Abstract
Purpose. To develop a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) technique for assessing in vivo properties of orally ingested gastric-retentive tablets under physiologic conditions.
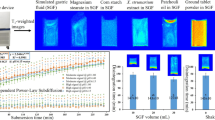
Methods. Tablets with different floating characteristics (tablet A-C) were marked with superparamagnetic Fe3O4 particles to analyze intragastric tablet position and residence time in human volunteers. Optimal Fe3O4 concentration was determined in vitro. Intragastric release characteristic of one slow-release tablet (tablet D) was analyzed by embedding gadolinium chelates (Gd-DOTA) as a drug model into the tablet. All volunteers underwent MRI in the sitting position. Tablet performance was analyzed in terms of relative position of tablet to intragastric meal level (with 100% at meal surface), intragastric residence time (min) and Gd-DOTA distribution volume (% of meal volume).
Results. Intragastric tablet floating performance and residence time of tablets (tablet A-D) as well as the intragastric Gd-DOTA distribution of tablet D could be monitored using MRI. Tablet floating performance was different between the tablets (A, 93%(95 − 9%); B, 80%(80 − 68%); C, 38%(63 − 32%); p < 0.05). The intragastric distribution volume of Gd-DOTA was 19.9% proximally and 35.5% distally.
Conclusions. The use of MRI allows the assessment of galenic properties of orally ingested tablets in humans in seated position.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
S. J. Hwang, H. Park, and K. Park. Gastric retentive drug-delivery systems. Crit. Rev. Ther. Drug Carrier Syst. 15:243-284 (1998).
B. N. Singh and K. H. Kim. Floating drug delivery systems: an approach to oral controlled drug delivery via gastric retention. J. Cont. Release 63:235-259 (2000).
L. Whitehead, J. T. Fell, J. H. Collett, H. L. Sharma, and A. Smith. Floating dosage forms: an in vivo study demonstrating prolonged gastric retention. J. Cont. Release 55:3-12 (1998).
G. Gusler, J. Gorsline, G. Levy, S. Z. Zhang, I. E. Weston, D. Naret, and B. Berner. Pharmacokinetics of metformin gastric-retentive tablets in healthy volunteers. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 41:655-661 (2001).
C. G. Wilson. In-vivo monitoring of dosage forms. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 50:383-386 (1998).
I. R. Wilding, A. J. Coupe, and S. S. Davis. The role of gamma-scintigraphy in oral drug delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 46:103-124 (2001).
W. Schwizer, R. Fraser, H. Maecke, K. Siebold, R. Funck, and M. Fried. Gd-DOTA as a gastrointestinal contrast agent for gastric emptying measurements with MRI. Magn. Reson. Med. 31:388-393 (1994).
P. Kunz, C. Feinle, W. Schwizer, M. Fried, and P. Boesiger. Assessment of gastric motor function during the emptying of solid and liquid meals in humans by MRI. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 9:75-80 (1999).
C. Feinle, P. Kunz, P. Boesiger, M. Fried, and W. Schwizer. Scintigraphic validation of a magnetic resonance imaging method to study gastric emptying of a solid meal in humans. Gut 44:106-111 (1999).
H. Faas, W. Schwizer, C. Feinle, H. Lengsfeld, C. de Smidt, P. Boesiger, M. Fried, and T. Rades. Monitoring the intragastric distribution of a colloidal drug carrier model by magnetic resonance imaging460. Pharm. Res. 18:460-466 (2001).
H. Faas, A. Steingoetter, C. Feinle, T. Rades, H. Lengsfeld, P. Boesiger, M. Fried, and W. Schwizer. Effects of meal consistency and ingested fluid volume on the intragastric distribution of a drug model in humans—a magnetic resonance imaging study. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 16:217-224 (2002).
P. Boulby, P. Gowland, V. Adams, and R. C. Spiller. Use of echo planar imaging to demonstrate the effect of posture on the intragastric distribution and emptying of an oil/water meal. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 9:41-47 (1997).
L. Marciani, P. Manoj, B. P. Hills, R. J. Moore, P. Young, A. Fillery-Travis, R. C. Spiller, and P. A. Gowland. Echo-planar imaging relaxometry to measure the viscosity of a model meal. J. Magn. Reson. 135:82-86 (1998).
P. Boulby, R. Moore, P. Gowland, and R. C. Spiller. Fat delays emptying but increases forward and backward antral flow as assessed by flow-sensitive magnetic resonance imaging. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 11:27-36 (1999).
