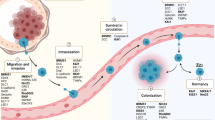
Abstract
Metastasis of primary tumors progresses stepwise — from change in biochemistry, morphology, and migratory patterns of tumor cells to the emergence of receptors on their surface that facilitate directional migration to target organs followed by the formation of a specific microenvironment in a target organ that helps attachment and survival of metastatic cells. A set of specific genes and signaling pathways mediate this process under control of microRNA. The molecular mechanisms underlying biological processes associated with tumor metastasis are reviewed in this publication using ovarian cancer, which exhibits high metastatic potential, as an example. Information and data on the genes and regulatory microRNAs involved in the formation of cancer stem cells, epithelial–mesenchymal transition, reducing focal adhesion, degradation of extracellular matrix, increasing migration activity of cancer cells, formation of spheroids, apoptosis, autophagy, angiogenesis, formation of metastases, and development of ascites are presented. Clusters of microRNAs (miR-145, miR-31, miR-506, miR-101) most essential for metastasis of ovarian cancer including the families of microRNAs (miR-200, miR-214, miR-25) with dual role, which is different in different histological types of ovarian cancer, are discussed in detail in a section of the review.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AKT:
-
AKT serine/threonine kinase
- AXL:
-
AXL receptor tyrosine kinase
- BDNF:
-
brain-derived neurotrophic factor
- BIM:
-
Bcl-2 interacting mediator of cell death
- CSC:
-
cancer stem cells
- CXCL12:
-
C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 12
- ECM:
-
extracellular matrix
- E2F2:
-
E2F transcription factor 2
- EGFR:
-
epidermal growth factor receptor
- EMT:
-
epithelial–mesenchymal transition
- ERK/MAPK:
-
mitogen-activated protein kinase
- FGFR:
-
fibroblast growth factor receptor
- HIF-1α:
-
hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha subunit
- HMGA2:
-
high-mobility group (non-histone chromosomal) protein isoform I-C
- MET:
-
mesenchymal–epithelial transition
- MMP2:
-
matrix metalloproteinase 2 (gelatinase A, type IV collagenase)
- MMP9:
-
matrix metalloproteinase 9 (gelatinase B)
- mTOR:
-
mammalian target of rapamycin
- NF-κB:
-
nuclear factor kappa B
- Notch:
-
Notch (Drosophila) homolog 1 (translocation-associated)
- PDGF:
-
platelet-derived growth factor
- PI3K:
-
phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate 3-kinase
- PTEN:
-
phosphatase and tensin homolog (phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate 3-phosphatase and dual-specificity protein phosphatase)
- P70S6K:
-
ribosomal protein S6 kinase
- RAC1:
-
Ras-related C3 botulinum toxin substrate 1
- SLUG/SNEIL2:
-
Slug (chicken homolog), zinc finger protein
- SMARCA4/BRG1:
-
SWI/SNF-related, matrix-associated, actin-dependent regulator of chromatin, subfamily A, member 4
- SNAIL:
-
Snail family transcriptional repressor
- SOX4/9:
-
SRY (sex determining region Y)-box 4/9 protein
- S1P:
-
sphingosine-1-phosphate
- SPHK1:
-
sphingosine kinase 1
- S1PR1/2:
-
sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 1/2
- TGF-β:
-
transforming growth factor beta
- TP53:
-
tumor protein P53
- TWIST:
-
Twist family BHLH transcription factor
- ULK1:
-
Unc-51 like autophagy-activating kinase 1
- uPA:
-
urokinase type plasminogen activator
- VEGF:
-
vascular endothelial growth factor
- VEGFR:
-
vascular endothelial growth factor receptor
- Wnt:
-
wingless-type MMTV integration site family
- ZBTB10:
-
zinc finger and BTB domain-containing protein 10
- ZEB:
-
zinc finger E-box binding homeobox 1/2
References
Chikina, A. S., and Aleksandrova, A. Yu. (2014) The cellular mechanisms and regulation of metastasis formation, Mol. Biol., 48, 165–180.
