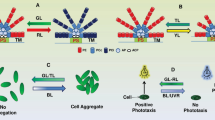
Abstract
The molecular mechanism of cAMP-mediated signal transduction from light reception to the physiological response via regulation of gene expression in cyanobacteria is described based on our recent works. Cyanobacteria are known as the organisms that acquired oxygen-evolving, higher plant type photosynthesis. We have found that the cellular cAMP level in the filamentous cyanobacteria Anabaena was oppositely regulated by red and far-red light, i.e., decreasing and increasing, respectively, suggesting that a phytochrome-like red/far-red photoreversible pigment regulates the activity of a certain adenylate cyclase. On the other hand, in the unicellular cyanobacterium Synechocystis cellular cAMP content was increased by blue light irradiation, which led to stimulation of cell motility. The cAMP signaling pathway is known to play an important role in the regulation of various biological activities by altering enzyme activities or controlling gene expression levels in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes. We have isolated genes for adenylate cyclases and cAMP receptor proteins and characterized their molecular properties. Disruption of these genes resulted in the loss of cell motility. It is concluded that the light signal was transmitted by cAMP signal cascade in cyanobacteria.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Watanabe, in CRC Handbook of Organic Photochemistry and Photobiology, ed. P. S. Horspool and P. S. Song, CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL, 1995.
C. Fankhauser, J. Chory, Light control of plant development, Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol., 1997, 13, 203–229.
J. M. Christie, W. R. Briggs, Blue light sensing in higher plants, J. Biol. Chem., 2001, 276, 11457–11460.
C. Lin, Blue light receptors and signal transduction, Plant Cell, 2002, 14Suppl, S207–225.
C. W. Mullineaux, How do cyanobacteria sense and respond to light?, Mol. Microbiol., 2001, 41, 965–971.
J. Hughes, T. Lamparter, F. Mittmann, E. Hartmann, W. Gärtner, A. Wilde, T. Borner, A prokaryotic phytochrome, Nature, 1997, 386, 663.
K. C. Yeh, S. H. Wu, J. T. Murphy, J. C. Lagarias, A cyanobacterial phytochrome two-component light sensory system, Science, 1997, 277, 1505–8.
D. M. Kehoe, A. R. Grossman, Similarity of a chromatic adaptation sensor to phytochrome and ethylene receptors, Science, 1996, 273, 1409–1412.
M. Ohmori, K. Ohmori, K. Hasunuma, Rapid change in cyclic 3′,5′-AMP concentration triggered by a light-off or light-on signal in cyanobacteria, Arch. Microbiol., 1988, 150, 203–204.
P. Cohen, Protein phosphorylation and the control of glycogen metabolism in skeletal muscle, Philos. Trans. R. Soc. London, Ser. B, 1983, 302, 13–25.
M. R. Montminy, L. M. Bilezikjian, Binding of a nuclear protein to the cyclic-AMP response element of the somatostatin gene, Nature, 1987, 328, 175–178.
S. A. Siegelbaum, J. S. Camardo, E. R. Kandel, Serotonin and cyclic AMP close single K+ channels in Aplysia sensory neurones, Nature, 1982, 299, 413–417.
J. L. Botsford, J. G. Harman, Cyclic AMP in prokaryotes, Microbiol. Rev., 1992, 56, 100–22.
M. J. Cann, Signalling through cyclic nucleotide monophospahtes in cyanobacteria, New Phytol., 2004, 159, 289–293.
R. Taussig, A. G. Gilman, Mammalian membrane-bound adenylyl cyclases, J. Biol. Chem., 1995, 270, 1–4.
J. Kawabe, G. Iwami, T. Ebina, S. Ohno, T. Katada, Y. Ueda, C. J. Homcy, Y. Ishikawa, Differential activation of adenylyl cyclase by protein kinase C isoenzymes, J. Biol. Chem., 1994, 269, 16554–16558.
