Abstract
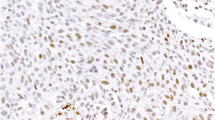
Aberrant c-Src protein kinase activation has been identified as one of the molecular alterations involved in human pancreatic carcinogenesis. It has been postulated that c-Src may induce transformation by causing the overexpression of the insulinlike growth factor-1 receptor (IGF-1R) in pancreatic tumor cell lines. To further study the interaction between c-Src and IGF-1R proteins in human pancreatic cancer, we examined their coexpression in 47 human pancreatic ductal adenocarcinomas (PDA). Formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded sections from 47 cases of PDA were stained using the immunohistochemical avidin–biotin–peroxidase method. We used an anti-human IGF-1R mouse monoclonal antibody (dilution 1:100 with antigen retrieval), and an anti-c-Src mouse monoclonal antibody (dilution 1:100 with antigen retrieval). The stains were semiquantitatively evaluated using the Allred score system, assessing intensity of stain and percentage of positive tumor cells. High cytoplasmic c-Src expression (Allred score 7–8) was seen in 33/47 (70%) tumors. In only 4 cases was c-Src either negative or low (Allred score 3). Strong and diffuse membranous IGF-1R stain (Allred score 7–8) was identified in 30/47 (64%) tumors. IGF-1R staining was low (Alled score 2–4) in 2 cases and negative in 1. Interestingly, in 40/47 (85%) cases c-Src and IGF-1R stains had similar scores. An inverse staining pattern was detected in only 6/47 (13%) tumors. Normal pancreatic ducts as well as areas of chronic pancreatitis were negative for IGF-1R. In conclusion, our data support the role of IGF-1R and c-Src in human pancreatic carcinogenesis; the coexpression of both these molecules may play an important role in transformation of pancreatic ductal cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gudjonsson B: Survival statistics gone awry: pancreatic cancer, a case in point. J Clin Gastroenterol 35(2): 180-184, 2002
Brooks JR, Culebras JM: Cancer of the pancreas, palliative operation, Whipple procedure, or total pancreatectomy. Am J Surg 131(4):516-520, 1976
Baylor SM, Berg JW: Cross-classification and survival characteristics of 5,000 cases of cancer of pancreas. J Surg Oncol 5:335-358, 1973
Poston GJ: Biology of pancreatic cancer. Gut 32:800-812, 1991
Jemal A, Thomas A, Murray T, Thun M: Cancer statistics, 2002. Ca Cancer J Clin 52:23-47, 2002
DiGiuseppe JA, Hruban RH, Goodman SN, Polak M, van den Berg FM, Alison DC, Cameron JL, Offerhavs GJ: Overexpression of p53 protein in adenocarcinoma of the pancreas. Am J Clin Pathol 101:684-688, 1994
Lundin J, Nordling S, von Boguslawsky K, Roberts PJ, Haglund C: Prognostic value of immunohistochemical expression of p53 in patients with pancreatic cancer. Oncology 53:104-111, 1996
Almoguera C, Shibata D, Forrester K, Martin J, Arnheim M, Perucho M: Most human carcinomas of the exocrine pancreas contain mutant c-K-ras genes. Cell 53:549-554, 1988
Gotoda T, Matsumura Y, Kondo H, Saitoh D, Shimada Y, Kosuge T, Kanai Y, Kakizoe T: Expression of CD44 variants and its association with survival in pancreatic cancer. Jpn J Cancer Res 89(10):1033-1140, 1998
Castella EM, Ariza A, Ojanguren I, Mate JL, Roca X, Fernandez-Vasalo A, Navas-Palacios JJ: Differential expression of CD44v6 in adenocarcinoma of the pancreas: an immunohistochemical study. Virchows Arch 429(4-5): 191–5, 1996
Tumminello FM, Leto G, Pizzolanti G, Candiloro V, Crescimanno M, Crosta L, Flandina C, Montalto G, Soresi M, Carroccio A, Bascone F, Ruggeri I, Ippolito S, Gebbia N: Cathepsin D, B and L circulating levels as prognostic markers of malignant progression. Anticancer Res 16(4B):2315-2319, 1996
Pelosi G, Pasini F, Bresaola E, Bogina G, Pederzoli P, Biolo S, Menard S, Zamboni G: High-affinity monomeric 67-kD laminin receptors and prognosis in pancreatic endocrine tumours. J Pathol 183(1):62-69, 1997
Cantero D, Friess H, Deflorin J, Zimmermann A, Brundler MA, Riesle E, Korc M, Buchler MW: Enhanced expression of urokinase plasminogen activator and its receptor in pancreatic carcinoma. Br J Cancer 75(3):388-395, 1997
Miyamoto Y, Hosotani R, Wada M, Lee JU, Koshiba T, Fujimoto K, Tsuji S, Nakajima S, Doi R, Kato M, Shimada Y, Imamura M: Immunohistochemical analysis of Bcl-2, Bax, Bcl-X, and Mcl-1 expression in pancreatic cancers. Oncology 56(1):73-82, 1999