Chan, S. H., and Wang, L. H. (2015) Regulation of cancer metastasis by microRNAs, J. Biomed. Sci., 22, 9.
Gerstein, M. B., Kundaje, A., Hariharan, M., Landt, S. G., Yan, K. K., Cheng, C., Mu, X. J., Khurana, E., Rozowsky, J., Alexander, R., Min, R., Alves, P., Abyzov, A., Addleman, N., Bhardwaj, N., Boyle, A. P., Cayting, P., Charos, A., Chen, D. Z., Cheng, Y., Clarke, D., Eastman, C., Euskirche, G., Frietze, S., Fu, Y., Gertz, J., Grubert, F., Harmanci, A., Jain, P., Kasowski, M., Lacroute, P., Leng, J., Lian, J., Monahan, H., O’Geen, H., Ouyang, Z., Partridge, E. C., Patacsil, D., Pauli, F., Raha, D., Ramirez, L., Reddy, T. E., Reed, B., Shi, M., Slifer, T., Wang, J., Wu, L., Yang, X., Yip, K. Y., Zilberman-Schapira, G., Batzoglou, S., Sidow, A., Farnham, P. J., Myers, R. M., Weissman, S. M., and Snyder, M. (2012) Architecture of the human regulatory network derived from ENCODE data, Nature, 489, 91–100.
Loginov, V. I., Rykov, S. V., Fridman, M. V., and Braga, E. A. (2015) Methylation of miRNA genes and oncogenesis, Biochemistry (Moscow), 80, 145–162.
Lopez-Serra, P., and Esteller, M. (2012) DNA methylationassociated silencing of tumor suppressor microRNAs in cancer, Oncogene, 31, 1609–1622.
Wang, Y., Kim, S., and Kim, I. M. (2014) Regulation of metastasis by microRNAs in ovarian cancer, Front. Oncol., 4, 143.
Chen, X., Zhang, J., Zhang, Z., Li, H., Cheng, W., and Liu, J. (2013) Cancer stem cells, epithelialmesenchymal transition, and drug resistance in highgrade ovarian serous carcinoma, Hum. Pathol., 44, 2373–2384.
Mittempergher, L. (2016) Genomic characterization of highgrade serous ovarian cancer: dissecting its molecular heterogeneity as a road towards effective therapeutic strategies, Curr. Oncol. Rep., 18, 44.
Chakraborty, C., Chin, K. Y., and Das, S. (2016) miRNA-regulated cancer stem cells: understanding the property and the role of miRNA in carcinogenesis, Tumor Biol., 37, 13039–13048.
Xu, C. X., Xu, M., Tan, L., Yang, H., Permuth-Wey, J., Kruk, P. A., Wenham, R. M., Nicosia, S. V., Lancaster, J. M., Sellers, T. A., and Cheng, J. Q. (2012) MicroRNA miR-214 regulates ovarian cancer cell stemness by targeting p53/Nanog, J. Biol. Chem., 287, 34970–34978.
Zaravinos, A. (2015) The regulatory role of microRNAs in EMT and cancer, J. Oncol., 865816.
Wellner, U., Schubert, J., Burk, U. C., Schmalhofer, O., Zhu, F., Sonntag, A., Waldvogel, B., Vannier, C., Darling, D., zur Hausen, A., Brunton, V. G., Morton, J., Sansom, O., Schuler, J., Stemmler, M. P., Herzberger, C., Hopt, U., Keck, T., Brabletz, S., and Brabletz, T. (2009) The EMT-activator ZEB1 promotes tumorigenicity by repressing stemnessinhibiting microRNAs, Nat. Cell. Biol., 11, 1487–1495.
Yeh, Y. M., Chuang, C. M., Chao, K. C., and Wang, L. H. (2013) MicroRNA-138 suppresses ovarian cancer cell invasion and metastasis by targeting SOX4 and HIF-1α, Int. J. Cancer, 133, 867–878.
