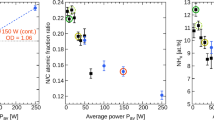
Abstract
A previously established human monocyte culture protocol was used to determine the effects of varying adsorbed proteins on monocyte/macrophage adhesion and survival on dimethyl-silane (DM) or RGD modified glass coverslips. Cells were allowed to adhere for 2 h in the absence of protein or in the presence of serum, fibrinogen (Fg), heat inactivated serum (HIS), serum supplemented with Fg or HIS with Fg. Cell adhesion and apoptosis rates were determined on days 0 (2 h), 3, 7 and 10 of culture. The presence of serum alone in the initial culture was sufficient to optimize monocyte/macrophage adhesion and survival rates. Adding Fg to serum did not increase adhesion nor decrease apoptotic rates. No protein or the addition of HIS during the initial incubation period significantly decreased monocyte/macrophage adhesion and survival on both surfaces, however, the addition of Fg to HIS restored adhesion and survival rates to those seen with in the presence of serum alone on RGD surfaces. These studies demonstrate that monocyte/macrophage adhesion and survival on biomaterial surfaces are optimized by adsorbed heat labile serum proteins while adsorbed Fg plays a surface property-dependent role.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. S. Sutton and L. Weiss, J. Cell Biol. 28 (1966) 303.
A. R. Murch, M. D. Grounds, C. A. Marshall and J. M. Papadimitriou, J. Pathol. 137 (1982) 177.
J. M. AndersonBiomaterials Science, edited by B. D. Ratner, A. S. Hoffman, F. J. Schoen and J. E. Lemons (Academic Press, New York, 1996) pp. 451-455.
Q. Zhao, N. Topham, J. M. Anderson, G. Lodoen and C. R. Payet, J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 25 (1991) 177.
Q. H. Zhao, A. K. Mcnally, K. R. Rubin, M. Reiner, Y. Wu, V. Rose-Caprara, J. M. Anderson, A. Hiltner, P. Urbanski and K. Stokes, ibid. 27 (1993) 379.
C. Jenney and J. Anderson, ibid. 49 (2000) 435.
A. K. Mcnally and J. M. Anderson, Am. J. Pathol. 147 (1995) 1487.
K. M. Defife, C. R. Jenney, A. K. Mcnally and J. M. Anderson, J. Immunol. 158 (1997) 3385.
A. K. Mcnally and J. M. Anderson, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 91 (1994) 10119.
L. Tang and J. W. Eaton, J. Exp. Med. 178 (1996) 2147.
L. Tang, T. P. Ugarova, E. F. Plow and J. W. Eaton, J. Clin. Invest. 97 (1996) 1329.
W. G. Brodbeck, M. S. Shive, E. Colton and J. M. Anderson, J. Lab. Clin. Med. 139 (2002) 90.
W. G. Brodbeck, M. S. Shive, E. Colton, Y. Nakayama, T. Matsuda and J. M. Anderson, J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 55 (2001) 661.
M. Shen and T. A. Horbett, ibid. 57 (2001) 336.
L. Tang, Y. Wu and R. B. Timmons, ibid. 1998 (1998) 156.
S. M. Slack, J. L. Bohnert and T. A. Horbett, Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 516 (1987) 223.
S. I. Ertel, B. D. Ratner, A. Kaul, M. B. Schway and T. A. Horbett, J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 6 (1994) 667.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Brodbeck, W.G., Colton, E. & Anderson, J.M. Effects of adsorbed heat labile serum proteins and fibrinogen on adhesion and apoptosis of monocytes/macrophages on biomaterials. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Medicine 14, 671–675 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1024951330265
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1024951330265