7, Ca2P2O9 and CaO. The UV lamp radiation enhanced the gas reactivity and atoms mobility during processing, increasing the tensile strength of the film, while the HA structure was destroyed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. F. Osborn, in “Bioceramics”, edited by H. Oenishi, H. Aoki, K. Sawai, (Ishiyaku EuroAmerica Inc., 1989) 388.
H. Zeng, W. R. Lacefield, S. Mirov, J. Biomed. Mater. Res., 50 (2000) 248.
Y. C. Tsui, C. Doyle, T. W. Clyne, Biomater. 19 (1998) 2015.
Y. C. Tsui, C. Doyle, T. W. Clyne, ibid. 19 (1998) 2031.
Pulsed Laser Deposition of Thin Films, edited by D. B. Chrisey and G. K. Hubler, (Wiley, New York, 1994).
C. M. Cotell, in Pulsed Laser Deposition of Thin Films, D. B. Chrisey and G. K. Hubler, (Wiley, New York, 1994) 549.
M. Jelinek, V. Olsan, L. Jastrabik, V. Studnicka, V. Hnatowicz, J. Kvitek, V. Havranek, T. Dostalova, I. Zergioti, A. Petrakis, E. Hontzopoulos, C. Fotakis, Thin Solid Films 257 (1995) 125.
J. M. Fernandez-Pradas, M. V. Garcia-Cuenca, L. Cleries, A. G. Sardin, J. L. Morenza, Appl. Surf. Sci. 186 (2002) 1.
V. Nelea, C. Ristoscu, C. Chiritescu, C. Ghica, I. N. Mihailescu, H. Pelletier, P. Mille, A. Cornet, ibid. 168 (2000) 127.
V. Nelea, H. Pelletier, D. Muller, N. Broll, P. Mille, C. Ristoscu, I. N. Mihailescu, ibid. 186 (2002) 483.
D. L. Baulch, R. A. Cox, R. F. Ohampson Jr., J. A. Kerr, J. Troe, R. T. Watson, J. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data 9 (1980) 295
I. W. Boyd, J. Y. Zhang, Nucl. Instrum. Meth. Phys. Res. B 121 (1997) 349
V. Craciun, R. K. Singh, Appl. Surf. Sci. 168 (2000) 239
J. Cohen-Sabban, Mesures 179 (1999) 85
W. C. Oliver, G. M. Pharr, J. Mat. Res 7(6) (1992) 1564
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nelea, V., Pelletier, H., Iliescu, M. et al. Calcium phosphate thin film processing by pulsed laser deposition and in situ assisted ultraviolet pulsed laser deposition. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Medicine 13, 1167–1173 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1021150207350
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1021150207350