Sun, Y., Guo, F., Bagnoli, M., Xue, F. X., Sun, B. C., Shmulevich, I., Mezzanzanica, D., Chen, K. X., Sood, A. K., Yang, D., and Zhang, W. (2015) Key nodes of a microRNA network associated with the integrated mesenchymal subtype of highgrade serous ovarian cancer, Chin. J. Cancer, 34, 28–40.
Dong, R., Liu, X., Zhang, Q., Jiang, Z., Li, Y., Wei, Y., Li, Y., Yang, Q., Liu, J., Wei, J. J., Shao, C., Liu, Z., and Kong, B. (2014) miR-145 inhibits tumor growth and metastasis by targeting metadherin in highgrade serous ovarian carcinoma, Oncotarget, 5, 10816–10829.
Mitra, A. K., Chiang, C. Y., Tiwari, P., Tomar, S., Watters, K. M., Peter, M. E., and Lengyel, E. (2015) Microenvironmentinduced downregulation of miR-193b drives ovarian cancer metastasis, Oncogene, 34, 5923–5932.
Li, H., Xu, Y., Qiu, W., Zhao, D., and Zhang, Y. (2015) Tissue miR-193b as a novel biomarker for patients with ovarian cancer, Med. Sci. Monit., 21, 3929–3934.
Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network (2011) Integrated genomic analyses of ovarian carcinoma, Nature, 474, 609–615.
Yang, D., Sun, Y., Hu, L., Zheng, H., Ji, P., Pecot, C. V., Zhao, Y., Reynolds, S., Cheng, H., Rupaimoole, R., Cogdell, D., Nykter, M., Broaddus, R., Rodriguez-Aguayo, C., Lopez-Berestein, G., Liu, J., Shmulevich, I., Sood, A. K., Chen, K., and Zhang, W. (2013) Integrated analyses identify a master microRNA regulatory network for the mesenchymal subtype in serous ovarian cancer, Cancer Cell, 23, 186–199.
Imam, J. S., Plyler, J. R., Bansal, H., Prajapati, S., Bansal, S., Rebeles, J., Chen, H. I., Chang, Y. F., Panneerdoss, S., Zoghi, B., Buddavarapu, K. C., Broaddus, R., Hornsby, P., Tomlinson, G., Dome, J., Vadlamudi, R. K., Pertsemlidis, A., Chen, Y., and Rao, M. K. (2012) Genomic loss of tumor suppressor miRNA-204 promotes cancer cell migration and invasion by activating AKT/mTOR/Rac1 signaling and actin reorganization, PLoS One, 7, e52397.
Wei, L. Q., Liang, H. T., Qin, D. C., Jin, H. F., Zhao, Y., and She, M. C. (2014) MiR-212 exerts suppressive effect on SKOV3 ovarian cancer cells through targeting HBEGF, Tumor Biol., 35, 12427–12434.
Li, J., Li, D., and Zhang, W. (2016) Tumor suppressor role of miR-217 in human epithelial ovarian cancer by targeting IGF1R, Oncol. Rep., 35, 1671–1679.
Zhang, H., Wang, Q., Zhao, Q., and Di, W. (2013) MiR-124 inhibits the migration and invasion of ovarian cancer cells by targeting SphK1, J. Ovarian Res., 6, 84.
Wen, Z., Zhao, S., Liu, S., Liu, Y., Li, X., and Li, S. (2015) MicroRNA-148a inhibits migration and invasion of ovarian cancer cells via targeting sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 1, Mol. Med. Rep., 12, 3775–3780.
Li, P., Sun, Y., and Liu, Q. (2016) MicroRNA-340 induces apoptosis and inhibits metastasis of ovarian cancer cells by inactivation of NF-x03BA;B1, Cell. Physiol. Biochem., 38, 1915–1927.
Chen, S., Chen, X., Xiu, Y. L., Sun, K. X., and Zhao, Y. (2015) Inhibition of ovarian epithelial carcinoma tumorigenesis and progression by microRNA 106b mediated through the RhoC pathway, PLoS One, 10, e0125714.