G. Iwami, J. Kawabe, T. Ebina, P. J. Cannon, C. J. Homcy, Y. Ishikawa, Regulation of adenylyl cyclase by protein kinase A, J. Biol. Chem., 1995, 270, 12481–12484.
D. Broek, N. Samiy, O. Fasano, A. Fujiyama, F. Tamanoi, J. Northup, M. Wigler, Differential activation of yeast adenylate cyclase by wild-type and mutant RAS proteins, Cell, 1985, 41, 763–769.
T. Toda, I. Uno, T. Ishikawa, S. Powers, T. Kataoka, D. Broek, S. Cameron, J. Broach, K. Matsumoto, M. Wigler, In yeast, RAS proteins are controlling elements of adenylate cyclase, Cell, 1985, 40, 27–36.
P. J. Bottomley, W. D. Stewart, ATP pools and transients in the blue-green alga Anabaena cylindrica, Arch. Microbiol., 1976, 108, 249–258.
G. Ruyters, N. Grotjohann, W. Kowallik, Phytochrome in Dunaliella, Chlorella and other green algae, Biochem. Physiol. Pflanzen, 1991, 187, 97–103.
A. L. Mancinelli, in Photomorphogenesis in Plants, ed. R. E. Kendrick and G. H. M. Kronenberg, Kluwer, Dordrecht, 1994, pp. 211–269.
K. Terauchi, M. Ohmori, Blue light stimulates cyanobacterial motility via a cAMP signal transduction system, Mol. Microbiol., 2004, 51, 567–577.
M. Ohmori, K. Terauchi, S. Okamoto, M. Watanabe, Regulation of cAMP-mediated photosignaling by a phytochrome in the cyanobacterium Anabaena cylindrica, Photochem. Photobiol., 2002, 75, 675–679.
A. R. Cashmore, J. A. Jarillo, Y. J. Wu, D. Liu, Cryptochromes: blue light receptors for plants and animals, Science, 1999, 284, 760–765.
W. R. Briggs, C. F. Beck, A. R. Cashmore, J. M. Christie, J. Hughes, J. A. Jarillo, T. Kagawa, H. Kanegae, E. Liscum, A. Nagatani, K. Okada, M. Salomon, W. Rüdiger, T. Sakai, M. Takano, M. Wada, J. C. Watson, The phototropin family of photoreceptors, Plant Cell, 2001, 13, 993-937.
M. Salomon, J. M. Christie, E. Knieb, U. Lempert, W. R. Briggs, Photochemical and mutational analysis of the FMN-binding domains of the plant blue light receptor, phototropin, Biochemistry, 2000, 39, 9401–9410.
W. Schmidt, J. Hart, P. Filner, K. L. Poff, Specific inhibition of phototropism in corn seedlings, Plant Physiol., 1977, 60, 736–738.
R. D. Vierstra, K. L. Poff, Mechanism of specific inhibition of phototropism by phenylacetic acid in corn seedling, Plant Physiol., 1981, 67, 1011–1015.
M. Iseki, S. Matsunaga, A. Murakami, K. Ohno, K. Shiga, K. Yoshida, M. Sugai, T. Takahashi, T. Hori, M. Watanabe, A blue-light-activated adenylyl cyclase mediates photoavoidance in Euglena gracilis, Nature, 2002, 415, 1047–1051.
S. Braatsch, M. Gomelsky, S. Kuphal, G. Klug, A single flavoprotein, AppA, integrates both redox and light signals in Rhodobacter sphaeroides, Mol. Microbiol., 2002, 45, 827–836.
S. Masuda, C. E. Bauer, AppA is a blue light photoreceptor that antirepresses photosynthesis gene expression in Rhodobacter sphaeroides, Cell, 2002, 110, 613–623.
