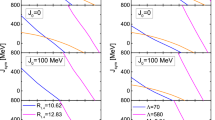
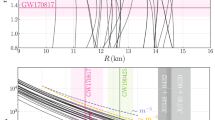
Abstract
Neutron star (NS) is a unique astronomical compact object where the four fundamental interactions have been revealed from the observation and studied in different ways. While the macroscopic properties of NS like mass and radius can be determined within the General Relativity using a realistic equation of state (EOS) of NS matter, such an EOS is usually generated by a nuclear structure model like, e.g., the nuclear mean-field approach to asymmetric nuclear matter. Given the radius of NS extended to above 10 km and its mass up to twice the solar mass, NS is expected to be tidally deformed when it is embedded in a strong tidal field. Such a tidal effect was confirmed unambiguously in the gravitation wave signals detected recently by the LIGO and Virgo laser interferometers from GW170817, the first ever direct observation of a binary NS merger. A nonrelativistic mean-field study is carried out in the present work within the Hartree–Fock formalism to construct the EOS of NS matter, which is then used to determine the tidal deformability, gravitational mass, and radius of NS. The mean-field results are compared with the constraints imposed for these quantities by the global analysis of the observed GW170817 data, and a strong impact by the incompressibility of nuclear matter on the hydrostatic configuration of NS is shown.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability Statement
This manuscript has no associated data or the data will not be deposited. [Author’s comment:This is a theoretical study with some comparison with the published data, and all data information is properly referenced.]
References
T. Hinderer, Astrophys. J. 677, 1216 (2008)
T. Hinderer, B.D. Lackey, R.N. Lang, J.S. Read, Phys. Rev. D 81, 123016 (2010)
B.P. Abbott et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 119, 161101 (2017)
B.P. Abbott et al., Astrophys. J. Lett. 848, L12 (2017)
B.P. Abbott et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 121, 161101 (2018)
F.J. Fattoyev, J. Piekarewicz, C.J. Horowitz, Phys. Rev. Lett. 120, 172702 (2018)
E. Annala, T. Gorda, A. Kurkela, A. Vuorinen, Phys. Rev. Lett. 120, 172703 (2018)
S. De, D. Finstad, J.M. Lattimer, D.A. Brown, E. Berger, C.M. Biwer, Phys. Rev. Lett. 121, 091102 (2018)
T. Malik, N. Alam, M. Fortin, C. Providência, B.K. Agrawal, T.K. Jha, B. Kumar, S.K. Patra, Phys. Rev. C 98, 035804 (2018)
T. Dietrich, M.W. Coughlin, P.T.H. Pang, M. Bulla, J. Heinzel, L. Issa, I. Tews, S. Antier, Science 370, 1450 (2020)
D.T. Loan, N.H. Tan, D.T. Khoa, J. Margueron, Phys. Rev. C 83, 065809 (2011)
N.H. Tan, D.T. Loan, D.T. Khoa, J. Margueron, Phys. Rev. C 93, 035806 (2016)
N. Anantaraman, H. Toki, G. Bertsch, Nucl. Phys. A 398, 269 (1983)
D.T. Khoa, G.R. Satchler, W. von Oertzen, Phys. Rev. C 56, 954 (1997)
D.T. Khoa, G.R. Satchler, Nucl. Phys. A 668, 3 (2000)
D.T. Khoa, W. von Oertzen, A. Ogloblin, Nucl. Phys. A 602, 98 (1996)
D.T. Khoa, H.S. Than, D.C. Cuong, Phys. Rev. C 76, 014603 (2007)
D.T. Khoa, B.M. Loc, D.N. Thang, Eur. Phys. J. A 50, 34 (2014)
N.H. Tan, D.T. Khoa, D.T. Loan, Phys. Rev. C 102, 045809 (2020)
A. Akmal, V.R. Pandharipande, D.G. Ravenhall, Phys. Rev. C 58, 1804 (1998)
S. Gandolfi, A.Y. Illarionov, S. Fantoni, J.C. Miller, F. Pederiva, K.E. Schmidt, Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. Lett. 404, L35 (2010)
U. Garg, G. Colò, Prog. Part. Nucl. Phys. 101, 55 (2018)
Y. Schutz, TAPS Collaboration, Nucl. Phys. A 599, 97c (1996)
D.T. Khoa, W. von Oertzen, H.G. Bohlen, S. Ohkubo, J. Phys. G 34, R111 (2007)
M.B. Tsang, Z. Chajecki, D. Coupland, P. Danielewicz, F. Famiano, R. Hodges, M. Kilburn, F. Lu, W.G. Lynch, J. Winkelbauer, M. Youngs, Y.X. Zhang, Prog. Part. Nucl. Phys. 66, 400 (2011)
A. Ono, P. Danielewicz, W.A. Friedman, W.G. Lynch, M.B. Tsang, Phys. Rev. C 68, 051601 (2003)
L. Trippa, G. Colò, E. Vigezzi, Phys. Rev. C 77, 061304 (2008)
R. Furnstahl, Nucl. Phys. A 706, 85 (2002)
J.M. Dong, L.J. Wang, W. Zuo, J.Z. Gu, Phys. Rev. C 97, 034318 (2018)
X.H. Fan, J.M. Dong, W. Zuo, Phys. Rev. C 89, 017305 (2014)
W.J. Xie, B.A. Li, Astrophys. J. 883, 174 (2019)
F. Douchin, P. Haensel, J. Meyer, Nucl. Phys. A 665, 419 (2000)
F. Douchin, P. Haensel, Astron. Astrophys. 380, 151 (2001)
E. Chabanat, P. Bonche, P. Haensel, J. Meyer, R. Schaeffer, Nucl. Phys. A 635, 231 (1998)
S.L. Shapiro, S.A. Teukolsky, Black Holes, White Dwarfs, and Neutron Stars (WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim, 2004), p. 24
I. Bombaci, in Isospin Physics in Heavy Ion Collisions at Intermediate Energies, ed. by B.A. Li, W.U. Schröder (Nova Science, New York, 2001), p. 35
J. Antoniadis et al., Science 340, 6131 (2013)
P. Bedaque, A.W. Steiner, Phys. Rev. Lett. 114, 031103 (2015)
H.T. Cromartie et al., Nat. Astron. 4, 72 (2020)
G. Raaijmakers et al., Astrophys. J. Lett. 893, L21 (2020)
J.M. Lattimer, M. Prakash, Phys. Rep. 442, 109 (2007)
Acknowledgements
We thank N. H. Phuc for his help in revising the isovector density dependence of the M3Y interaction. The present research was supported, in part, by the National Foundation for Science and Technology Development of Vietnam (NAFOSTED Project No. 103.04-2017.317).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Jerome Margueron.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tan, N.H., Khoa, D.T. & Loan, D.T. Equation of state of asymmetric nuclear matter and the tidal deformability of neutron star. Eur. Phys. J. A 57, 153 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1140/epja/s10050-021-00467-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epja/s10050-021-00467-y