Lin, K. T., Yeh, Y. M., Chuang, C. M., Yang, S. Y., Chang, J. W., Sun, S. P., Wang, Y. S., Chao, K. C., and Wang, L. H. (2015) Glucocorticoids mediate induction of microRNA-708 to suppress ovarian cancer metastasis through targeting Rap1B, Nat. Commun., 6, 5917.
Cowden Dahl, K. D., Dahl, R., Kruichak, J. N., and Hudson, L. G. (2009) The epidermal growth factor receptor responsive miR-125a represses mesenchymal morphology in ovarian cancer cells, Neoplasia, 11, 1208–1215.
Yang, Y., Jiang, Y., Wan, Y., Zhang, L., Qiu, J., Zhou, S., and Cheng, W. (2016) UCA1 functions as a competing endogenous RNA to suppress epithelial ovarian cancer metastasis, Tumor Biol., 37, 10633–10641.
Vang, S., Wu, H. T., Fischer, A., Miller, D. H., MacLaughlan, S., Douglass, E., Comisar, L., Steinhoff, M., Collins, C., Smith, P. J., Brard, L., and Brodsky, A. S. (2013) Identification of ovarian cancer metastatic miRNAs, PLoS One, 8, e58226.
Pan, Y., Robertson, G., Pedersen, L., Lim, E., Hernandez-Herrera, A., Rowat, A. C., Patil, S. L., Chan, C. K., Wen, Y., Zhang, X., Basu-Roy, U., Mansukhani, A., Chu, A., Sipahimalani, P., Bowlby, R., Brooks, D., Thiessen, N., Coarfa, C., Ma, Y., Moore, R. A., Schein, J. E., Mungall, A. J., Liu, J., Pecot, C. V., Sood, A. K., Jones, S. J., Marra, M. A., and Gunaratne, P. H. (2016) miR-509-3p is clinically significant and strongly attenuates cellular migration and multicellular spheroids in ovarian cancer, Oncotarget, 7, 25930–25948.
Lin, J., Zhang, L., Huang, H., Huang, Y., Huang, L., Wang, J., Huang, S., He, L., Zhou, Y., Jia, W., Yun, J., Luo, R., and Zheng, M. (2015) MiR-26b/KPNA2 axis inhibits epithelial ovarian carcinoma proliferation and metastasis through downregulating OCT4, Oncotarget, 6, 23793–23806.
Lam, S. S., Ip, C. K., Mak, A. S., and Wong, A. S. (2016) A novel p70 S6 kinase–microRNA biogenesis axis mediates multicellular spheroid formation in ovarian cancer progression, Oncotarget, 7, 38064–38077.
Titone, R., Morani, F., Follo, C., Vidoni, C., Mezzanzanica, D., and Isidoro, C. (2014) Epigenetic control of autophagy by microRNAs in ovarian cancer, Biomed. Res. Int., 2014, 343542.
Fang, Y., Xu, C., and Fu, Y. (2015) MicroRNA-17-5p induces drug resistance and invasion of ovarian carcinoma cells by targeting PTEN signaling, J. Biol. Res. (Thessalon), 22, 12.
Lou, Y., Yang, X., Wang, F., Cui, Z., and Huang, Y. (2010) MicroRNA-21 promotes the cell proliferation, invasion and migration abilities in ovarian epithelial carcinomas through inhibiting the expression of PTEN protein, Int. J. Mol. Med., 26, 819–827.
Penna, E., Orso, F., and Taverna, D. (2015) miR-214 as a key hub that controls cancer networks: small player, multiple functions, J. Invest. Dermatol., 135, 960–969.
Shen, Y., Li, D. D., Wang, L. L., Deng, R., and Zhu, X. F. (2008) Decreased expression of autophagyrelated proteins in malignant epithelial ovarian cancer, Autophagy, 4, 1067–1068.