T. Kaneko, S. Sato, H. Kotani, A. Tanaka, E. Asamizu, Y. Nakamura, N. Miyajima, M. Hirosawa, M. Sugiura, S. Sasamoto, T. Kimura, T. Hosouchi, A. Matsuno, A. Muraki, N. Nakazaki, K. Naruo, S. Okumura, S. Shimpo, C. Takeuchi, T. Wada, A. Watanabe, M. Yamada, M. Yasuda, S. Tabata, Sequence analysis of the genome of the unicellular cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. strain PCC6803. II. Sequence determination of the entire genome and assignment of potential protein-coding regions, DNA Res., 1996, 3, 109–136.
T. Kaneko, Y. Nakamura, C. P. Wolk, T. Kuritz, S. Sasamoto, A. Watanabe, M. Iriguchi, A. Ishikawa, K. Kawashima, T. Kimura, Y. Kishida, M. Kohara, M. Matsumoto, A. Matsuno, A. Muraki, N. Nakazaki, S. Shimpo, M. Sugimoto, M. Takazawa, M. Yamada, M. Yasuda, S. Tabata, Complete genomic sequence of the filamentous nitrogen-fixing cyanobacterium Anabaena sp. strain PCC 7120, DNA Res., 2001, 8, 205–213; 227–253.
L. Aravind, C. P. Ponting, The GAF domain: an evolutionary link between diverse phototransducing proteins, Trends Biochem. Sci., 1997, 22, 458–459.
R. D. Vierstra, S. J. Davis, Bacteriophytochromes: new tools for understanding phytochrome signal transduction, Semin. Cell Dev. Biol., 2000, 11, 511–521.
S. Yoshihara, F. Suzuki, H. Fujita, X. X. Geng, M. Ikeuchi, Novel putative photoreceptor and regulatory genes required for the positive phototactic movement of the unicellular motile cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803, Plant Cell Physiol., 2000, 41, 1299–1304.
O. Schmitz, M. Katayama, S. B. Williams, T. Kondo, S. S. Golden, CikA, a bacteriophytochrome that resets the cyanobacterial circadian clock, Science, 2000, 289, 765–768.
B. L. Taylor, I. B. Zhulin, PAS domains: internal sensors of oxygen, redox potential, and light, Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev., 1999, 63, 479–506.
S. Crosson, K. Moffat, Structure of a flavin-binding plant photoreceptor domain: insights into light-mediated signal transduction, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 2001, 98, 2995–3000.
A. Danchin, Phylogeny of adenylyl cyclases, Adv. Second Messenger Phosphoprotein Res., 1993, 27, 109–162.
M. Katayama, Y. Wada, M. Ohmori, Molecular cloning of the cyanobacterial adenylate cyclase gene from the filamentous cyanobacterium Anabaena cylindrica, J. Bacteriol., 1995, 177, 5197.
M. Katayama, M. Ohmori, Isolation and characterization of multiple adenylate cyclase genes from the cyanobacterium Anabaena sp. strain PCC 7120, J. Bacteriol., 1997, 179, 3588–3593.
K. Yashiro, T. Sakamoto, M. Ohmori, Molecular characterization of an adenylate cyclase gene of the cyanobacterium Spirulina platensis, Plant Mol. Biol., 1996, 31, 175–181.
K. Terauchi, M. Ohmori, An adenylate cyclase, Cya1, regulates cell motility in the cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803, Plant Cell Physiol., 1999, 40, 248–251.
M. Kasahara, K. Yashiro, T. Sakamoto, M. Ohmori, The Spirulina platensis adenylate cyclase gene, cyaC, encodes a novel signal transduction protein, Plant Cell Physiol, 1997, 38, 828–836.
M. Kasahara, T. Unno, K. Yashiro, M. Ohmori, CyaG, a novel cyanobacterial adenylyl cyclase and a possible ancestor of mammalian guanylyl cyclases, J. Biol. Chem., 2001, 276, 10564–10569.
O. Gascuel, A. Danchin, Protein export in prokaryotes and eukaryotes: indications of a difference in the mechanism of exportation, J. Mol. Evol., 1986, 24, 130–142.
