Abstract
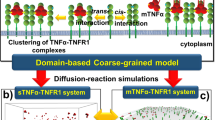
We consider stochastic reaction-diffusion dynamics involved in the formation of a trimeric protein receptor complex, where diffusion is modulated by the presence of small, fixed membrane microdomains. Compartmentalisation of cell membrane signalling proteins may optimise signal transduction but previous modelling work suggests that signalling is only augmented if microdomains are highly mobile. Using a Gillespie algorithm-based spatial numerical simulation, we examine the effect of the presence, size and total coverage of microdomains, which either slow protein diffusion or trap proteins at their boundary. We examine scenarios where protein-protein interactions take place within microdomains, and also where interactions are favoured at the microdomain boundary. This model is motivated by the formation of the high-affinity receptor for the cytokine IL-2. Proliferation requires a threshold number of bound receptors, but pleiotropic effects of IL-2 on other cell types means that high ligand concentrations are undesirable. Hence, optimising T cell sensitivity to IL-2 is essential. In agreement with earlier models, we find that small microdomain sizes result in the greatest augmentation in receptor formation, but that static microdomains can also confer an increased sensitivity in the case of heterotrimeric receptor complex formation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
K. Simons, E. Ikonen, Nature 387, 569 (1997)
R. Xavier, T. Brennan, Q. Li, C. McCormack, B. Seed, Immunity 8, 6 (1998)
A. Grakoui, S. Bromley, C. Sumen, M. Davis, A. Shaw, P. Allen, M. Dustin, Science 285, 221 (1999)
T. Zech, C.S. Ejsing, K. Gaus, B. de Wet, A. Shevchenko, K. Simons, T. Harder, EMBO J. 28, 5 (2009)
M.A. Burchill, J. Yang, K.B. Vang, M.A. Farrar, Immunol. Lett. 114, 1 (2007)
S. Singer, G. Nicolson, Science 175, 720 (1972)
F.M. Goñi, A. Alonso, L.A. Bagatolli, R.E. Brown, D. Marsh, M. Prieto, J.L. Thewalt, Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1781, 665 (2008)
B.C. Lagerholm, G.E. Weinreb, K. Jacobson, N.L. Thompson, Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem. 56, 309 (2005)
M.S. Turner, P. Sens, N.D. Socci, Phys. Rev. Lett. 95, 16 (2005)
M. Venturoli, M.M. Sperotto, M. Kranenburg, B. Smit, Phys. Rep. 437, 1 (2006)
S.A. Pandit, Biophys. J. 87, 5 (2004)
H.J. Risselada, S.J. Marrink, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 105, 45 (2008)
G. Nudelman, M. Weigert, Y. Louzoun, Mol. Immunol. 46, 15 (2009)
D.V. Nicolau, K. Burrage, R.G. Parton, J.F. Hancock, Mol. Cell. Biol. 26, 1 (2006)
A. Bodnár, E. Nizsalóczki, G. Mocsár, N. Szalóki, Immunol. Lett. 116, 117 (2008)
T. Taniguchi, Science 268, 251 (1995)
J. Matkó, A. Bodnár, G. Vereb, L. Bene, G. Vámosi, Eur. J. Biochem. 269, 1199 (2002)
G. Vereb, J. Matkó, G. Vámosi, S.M. Ibrahim, E. Magyar, S. Varga, J. Szöllosi, A. Jenei, R. Gáspár, T.A. Waldmann, S. Damjanovich, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 97, 11 (2000)
J. Goebel, K. Forrest, L. Morford, T.L. Roszman, J. Leukoc. Biol. 72, 1 (2002)
M. Marmor, M. Julius, Blood (2001)
A. Ma, R. Koka, P. Burkett, Annu. Rev. Immunol. 16, 33 (2010)
H.P. Kim, J. Imbert, W.J. Leonard, Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 17, 349 (2006)
T.A. Waldmann, J. Clin. Immunol. 22, 2 (2002)
E.M. Fallon, D.A. Lauffenburger, Biotechnol. Prog. 16, 5 (2000)
J.M. Ellery, P.J. Nicholls, Immunol. Cell. Biol. 80, 4 (2002)
M. Gibson, J. Bruck, J. Phys. Chem. A 104, 1876 (2000)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Long, E., Henderson, B. & Zaikin, A. In silico analysis of microdomain-mediated trimer formation in the T cell membrane. Eur. Phys. J. Spec. Top. 187, 21–30 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjst/e2010-01267-2
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epjst/e2010-01267-2