Bunkholt, E. M., Dong, H. P., Odegaard, E., Holth, A., Elloul, S., Reich, R., Trope, C. G., and Davidson, B. (2010) Mammalian target of rapamycin is a biomarker of poor survival in metastatic serous ovarian carcinoma, Hum. Pathol., 41, 794–804.
Vecchione, A., Belletti, B., Lovat, F., Volinia, S., Chiappetta, G., Giglio, S., Sonego, M., Cirombella, R., Onesti, E. C., Pellegrini, P., Califano, D., Pignata, S., Losito, S., Canzonieri, V., Sorio, R., Alder, H., Wernicke, D., Stoppacciaro, A., Baldassarre, G., and Croce, C. M. (2013) A microRNA signature defines chemoresistance in ovarian cancer through modulation of angiogenesis, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 110, 9845–9850.
Luo, Z., Wang, Q., Lau, W. B., Lau, B., Xu, L., Zhao, L., Yang, H., Feng, M., Xuan, Y., Yang, Y., Lei, L., Wang, C., Yi, T., Zhao, X., Wei, Y., and Zhou, S. (2016) Tumor microenvironment: the culprit for ovarian cancer metastasis? Cancer Lett., 377, 174–182.
Joshi, H. P., Subramanian, I. V., Schnettler, E. K., Ghosh, G., Rupaimoole, R., Evans, C., Saluja, M., Jing, Y., Cristina, I., Roy, S., Zeng, Y., Shah, V. H., Sood, A. K., and Ramakrishnan, S. (2014) Dynamin 2 along with microRNA-199a reciprocally regulate hypoxiainducible factors and ovarian cancer metastasis, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 111, 5331–5336.
Lv, Y., Lei, Y., Hu, Y., Ding, W., Zhang, C., and Fang, C. (2015) miR-448 negatively regulates ovarian cancer cell growth and metastasis by targeting CXCL12, Clin. Transl. Oncol., 17, 903–909.
Schmid, G., Notaro, S., Reimer, D., Abdel-Azim, S., Duggan-Peer, M., Holly, J., Fiegl, H., Rössler, J., Wiedemair, A., Concin, N., Altevogt, P., Marth, C., and Zeimet, A. G. (2016) Expression and promotor hypermethylation of miR-34a in the various histological subtypes of ovarian cancer, BMC Cancer, 16, 102.
Li, R., Shi, X., Ling, F., Wang, C., Liu, J., Wang, W., and Li, M. (2015) MiR-34a suppresses ovarian cancer proliferation and motility by targeting AXL, Tumor Biol., 36, 7277–7283.
Dong, P., Xiong, Y., Watari, H., Hanley, S. J., Konno, Y., Ihira, K., Yamada, T., Kudo, M., Yue, J., and Sakuragi, N. (2016) MiR-137 and miR-34a directly target Snail and inhibit EMT, invasion and sphereforming ability of ovarian cancer cells, J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res., 35, 132.
Kim, T. H., Song, J. Y., Park, H., Jeong, J. Y., Kwon, A. Y., Heo, J. H., Kang, H., Kim, G., and An, H. J. (2015) miR-145, targeting highmobility group A2, is a powerful predictor of patient outcome in ovarian carcinoma, Cancer Lett., 28, 937–945.
Chen, X., Dong, C., Law, P., Chan, M. T., Su, Z., Wang, S., Wu, W. K., and Xu, H. (2015) MicroRNA-145 targets TRIM2 and exerts tumorsuppressing functions in epithelial ovarian cancer, Gynecol. Oncol., 139, 513–519.
Zhang, W., Wang, Q., Yu, M., Wu, N., and Wang, H. (2014) MicroRNA-145 function as a cell growth repressor by directly targeting c-Myc in human ovarian cancer, Technol. Cancer Res. Threat., 13, 161–168.
Xu, Q., Liu, L. Z., Qian, X., Chen, Q., Jiang, Y., Li, D., Lai, L., and Jiang, B. H. (2012) MiR-145 directly targets p70S6K1 in cancer cells to inhibit tumor growth and angiogenesis, Nucleic Acids Res., 40, 761–774.