Wilentz RE, Iacobuzio-Donahue CA, Argani P, McCarthy DM, Parsons JL, Yeo CJ, Kern SE, Hruban RH: Loss of expression of Dpc4 in pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasia: evidence that DPC4 inactivation occurs late in neoplastic progression. Cancer Res 60(7):2002-6, 2000
Barton CM, Hall PA, Hughes CM, Gullick WJ, Lemoine NR: Transforming growth factor alpha and epidermal growth factor in human pancreatic cancer. J Pathol 163:111-116, 1991
Korc M, Meltzer P, Trent J: Enhanced expression of epidermal growth factor receptor correlates with alterations of chromosome 7 in human pancreatic cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83:5141-5144, 1986
Szepeshazi K, Halmos G, Schally AV, Arencibia JM, Groot K, Vadillo-Buenfil M, Rodriguez-Martin E: Growth inhibition of experimental pancreatic cancers and Sustained reduction in epidermal growth factor receptors during therapy with hormonal peptide analogs. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 125(8–9):444-452, 1999
Alexandrow MG, Moses HL: Transforming growth factor beta and cell cycle regulation. Cancer Res 55(7):1452-1457, 1995
Wagner M, Kleeff J, Friess H, Buchler MW, Korc M: Enhanced expression of the type II transforming growth factor-beta receptor is associated with decreased survival in human pancreatic cancer. Pancreas 19(4):370-376, 1999
Kornmann M, Tangvoranuntakul P, Korc M: TGF-beta-1 up-regulates cyclin D1 expression in COLO-357 cells, whereas suppression of cyclin D1 levels is associated with down-regulation of the type I TGF-beta receptor. Int J Cancer 83(2):247-254, 1999
Bergmann U, Funatomi H, Yokoyama M, Berger HG, Korc M: Insulin-like growth factor I overexpression in human pancreatic cancer: evidence for autocrine and paracine roles. Cancer Res 55(10):2007-11, 1995
Ohmura E, Okada M, Onoda N, Kamiya Y, Murakami H, Tsushima T, Shizume K: Insulin-like growth factor I and transforming growth factor alpha as autocrine growth factors in human pancreatic cancer cell growth. Cancer Res 50(1):103-107, 1990
Flossmann-Kast BB, Jehle PM, Hoeflich A, Adler G, Lutz MP: Src stimulates insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I)-dependent cell proliferation by increasing IGF-I receptor number in human pancreatic carcinoma cells. Cancer Res 58(16):3551-3554, 1998
Cartwright CA, Kamps MP, Meisier AI, Pipas JM, Eckhart W: pp60c-src activation in human colon carcinoma. J Clin Invest 83:2025-2033, 1989
Garcia R, Bowman TL, Niu G, Yu H, Minton S, Muro-Cacho CA, Cox CE, Falcone R, Fairclough R, Parsons S, Laudano A, Gazit A, Levitzki A, Kraker A, Jove R: Constitutive activation of Stat3 by the Src and JAK tyrosine kinases participates in growth regulation of human breast carcinoma cells. Oncogene 20(20):2499-2513, 2001
Masaki T, Tokuda M, Shiratori Y, Shirai M, Matsumoto K, Nishioka M, Omata M: A possible novel src-related tyrosine kinase in cancer cells of LEC rats that develop hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol 32(1):92-9, 2000
Irby RB, Mao W, Coppola D, Kang J, Loubeau JM, Trudeau W, Karl R, Fujita DJ, Jove R, Yeatman TJ: Activating Src mutation in a subset of advanced human colon cancers. Nat Genet 21(2): 187-190, 1999
Lutz MP, Esser IB, Flossmann-Kast BB, Vogelmann R, Luhrs H, Friess H, Buchler MW, Adler G: Overexpression and activation of the tyrosine kinase Src in human pancreatic carcinoma. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 243(2):503-8, 1998
MacMillan-Crow LA, Greendorfer JS, Vickers SM, Thompson JA: Tyrosine nitration of c-Src tyrosine kinase in human pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Arch Biochem Biophys 377(2):350-356, 2000
Kozma LM, Reynolds AB, Weber MJ: Glycoprotein tyrosine phosphorylation in Rous Sarcoma virus-transformed chicken embryo fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol 10:837-841, 1990
Peterson JE, Jelinek T, Kaleko M, Weber M: C-phosphorylation and activation of the IGF-1 receptor in src-transformed cells. J Biol Chem 269:27315-27321, 1994
Peterson JE, Kulik G, Jelinek T, Reuter CW, Shannon JA, Weber MJ: Src phosphorylates the insulin-like growth factor type I receptor on the auto-phosphorylation sites. Requirement for transformation by src. J Biol Chem 271(49):31562-31571, 1996.