G. S. Pitt, N. Milona, J. Borleis, K. C. Lin, R. R. Reed, P. N. Devreotes, Structurally distinct and stage-specific adenylyl cyclase genes play different roles in Dictyostelium development, Cell, 1992, 69, 305–315.
E. Pays, P. Tebabi, A. Pays, H. Coquelet, P. Revelard, D. Salmon, M. Steinert, The genes and transcripts of an antigen gene expression site from T. brucei, Cell, 1989, 57, 835–845.
M. A. Sanchez, D. Zeoli, E. M. Klamo, M. P. Kavanaugh, S. M. Landfear, A family of putative receptor-adenylate cyclases from Leishmania donovani, J. Biol. Chem., 1995, 270, 17551–17558.
T. Tada, H. Sekimoto, M. Ohmori, Biochemical characterization of an adenylate cyclase, CyaB1, in the cyanobacterium Anabaena sp. PCC7120, J. Plant Res., 2001, 114, 387–394.
L. M. McAllister-Lucas, T. L. Haik, J. L. Colbran, W. K. Sonnenburg, D. Seger, I. V. Turko, J. A. Beavo, S. H. Francis, J. D. Corbin, An essential aspartic acid at each of two allosteric cGMP-binding sites of a cGMP-specific phosphodiesterase, J. Biol. Chem., 1995, 270, 30671–30679.
M. Ohmori, K. Hasunuma, K. Furukawa, GTP-binding proteins in a cyanobacterium Anabaena cylindrica, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 1988, 151, 215–221.
T. Kanacher, A. Schultz, J. U. Linder, J. E. Schultz, A GAF-domain-regulated adenylyl cyclase from Anabaena is a self-activating cAMP switch, Embo J., 2002, 21, 3672–3680.
J. B. Stock, A. J. Ninfa, A. M. Stock, Protein phosphorylation and regulation of adaptive responses in bacteria, Microbiol. Rev., 1989, 53, 450–490.
M. Kasahara, M. Ohmori, Activation of a cyanobacterial adenylate cyclase, CyaC, by autophosphorylation and a subsequent phosphotransfer reaction, J. Biol. Chem., 1999, 274, 15167–15172.
J. M. Stone, M. A. Collinge, R. D. Smith, M. A. Horn, J. C. Walker, Interaction of a protein phosphatase with an Arabidopsis serine-threonine receptor kinase, Science, 1994, 266, 793–795.
Z. Zhouand, S. J. Elledge, DUN1 encodes a protein kinase that controls the DNA damage response in yeast, Cell, 1993, 75, 1119–1127.
Y. Chen, M. J. Cann, T. N. Litvin, V. Iourgenko, M. L. Sinclair, L. R. Levin, J. Buck, Soluble adenylyl cyclase as an evolutionarily conserved bicarbonate sensor, Science, 2000, 289, 625–628.
K. Ogata, H. Umeyama, An automatic homology modeling method consisting of database searches and simulated annealing, J. Mol. Graphics Modell., 2000, 18, 258–272.
C. Chang, S. F. Kwok, A. B. Bleecker, E. M. Meyerowitz, Arabidopsis ethylene-response gene ETR1: similarity of product to two-component regulators, Science, 1993, 262, 539–544.
I. T. Weberand, T. A. Steitz, Structure of a complex of catabolite gene activator protein and cyclic AMP refined at 2.5 A resolution, J. Mol. Biol., 1987, 198, 311–326.
S. C. Schultz, G. C. Shields, T. A. Steitz, Crystal structure of a CAP-DNA complex: the DNA is bent by 90 degrees, Science, 1991, 253, 1001–1007.
I. T. Weber, T. A. Steitz, J. Bubis, S. S. Taylor, Predicted structures of cAMP binding domains of type I and II regulatory subunits of cAMP-dependent protein kinase, Biochemistry, 1987, 26, 343–351.