Creighton, C. J., Fountain, M. D., Yu, Z., Nagaraja, A. K., Zhu, H., Khan, M., Olokpa, E., Zariff, A., Gunaratne, P. H., Matzuk, M. M., and Anderson, M. L. (2010) Molecular profiling uncovers a p53-associated role for microRNA-31 in inhibiting the proliferation of serous ovarian carcinomas and other cancers, Cancer Res., 70, 1906–1915.
Mitamura, T., Watari, H., Wang, L., Kanno, H., Hassan, M. K., Miyazaki, M., Katoh, Y., Kimura, T., Tanino, M., Nishihara, H., Tanaka, S., and Sakuragi, N. (2013) Downregulation of miRNA-31 induces taxane resistance in ovarian cancer cells through increase of receptor tyrosine kinase MET, Oncogenesis, 25, e40.
Guo, F., Cogdell, D., Hu, L., Yang, D., Sood, A. K., Xue, F., and Zhang, W. (2014) MiR-101 suppresses the epithelialtomesenchymal transition by targeting ZEB1 and ZEB2 in ovarian carcinoma, Oncol. Rep., 31, 2021–2028.
Kinose, Y., Sawada, K., Nakamura, K., and Kimura, T. (2014) The role of microRNAs in ovarian cancer, Biomed. Res. Int., 249393.
Sulaiman, S. A., Ab Mutalib, N. S., and Jamal, R. (2016) miR-200c regulation of metastases in ovarian cancer: potential role in epithelial and mesenchymal transition, Front. Pharmacol., 7, 271.
Tang, M. K., and Wong, A. S. (2015) Exosomes: emerging biomarkers and targets for ovarian cancer, Cancer Lett., 367, 26–33.
Gong, C., Yang, Z., Wu, F., Han, L., Liu, Y., and Gong, W. (2016) miR-17 inhibits ovarian cancer cell peritoneal metastasis by targeting ITGA5 and ITGB1, Oncol. Rep., 36, 2177–2183.
Xie, J., Liu, M., Li, Y., Nie, Y., Mi, Q., and Zhao, S. (2014) Ovarian tumorassociated microRNA-20a decreases natural killer cell cytotoxicity by downregulating MICA/B expression, Cell Mol. Immunol., 11, 495–502.
Yan, J., Jiang, J. Y., Meng, X. N., Xiu, Y. L., and Zong, Z. H. (2016) MiR-23b targets cyclin G1 and suppresses ovarian cancer tumorigenesis and progression, J. Clin. Cancer Res., 35, 31.
Ibrahim, F. F., Jamal, R., Syafruddin, S. E., Ab Mutalib, N. S., Saidin, S., MdZin, R. R., Hossain Mollah, M. M., and Mokhtar, N. M. (2015) MicroRNA-200c and microRNA-31 regulate proliferation, colony formation, migration and invasion in serous ovarian cancer, J. Ovarian Res., 8, 56.
Chen, L., Zhang, F., Sheng, X. G., Zhang, S. Q., Chen, Y. T., and Liu, B. W. (2016) MicroRNA-106a regulates phosphatase and tensin homologue expression and promotes the proliferation and invasion of ovarian cancer cells, Oncol. Rep., 36, 2135–2141.
Chen, S., Chen, X., Xiu, Y. L., Sun, K. X., and Zhao, Y. (2015) Inhibition of ovarian epithelial carcinoma tumorigenesis and progression by microRNA 106b mediated through the RhoC pathway, PLoS One, 10, e0125714.
Chai, Y., Liu, J., Zhang, Z., and Liu, L. (2016) HuR-regulated lncRNA NEAT1 stability in tumorigenesis and progression of ovarian cancer, Cancer Med., 5, 1588–1598.