L. Marciani, P. A. Gowland, R. C. Spiller, P. Manoj, R. J. Moore, P. Young, S. Al-Sahab, D. Bush, J. Wright, and A. J. Fillery-Travis. Gastric response to increased meal viscosity assessed by echo-planar magnetic resonance imaging in humans. J. Nutr. 130:122-127 (2000).
L. Marciani, P. A. Gowland, R. C. Spiller, P. Manoj, R. J. Moore, P. Young, and A. J. Fillery-Travis. Effect of meal viscosity and nutrients on satiety, intragastric dilution, and emptying assessed by MRI. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 280:G1227-G1233 (2001).
J. F. Schenck. The role of magnetic susceptibility in magnetic resonance imaging: MRI magnetic compatibility of the first and second kinds. Med. Phys. 23:815-850 (1996).
A. C. Perkins and M. Frier. Nuclear medicine techniques in the evaluation of pharmaceutical formulations. Pharm. World Sci. 18:97-104 (1996).
J. Borovicka, R. Lehmann, P. Kunz, R. Fraser, C. Kreiss, G. Crelier, P. Boesiger, G. A. Spinas, M. Fried, and W. Schwizer. Evaluation of gastric emptying and motility in diabetic gastroparesis with magnetic resonance imaging: effects of cisapride. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 94:2866-2873 (1999).
L. Marciani, P. Young, J. Wright, R. J. Moore, D. F. Evans, R. C. Spiller, and P. A. Gowland. Echoplanar imaging in GI clinical practice: assessment of gastric emptying and antral motility in four patients. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 12:343-346 (2000).
T. Bach-Gansmo. Ferrimagnetic susceptibility contrast agents. Acta Radiol. Suppl. 387:1-30 (1993).
W. K. Johnson, C. Stoupis, G. M. Torres, E. B. Rosenberg, and P. R. Ros. Superparamagnetic iron oxide (SPIO) as an oral contrast agent in gastrointestinal (GI) magnetic resonance imaging (MRI): comparison with state-of-the-art computed tomography (CT). Magn. Reson. Imaging 14:43-49 (1996).
C. E. Sjogren, C. Johansson, A. Naevestad, P. C. Sontum, K. Briley-Saebo, and A. K. Fahlvik. Crystal size and properties of superparamagnetic iron oxide (SPIO) particles. Magn. Reson. Imaging 15:55-67 (1997).
P. A. Rinck and R. N. Muller. Field strength and dose dependence of contrast enhancement by gadolinium-based MR contrast agents. Eur. Radiol. 9:998-1004 (1999).
M. A. Patak, D. Weishaupt, J. M. Frohlich, and J. F. Debatin. Sequential fast 3D MRI following oral ingestion of Gd-DOTA: A new means to assess intestinal transit time. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 10:474-476 (1999).
L. M. Akkermans and J. W. van Isselt. Gastric motility and emptying studies with radionuclides in research and clinical settings. Dig. Dis. Sci. 39:95S-96S (1994).
M. J. Bruno, E. B. Haverkort, G. N. Tytgat, and D. J. van Leeuwen. Maldigestion associated with exocrine pancreatic insufficiency: implications of gastrointestinal physiology and properties of enzyme preparations for a cause-related and patient-tailored treatment. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 90:1383-1393 (1995).
P. G. Hillel, W. B. Tindale, C. J. Taylor, M. Frier, S. Senior, and S. Ghosal. The use of dual-isotope imaging to compare the gastrointestinal transit of food and pancreatic enzyme pellets in cystic fibrosis patients. Nucl. Med. Commun. 19:761-769 (1998).
M. Anvari, M. Horowitz, R. Fraser, A. Maddox, J. Myers, J. Dent, and G. G. Jamieson. Effects of posture on gastric emptying of nonnutrient liquids and antropyloroduodenal motility. Am. J. Physiol. 268:G868-G871 (1995).
S. Doran, K. L. Jones, J. M. Andrews, and M. Horowitz. Effects of meal volume and posture on gastric emptying of solids and appetite. Am. J. Physiol. 275:R1712-R1718 (1998).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Steingoetter, A., Weishaupt, D., Kunz, P. et al. Magnetic Resonance Imaging for the in Vivo Evaluation of Gastric-Retentive Tablets. Pharm Res 20, 2001–2007 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:PHAM.0000008049.40370.5a
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:PHAM.0000008049.40370.5a