S. S. Taylor, J. Bubis, J. Toner-Webb, L. D. Saraswat, E. A. First, J. A. Buechler, D. R. Knighton, J. Sowadski, cAMP-dependent protein kinase: prototype for a family of enzymes, FASEB J., 1988, 2, 2677–2685.
S. S. Taylor, J. A. Buechler, W. Yonemoto, cAMP-dependent protein kinase: framework for a diverse family of regulatory enzymes, Annu. Rev. Biochem., 1990, 59, 971–1005.
A. Kolb, S. Busby, H. Buc, S. Garges, S. Adhya, Transcriptional regulation by cAMP and its receptor protein, Annu. Rev. Biochem., 1993, 62, 749–795.
K. Moriand, H. Aiba, Evidence for negative control of cya transcription by cAMP and cAMP receptor protein in intact Escherichia coli cells, J. Biol. Chem., 1985, 260, 14838–14843.
A. Hanamura, H. Aiba, Molecular mechanism of negative autoregulation of Escherichia coli crp gene, Nucleic Acids Res., 1991, 19, 4413–4419.
P. Valentin-Hansen, L. Sogaard-Andersen, H. Pedersen, A flexible partnership: the CytR anti-activator and the cAMP-CRP activator protein, comrades in transcription control, Mol. Microbiol., 1996, 20, 461–466.
T. Kaneko, S. Sato, H. Kotani, A. Tanaka, E. Asamizu, Y. Nakamura, N. Miyajima, M. Hirosawa, M. Sugiura, S. Sasamoto, T. Kimura, T. Hosouchi, A. Matsuno, A. Muraki, N. Nakazaki, K. Naruo, S. Okumura, S. Shimpo, C. Takeuchi, T. Wada, A. Watanabe, M. Yamada, M. Yasuda, S. Tabata, Sequence analysis of the genome of the unicellular cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. strain PCC6803. II. Sequence determination of the entire genome and assignment of potential protein-coding regions (supplement), DNA Res., 1996, 3, 185–209.
CyanoBase, http://www.kazusa.or.jp/cyano/cyano.html.
M. C. Vaney, G. L. Gilliland, J. G. Harman, A. Peterkofsky, I. T. Weber, Crystal structure of a cAMP-independent form of catabolite gene activator protein with adenosine substituted in one of two cAMP-binding sites, Biochemistry, 1989, 28, 4568–4574.
H. Yoshimura, S. Yanagisawa, M. Kanehisa, M. Ohmori, Screening for the target gene of cyanobacterial cAMP receptor protein SYCRP1, Mol. Microbiol., 2002, 43, 843–853. http://www.genome.ad.jp/kegg/expression.
A. Filloux, G. Michel, M. Bally, GSP-dependent protein secretion in gram-negative bacteria: the Xcp system of Pseudomonas aeruginosa, FEMS Microbiol. Rev., 1998, 22, 177–198.
D. Walland, D. Kaiser, Type IV pili and cell motility, Mol. Microbiol., 1999, 32, 1–10.
S. Yoshihara, X. Geng, S. Okamoto, K. Yura, T. Murata, M. Go, M. Ohmori, M. Ikeuchi, Mutational analysis of genes involved in pilus structure, motility and transformation competency in the unicellular motile cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803, Plant Cell Physiol., 2001, 42, 63–73.
H. Yoshimura, S. Yoshihara, S. Okamoto, M. Ikeuchi, M. Ohmori, A cAMP receptor protein, SYCRP1, is responsible for the cell motility of Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803, Plant Cell Physiol., 2002, 43, 460–463.
B. Diehn, M. E. Feinleib, W. Haupt, E. Hildebrand, F. Lenci, W. Nultch, Terminology of behavioral response of motile microorganisms, Photochem. Photobiol., 1979, 26, 559–560.