Wang, L., He, J., Xu, H., Xu, L., and Li, N. (2016) MiR-143 targets CTGF and exerts tumorsuppressing functions in epithelial ovarian cancer, Am. J. Transl. Res., 8, 2716–2726.
Jin, M., Yang, Z., Ye, W., Xu, H., and Hua, X. (2014) MicroRNA-150 predicts a favorable prognosis in patients with epithelial ovarian cancer, and inhibits cell invasion and metastasis by suppressing transcriptional repressor ZEB1, PLoS One, 9, e103965.
Liang, T., Li, L., Cheng, Y., Ren, C., and Zhang, G. (2016) MicroRNA-194 promotes the growth, migration, and invasion of ovarian carcinoma cells by targeting protein tyrosine phosphatase nonreceptor type 12, Onco Targets Ther., 9, 4307–4315.
Niu, K., Shen, W., Zhang, Y., Zhao, Y., and Lu, Y. (2015) MiR-205 promotes motility of ovarian cancer cells via targeting ZEB1, Gene, 574, 330–336.
Zhang, Y., Shi, B., Chen, J., Hu, L., and Zhao, C. (2016) MiR-338-3p targets pyruvate kinase M2 and affects cell proliferation and metabolism of ovarian cancer, Am. J. Transl. Res., 8, 3266–3273.
Zhang, Z., Cheng, J., Wu, Y., Qiu, J., Sun, Y., and Tong, X. (2016) LncRNA HOTAIR controls the expression of Rab22a by sponging miR-373 in ovarian cancer, Mol. Med. Rep., 14, 2465–2472.
Sun, Y., Hu, L., Zheng, H., Bagnoli, M., Guo, Y., Rupaimoole, R., Rodriguez-Aguayo, C., Lopez-Berestein, G., Ji, P., Chen, K., Sood, A. K., Mezzanzanica, D., Liu, J., Sun, B., and Zhang, W. (2015) MiR-506 inhibits multiple targets in the epithelialtomesenchymal transition network and is associated with good prognosis in epithelial ovarian cancer, J. Pathol., 235, 25–36.
Rupaimoole, R., Ivan, C., Yang, D., Gharpure, K. M., Wu, S. Y., Pecot, C. V., Previs, R. A., Nagaraja, A. S., Armaiz-Pena, G. N., McGuire, M., Pradeep, S., Mangala, L. S., Rodriguez-Aguayo, C., Huang, L., Bar-Eli, M., Zhang, W., Lopez-Berestein, G., Calin, G. A., and Sood, A. K. (2016) Hypoxiaupregulated microRNA-630 targets Dicer, leading to increased tumor progression, Oncogene, 35, 4312–4320.
Wang, Y., Yan, S., Liu, X., Zhang, W., Li, Y., Dong, R., Zhang, Q., Yang, Q., Yuan, C., Shen, K., and Kong, B. (2014) miR-1236-3p represses the cell migration and invasion abilities by targeting ZEB1 in highgrade serous ovarian carcinoma, Oncol. Rep., 31, 1905–1910.
Piletic, K., and Kunej, T. (2016) MicroRNA epigenetic signatures in human disease, Arch. Toxicol., 90, 2405–2419.
Baylin, S. B., and Jones, P. A. (2016) Epigenetic determinants of cancer, Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol., 8, a019505.
Malladi, S., Macalinao, D. G., Jin, X., He, L., Basnet, H., Zou, Y., De Stanchina, E., and Massague, J. (2016) Metastatic latency and immune evasion through autocrine inhibition of WNT, Cell, 165, 45–60.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
To whom correspondence should be addressed.
Original Russian Text © E. A. Braga, M. V. Fridman, N. E. Kushlinskii, 2017, published in Biokhimiya, 2017, Vol. 82, No. 5, pp. 717-731.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Braga, E.A., Fridman, M.V. & Kushlinskii, N.E. Molecular mechanisms of ovarian carcinoma metastasis: Key genes and regulatory microRNAs. Biochemistry Moscow 82, 529–541 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0006297917050017
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0006297917050017