Allred DC, Clark GM, Ellfdge R, Fuqua SAW, Brown RW, Chambers GC, Osborne CK, McGuire WL: Association of p53 protein expression with tumor cell proliferation rate and clinical outcome in node-negative breast cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst 85:200-206, 1993
Kalthoff H, Schmiegel W, Roeder C, et al: p53 and K-ras alterations in pancreatic epithelial cell lesions. Oncogene 8:289-298, 1993
Ruggeri B, Zhang S, Caamano J, et al: Human pancreatic cancer reveals frequent and multiple alterations in the p53 and RB-1 tumor suppressors genes. Proc Annu Meet Am Assoc Cancer Res 33:A2320, 1992
Hunter T: A tale of two src's: mutatis mutandis. Cell 49:1-4, 1987
Cooper JA, Howell B: The when and how of src regulation. Cell 73:1051-1054, 1993
Xu W, Harrison SC, Eck MJ: Three-dimensional structure of the tyrosine kinase c-Src. Nature 385:595-602, 1997
Iravani S, Mao Weiguang, Ling F, Karl R, Yeatman T, Jove R, Coppola D: Elevated c-Src protein expression is an early event in colonic neoplasia. Lab Invest 78:365-371, 1998
Ullrich A, Gray A, Tam AW, Yang-Feng T, Tsubokawa M, Collins C, Henzel W, LeBon T, Kahuria S, Chen E, Jacobs S, Francke U, Ramachandran J, Fujita Yamaguchi Y: Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor primary structure: comparison with insulin receptor suggests structural determinants that define functional specificity. EMBO J 5:2503-2512, 1986
White MF, Kahn CR: The insulin signaling system. J Biol Chem 269:1-4, 1994
Myers MG, Sun XJ, Cheatham B, Jachna BR, Glasheen EM, Backer JM, White MF: IRS-1 is a common element in insulin and insulin-like growth factor-1 signaling to the phosphatidylinositol 3”-kinase. Endocrinology 132:1421-1430, 1993
Rubin R, Baserga R: Biology of disease: insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor. Its role in cell proliferation, apoptosis, and tumorigenicity. Lab Invest 73:311-331, 1995
Baserga R. Controlling IGF-receptor function: a possible strategy for tumor therapy. Trends Biotechnol 14:150-152, 1996
Resnicoff M, Abraham D, Yutanawiboonchai W, Rotman HL, Kajstura J, Rubin R, Zoltick P, Baserga R: The insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor protects tumor cells from apoptosis in vivo. Cancer Res 55:2463-2469, 1995
O'Connor R, Kauffmann-Zeh A, Liu Y, Lehar S, Evan GI, Baserga R, Blattler WA: Identification of domains of the insulin-like growth factor I receptor that are required for protection from apoptosis. Mol Cell Biol 17:427-435, 1997
Harrington EA, Bennett MR, Fanidi A, Evan GI: c-Myc induced apoptosis in fibroblasts is inhibited by specific cytokines. EMBO J 13:3286-3295, 1994
Valentinis B, Morrione A, Taylor SJ, Baserga R: Insulin-like growth factor I receptor signaling in transformation by src oncogenes. Mol Cell Biol. 17(7):3744-3754, 1997
Visser CJ, Rijksen G, Wuotersen RA, DeGeger RA: Increased immunoreactivity and protein tyrosine kinase activity of the protooncogene pp60c-src in preneoplastic lesions in rat pancreas. Lab Invest 74(1):2-11, 1996
MacMillan-Crow LA, Greendorfer JS, Vickers SM, Thompson JA: Tyrosine nitration of c-Src tyrosine kinase in human pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Arch Biochem Biophys 377(2):350-356, 2000
Freeman JM, Mattingly CA, Strodel WE: Increase tumorigenicity in the human pancreatic cell line MIA PaCa-2 is associated with an aberrant regulation of an IGF-1 autocrine loop and lack of expression of the TGF-beta type RII receptor. J Cell Physiol 165(1):155-163, 1995
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hakam, A., Fang, Q., Karl, R. et al. Coexpression of IGF-1R and c-Src Proteins in Human Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. Dig Dis Sci 48, 1972–1978 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1026122421369
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1026122421369