D. P. Häder, Photosensory behavior in procaryotes, Microbiol. Rev., 1987, 51, 1–21.
K. Ohmori, M. Hirose, M. Ohmori, function of cAMP as a mat-forming factor in the cyanobacterium Spirulina platensis, Plant and Cell Physiol., 1992, 33, 21–25.
E. Hoiczyk, Gliding motility in cyanobacterial: observations and possible explanations, Arch. Microbiol., 2000, 174, 11–17.
B. Brahamsha, An abundant cell-surface polypeptide is required for swimming by the nonflagellated marine cyanobacterium Synechococcus, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 1996, 93, 6504–6509.
R. Y. Stanier, R. Kunisawa, M. Mendel, B. G. Cohen, Purification and properties of unicellular blue-green algae (order Chroococcales), Bacteriological. Rev., 1971, 35, 171–205.
D. Bhaya, N. Watanabe, T. Ogawa, A. R. Grossman, The role of an alternative sigma factor in motility and pilus formation in the cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. strain PCC 6803, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 1999, 96, 3188–3193.
D. Bhaya, N. R. Bianco, D. Bryant, A. Grossman, Type IV pilus biogenesis and motility in the cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC6803, Mol. Microbiol., 2000, 37, 941–951.
S. Okamoto, M. Ohmori, The cyanobacterial PilT protein responsible for cell motility and transformation hydrolyzes ATP, Plant Cell Physiol., 2002, 43, 1127–1136.
K. Ohmori, M. Hirose, M. Ohmori, An increase in the intracellular concentration of cAMP triggers formation of an algal mat by the cyanobacterium Spirulina platensis, Plant Cell Physiol., 1993, 34, 169–171.
J. S. Choi, Y. H. Chung, Y. J. Moon, C. Kim, M. Watanabe, P. S. Song, C. O. Joe, L. Bogorad, Y. M. Park, Photomovement of the gliding cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803, Photochem. Photobiol., 1999, 70, 95–102.
A. Wilde, B. Fiedler, T. Borner, The cyanobacterial phytochrome Cph2 inhibits phototaxis towards blue light, Mol. Microbiol., 2002, 44, 981–988.
W. O. Ng, A. R. Grossman, D. Bhaya, Multiple light inputs control phototaxis in Synechocystis sp. strain PCC6803, J. Bacteriol., 2003, 185, 1599–1607.
R. W. Castenholz, in The Biology of Cyanobacteria ed. N. G. Carr and B. A. Whitton, University of California Press, Los Angeles, 1982, pp. 413–439.
T. Matsunaga, K.-I. Iwagamai, Y. Takada, N. Fukunaga, Na+-coupled energetics of a psychrotrophic bacterium isolated from lake Vanda, Antarctica, Microb. Environ., 1999, 14, 139–149.
T. Sakamoto, N. Murata, M. Ohmori, The concentration of cAMP and adenylate-cyclase activity in cyanobacteria, Plant Cell Physiol., 1991, 32, 581–584.
A. Abeliovich, J. Gan, Site of Ca2+ action in triggering motility in the cyanobacterium Spirulina subsalsa, Cell Motil., 1982, 2, 393–403.
T. Ogawa, G. Terui, Studies on the growth of Spirulina platensis, J. Ferment. Technol., 1970, 48, 361–367.
E. E. Hood, S. Armour, J. D. Ownby, A. K. Handa, R. A. Bressan, Effect of nitrogen starvation on the level of adenosine 3′,5′-monophosphate in Anabaena variabilis, Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1979, 588, 193–200.
M. Katayama, M. Ohmori, Expression of adenylate cyclase gene of Anabeana cylindrica in the cyanobacterium Anabaena sp. strain PCC 7120, Plant Cell Physiol., 1998, 39, 786–789.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ohmori, M., Okamoto, S. Photoresponsive cAMP signal transduction in cyanobacteria. Photochem Photobiol Sci 3, 503–511 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1039/b401623h
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/b401623h