Abstract
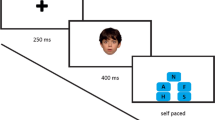
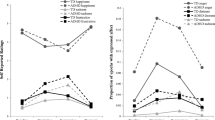
The current study investigated whether students' classification of learning disabled (LD), learning disabled with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (LD/ADHD), or no classification (REG) was related to their ability to perceive nonverbal social cues. Participants in the study were 57 students between the ages of six and ten years identified as being LD, LD/ADHD, or REG. The Diagnostic Analysis of Nonverbal Accuracy test (DANVA) and the Social Perception Behavior Rating Scale (SPBRS) were used to measure social perception. A MANOVA was computed for the four subtests of the DANVA (Facial Expressions, Postures, Gestures, and Paralanguage). A separate ANOVA was computed on the SPBRS. Significant differences were found for Facial Expressions and SPBRS scores. Follow-up analysis revealed that on the Facial Expressions subtest, students with LD demonstrated significantly more difficulty in the accurate perception of cues than the REG or LD/ ADHD groups. On the SPBRS, the LD/ADHD group was rated by teachers as significantly less socially perceptive than the REG group.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
American Psychiatric Association. (1994). Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (4th ed.). Washington, DC: Author.
Berlin, D. F. (1991). Tactile discrimination, response mode, and interhemispheric communication by learning disabled children. Perceptual and Motor Skills, 72, 504–506.
Brumback, R. A., & Staton, D. R. (1982). An hypothesis regarding the commonality of right hemisphere involvement in learning disability, attentional disorder, and childhood major depressive disorder. Perceptual and Motor Skills, 55, 1091–1097.
Cahn, D. D., & Frey, L. R. (1992). Listeners' perceived verbal and nonverbal behaviors associated with communicators' perceived understanding and misunderstanding. Perceptual and Motor Skills, 74, 1059–1064.
Cantwell, D. P., & Baker, L. (1991). Association between attention deficit-hyperactivity disorder and learning disorders. Journal of Learning Disabilities, 24, 88–95.
Carrol, A., Bain, A., & Houghton, S. (1994). The effects of interactive versus linear video on the levels of attention and comprehension of social behavior by children with attention disorders. School Psychology Review, 23 29–43.
Creasey, G. L., & Jarvis, P. A. (1987). Sensitivity to nonverbal communication among male learning disabled adolescents. Perceptual and Motor Skills, 64, 873–874.
Flicek, M. (1992). Social status of boys with both academic problems and attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 20, 353–366.
Gillis, J. J., Gilger, J. W., Pennington, B. F., & DeFries, J. C. (1992). Attention deficit disorder in reading-disabled twins: Evidence for a genetic etiology. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 20, 303–315.
Johnson, D., & Myklebust, H. (1967). Learning disabilities: Educational principles and practices. NY York: Grune & Stratton.
Kataria, S., Hall, C. W., Wong, M. M., & Keys, G. F. (1992). Learning styles of LD and NLD ADHD children. Journal of Clinical Psychology, 48, 371–378.
Keefe, C. H. (1988). Social skills: A basic subject. Academic Therapy, 23, 367–373.
Kupietz, S. S. (1990). Sustained attention in normal and in reading-disabled youngsters with and without ADHD. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 18, 357–372.
Loveland, K., Fletcher, J., & Bailey, V. (1990). Verbal and nonverbal communication of events in learning-disability subtypes. Journal of Clinical and Experimental Neuropsychology, 12, 443–447.
Maheady, L., & Harper, G. (1986). The Social Perception Behavior Rating Scale: Initial evidence. Diagnostique, 11, 91–103.
McKinney, J. D. (1989). Longitudinal research on the behavioral characteristics of children with learning disabilities. Journal of Learning Disabilities, 22, 141–150.
Nabuzoka, D., & Smith, P. (1995). Identification of Expressions of emotions by children with and without learning disabilities. Learning Disabilities Research and Practice, 10 91–101.
Nowicki, S., & Duke, M. (1989). A measure of nonverbal social processing ability in children between the ages of 6 and 10. Paper presented at meeting of the American Psychological Society, Alexandria, VA.
Nowicki, S., & Duke, M. (1994). Individual differences in the nonverbal communication of affect: The Diagnostic Analysis of Nonverbal Accuracy Scale. Journal of Nonverbal Behavior, 18 9–35.
Ordway, A. (1993). Social perception and cognitive abilities in students with learning disabilities. Unpublished master's thesis, East Carolina University, Greenville, NC.
Robins, P. M. (1992). A comparison of behavioral and attentional functioning in children diagnosed as hyperactive or learning-disabled. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 20, 65–82.
Russell, R. L., Stokes, J., Jones, M. E., Czogalik, D., & Rohleder, L. (1993). The role of nonverbal sensitivity in childhood psychopathology. Journal of Nonverbal Behavior, 17, 69–83.
Semrud-Clikeman, M., & Hynd, G. W. (1990). Right hemispheric dysfunction in nonverbal learning disabilities: Social, academic, and adaptive functioning in adults and children. Psychological Bulletin, 107, 196–209.
Tarnowski, K. J., & Nay, S. M. (1989). Locus of control in children with learning disabilities and hyperactivity: A subgroup analysis. Journal of Learning Disabilities, 22, 381–383.
Wechsler, D. (1991). Manual for the Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children-Third Edition. New York: Psychological Corp.
Whalen, C. K., Henker, B., & Granger, D. A. (1990). Social judgment processes in hyperactive boys: Effects of methylphenidate and comparisons with normal peers. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 18, 297–316.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sprouse, C.A., Hall, C.W., Webster, R.E. et al. Social Perception in Students with Learning Disabilities and Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder. Journal of Nonverbal Behavior 22, 125–134 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022932315274
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022932315274