Abstract
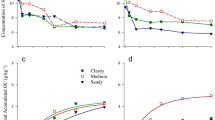
In order to assess the potential impact of long-term sewage sludge application on soil health, the equivalent of about 25 years of agronomic applications of low-metal (`EQ') sewage sludge products were made to greenhouse soil columns. After a 6-year period of `equilibration', during which time successive crops were grown with irrigation by simulated acid rain, the plant-available quantities of trace elements were estimated in the soils by extraction with 0.01 M CaCl2 at 90 °C, and measured directly by uptake into a crop of red clover (Trifolium pratense L.). Soil pH had a strong influence on the level of extractable and plant-available metals, and because the tested sludge products affected soil pH differently, pH was directly factored into the comparison of different sludge treatments with controls. CaCl2-extractable levels of several metals (Cu, Zn, Mo), sulfur and phosphorus were found to be higher in the soils amended with organic-rich sludge products than in the control soils. However, extractable Cd and Ni were not significantly elevated by the sludge amendments, presumably because of the low total loading of these metals. Copper, Zn and Mo applied in the form of sludge ash had low soil extractability, suggesting that these trace metals were trapped in high-temperature mineral phases formed during sludge incineration, and resisted subsequent weathering in the soil environment. Extractable soil metals in the alkaline-stabilized sludge treatment were also generally low. Phytotoxicity from the sludge metal loadings (Zn≤125, Cu≤135 kg/ha), was not clearly indicated as long as soil pH was maintained in the 6–7 range by lime amendment. Nevertheless, unexplained depressions in yield were noted with some of the sludge products applied, particularly the dewatered and composted materials. On limed soil columns, the most consistent effect of sludge product amendment on red clover composition was a marked increase in plant Mo.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abanades S, Flamant G and Gauthier D 2002 Kinetics of heavy metal vaporization from model wastes in a fluidized bed. Environ. Sci. Technol. 36, 3879-3884.
Antoniadis V and Alloway B J 2002 The role of dissolved organic carbon in the mobility of Cd, Ni and Zn in sewage sludge-amended soils. Environ. Pollut. 117, 515-521.
Baveye P, McBride M B, Bouldin D, Hinesly, T D, Dahdoh M S A and Abdel-sabour M F 1999 Mass balance and distribution of sludge-borne trace elements in a silt loam soil following longterm applications of sewage sludge. Sci. Total Environ. 227, 13-28.
Chaudri A M, Allain CMG, Barbosa-Jefferson V L, Nicholson F A, Chambers B J and McGrath S P 2000 A study of the impacts of Zn and Cu on two rhizobial species in soils of a long-term field experiment. Plant Soil 221, 167-179.
Goldberg S and Forster H S 1998. Factors affecting molybdenum adsorption by soils and minerals. Soil Sci. 163, 109-114.
Gove, L, Cooke C M, Nicholson F A and Beck A J 2001 Movement of water and heavy metals (Zn, Cu, Pb and Ni) through sand and sandy loam amended with biosolids under steady-state hydrological conditions. Biores. Technol. 78, 171-179.
Gunkel P, Jezequel K and Fabre B 2002 Temporal evolution of copper distribution in soil fractions, influence of soil pH and organic carbon level on copper distribution. Environ. Technol. 23, 1001-1008.
Harrison E Z, McBride M B and Bouldin D R 1999 Land application of sewage sludges: an appraisal of the US regulations. Int. J. Environ. Pollut. 11, 1-36.
Houba V J G, Novozamsky I, Huijbregts A W M and van der Lee J J 1986 Comparison of soil extractions by 0.01 M CaCl2, by EUF and by some conventional extraction procedures. Plant Soil 96, 433-437.
Houba V J G, Novozamsky I, Lexmond Th M and van der Lee J J 1990 Applicability of 0.01 M CaCl2 as a single extraction solution for the assessment of the nutrient status of soils and other diagnostic purposes. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 21, 2281-2290.
Houba V J G, Temminghoff E J M, Gaikhorst G A and van Vark W. 2000 Soil analysis procedures using 0.01 M CaCl2 as extraction reagent. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 31, 1299-1396.
Keller C, McGrath S P and Dunham S J 2002 Heavy metals in the environment-Trace metal leaching through a soil-grassland system after sewage sludge application. J. Environ. Qual. 31, 1550-1560.
Knight B P, Chaudri A M, McGrath S P and Giller K E 1998 Determination of chemical availability of cadmium and zinc in soils using inert soil moisture samplers. Environ. Pollut. 99, 293-298.
Mbila M O, Thompson M L, Mbagwu J S C and Laird D A 2001 Distribution and movement of sludge-derived trace metals in selected Nigerian soils. J. Environ. Qual. 30, 1667-1674.
McBride M B, Martinez C E, Topp E and Evans L 2000a Trace metal solubility and speciation in a calcareous soil 18 years after no-till sludge application. Soil Sci.165, 646-656.
McBride M B, Richards B K, Steenhuis T, Russo J J and Sauvé S 1997 Mobility and solubility of toxic metals and nutrients in soil fifteen years after sludge application. Soil Sci. 162, 487-500.
McBride M B, Richards B K, Steenhuis T and Spiers G 2000b Molybdenum uptake by forage crops grown on sewage sludgeamended soils in the field and greenhouse. J. Environ. Qual. 29, 848-854.
McBride M B, Richards B K, Steenhuis T and Spiers G 1999 Longterm leaching of trace elements in a heavily sludge-amended silty clay loam soil. Soil Sci. 164, 613-623.
McBride M B, Nibarger E A, Richards B K and Steenhuis T 2003 Trace metal accumulation by red clover grown on sewage sludge-amended soils and correlation to Mehlich 3 and calcium chloride-extractable metals. Soil Sci. 168, 29-38.
McBride M B 1998 Soluble trace metals in alkaline stabilized sludge products. J. Environ. Qual. 27, 578-584.
Richards B K, Steenhuis T S, Peverly J H and McBride M B 2000 Effect of sludge-processing mode, soil texture and soil pH on metal mobility in undisturbed soil columns under accelerated loading. Environ. Pollut. 109, 327-346.
Richards B K, Steenhuis T S, Peverly J H and McBride M B 1998 Metal mobility at an old, heavily loaded sludge application site. Environ. Pollut. 99, 365-377.
Richards B K, Steenhuis T S, Peverly J H and Liebowitz B N 1997 Effect of processing mode on trace elements in dewatered sludge products. J. Environ. Qual. 26, 782-788.
Sanders J R, McGrath S P and Adams T McM 1987 Zinc, copper and nickel concentrations in soil extracts and crops grown on four soils treated with metal-loaded sewage sludges. Environ. Pollut. 44, 193-210.
Smith S R 1994 Effect of soil pH on availability to crops of metals in sewage sludge-treated soils. I. Nickel, copper and zinc uptake and toxicity to ryegrass. Environ. Pollut. 85, 321-327.
USEPA. 1993 The Standards for the Use or Disposal of Sewage Sludge, Title 40 of the Code of Federal Regulations, Part 503.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
McBride, M., Richards, B. & Steenhuis, T. Bioavailability and crop uptake of trace elements in soil columns amended with sewage sludge products. Plant and Soil 262, 71–84 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:PLSO.0000037031.21561.34
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:PLSO.0000037031.21561.34