Abstract
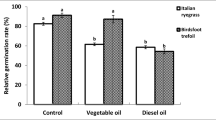
When petroleum hydrocarbons contaminate soil, the carbon:nitrogen (C:N) ratio of the soil is altered. The added carbon stimulates microbial numbers but causes an imbalance in the C:N ratio which may result in immobilization of soil nitrogen by the microbial biomass, leaving none available for plant growth. As members of Leguminosae fix atmospheric nitrogen to produce their own nitrogen for growth, they may prove more successful at growing on petroleum hydrocarbon contaminated sites. During a wider study on phytoremediation of diesel fuel contaminated soil, particular attention was given to the performance of legumes versus other plant species. During harvesting of pot experiments containing leguminous plants, a recurring difference in the number and formation of root nodules present on control and contaminated Common vetch (Vicia sativa L.) plants was observed. The total number of nodules per plant was significantly reduced in contaminated plants compared to control plants but nodules on contaminated plants were more developed than corresponding nodules on control plants. Plant performance of Common vetch and Westerwold's ryegrass (Lolium multiflorum L.) was compared to illustrate any difference between the ability of legumes and grasses to grow on diesel fuel contaminated soil. Common vetch was less affected by diesel fuel and performed better in low levels of diesel fuel contaminated soil than Westerwold’s ryegrass. The total amount of diesel fuel remaining after 4 months in Common vetch planted soil was slightly less than in Westerwold’s ryegrass planted soil.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson, T.A., Guthrie, E.A. and Walton, B.T.: 1993, Bioremediation, Environmental Science and Technology 27, 2630-2636.
Carr, R.H.: 1919, Vegetative growth in soils containing crude petroleum, Soil Science 66-69.
Casella, S., Frassinetti, S., Lupi, F. and Squartini, A.: 1988, Effect of cadmium, chromium and copper on symbiotic and free living Rhizobium leguminosarum biovar trifolii, FEMS Microbiology Letters 49, 343-347.
US EPA: 1986, Method 3540C non-volatile and semi-volatile organic compounds, www.epa.gov.
Greirson, D. and Covey, S.: 1988, Gene expression during development of nitrogen-fixing root nodules, in: Plant Molecular Biology, 2nd edn, Blackie and Son Ltd., Glasgow.
Gudin, C. and Syratt, W.J.: 1975, Biological aspects of land rehabilitation following hydrocarbon contamination, Environmental Pollution 8, 107-112.
Mårtensson, A.M.: 1992, Effects of agrochemicals and heavy metals on fast growing rhizobia and their symbiosis with small-seeded legumes, Soil Biology and Biochemistry 24, 435-445.
Porter, J.R. and Sheridan, R.P.: 1981, Inhibition of nitrogen fixation in alfalfa by arsenate, heavy metals, fluoride and simulated acid rain, Plant Physiology 68, 143-148.
Song, H.G., Wang, X. and Bartha, R.: 1990, Bioremediation potential of terrestrial fuel spills, Applied and Environmental Microbiology 56(3), 652-656.
Wetzel, A. and Werner, D.: 1995, Ecotoxicological evaluation of contaminated soil using legume root nodule symbiosis as effect parameter, Environmental Toxicology and Water Quality 10, 127-133.
Xu, J.G. and Johnson, R.L.: 1997, Nitrogen dynamics in soils with different hydrocarbon contents planted to barley and field pea, Canadian Journal of Soil Science 77, 453-458.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Adam, G., Duncan, H. The Effect of Diesel Fuel on Common Vetch (Vicia Sativa L.) Plants. Environmental Geochemistry and Health 25, 123–130 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1021228327540
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1021228327540