Abstract.
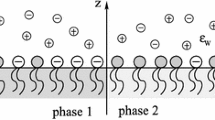
We use coarse-grained Monte Carlo simulations to study the elastic properties of charged membranes in solutions of monovalent and pentavalent counterions. The simulation results of the two cases reveal trends opposite to each other. The bending rigidity and projected area increase with the membrane charge density for monovalent counterions, while they decrease for the pentavalent ions. These observations can be related to the counterion screening of the lipid charges. While the monovalent counterions only weakly screen the Coulomb interactions, which implies a repulsive Coulomb system, the multivalent counterions condense on the membrane and, through spatial charge correlations, make the effective interactions due to the charged lipids attractive. The differences in the elastic properties of the charged membranes in monovalent and multivalent counterion solutions are reflected in the mechanisms leading to their mechanical instability at high charge densities. In the former case, the membranes develop pores to relieve the electrostatic tensile stresses, while in the latter case, the membrane exhibits large wavelength bending instability.
Graphical abstract

Similar content being viewed by others
References
B. Alberts, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Garland Science, New York, 2002)
W. Helfrich, Z. Naturforsch. 28C, 693 (1973)
O. Farago, P. Pincus, J. Phys. Chem. 120, 2934 (2004)
For a comprehensive review see: D. Andelman, in Structure and Dynamics of Membranes, edited by R. Lipowsky, E. Sackmann (Elsevier, Amsterdam, 1995)
A.W.C. Lau, P. Pincus, Phys. Rev. Lett. 81, 1338 (1998)
T.T. Nguyen, I. Rouzina, B.I. Shklovskii, Phys. Rev. E 60, 7032 (1999)
R.R. Netz, Phys. Rev. E 64, 051401 (2001)
Y.W. Kim, W. Sung, Europhys. Lett. 58, 147 (2002)
A.W.C. Lau, D.B. Lukatsky, P. Pincus, S.A. Safran, Phys. Rev. E 65, 051502 (2002)
A.G. Moreira, R.R. Netz, Eur. Phys, J. E 8, 33 (2002)
I. Rouzina, V.A. Bloomfield, J. Phys. Chem. 100, 9977 (1996)
N. Grøn, Phys. Rev. Lett. 78, 2477 (1997)
N. Grøn, Physica A 261, 74 (1998)
C.C. Fleck, R.R. Netz, Phys. Rev. Lett. 95, 128101 (2005)
E. Lindhal, O. Edholm, Biophys. J. 79, 426 (2000)
S.J. Marrink, A.E. Mark, J. Phys. Chem. 105, 6122 (2001)
O. Farago, J. Chem. Phys. 119, 596 (2003)
F. Brown, Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem. 59, 685 (2008)
I.R. Cooke, K. Kremer, M. Deserno, Phys. Rev. E 72, 011506 (2005) (we slightly modified the model to avoid occasional escape of lipids from the bilayer)
N. Grønbech-Jensen, G. Hummer, K.M. Beardmore, Mol. Phys. 92, 941 (1997)
R.J. Mashl, N. Grønbech-Jensen, J. Chem. Phys. 109, 4617 (1998)
O. Farago, N. Grønbech-Jensen, Biophys. J. 92, 3228 (2007)
O. Farago, J. Chem. Phys. 128, 184105 (2008)
H.I. Petrach, S. Tristram-Nagle, K. Gawrisch, D. Harries, V.A. Persegian, J.F. Nagle, Biophys. J. 86, 1574 (2004)
P. Mukhopadhyay, L. Monticelli, D.P. Tieleman, Biophys. J. 86, 1601 (2004)
W. Rawicz, K.C. Olbrich, T. McIntosh. D. Needham, E. Evans, Biophys. J. 79, 328 (2000)
S. Buyukdagli, M. Manghi, J. Palmeri, Phys. Rev. E 81, 041601 (2010)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Avital, Y., Grønbech-Jensen, N. & Farago, O. Elasticity and mechanical instability of charged lipid bilayers in ionic solutions. Eur. Phys. J. E 37, 69 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1140/epje/i2014-14069-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epje/i2014-14069-2