Abstract
Objective
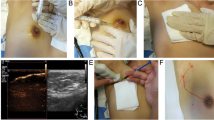
The aim of this study was to review our experience with ultrasound (US)-guided localization of axillary lymph nodes using activated charcoal for the guidance of axillary surgery after neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NAC) in clinically node-positive breast cancer patients.
Methods
Between April 2016 and April 2017, US-guided localization of the most suspicious axillary lymph nodes at restaging US using activated charcoal (Charcotrace™) was performed in 45 consecutive, clinically node-positive breast cancer patients who had less than two suspicious nodes after NAC and axillary surgery with sentinel node biopsy. Sentinel nodes were defined as radioactive nodes or nodes containing blue dye. The concordance between final pathological results for both the tattooed and sentinel nodes was analyzed.
Results
Sentinel node biopsy failed in five patients (11%) in whom axillary surgery was performed under the guidance of the tattooed node. The tattooed nodes were identified in the surgical field in 44 patients (98%). Of the 44 tattooed nodes, 25 (57%) were concordant with the sentinel nodes and 19 (43%) were non-sentinel nodes, including the five nodes with failed sentinel node biopsy. In the final pathological results, 18 patients (40%) had metastatic nodes. The sensitivities for detecting axillary metastasis of the sentinel node biopsy, tattooed node biopsy, and the sentinel and/or tattooed node biopsy were 61% (11/18), 67% (12/18), and 78% (14/18), respectively.
Conclusion
US-guided localization of axillary lymph nodes using activated charcoal at restaging after NAC in clinically node-positive breast cancer patients is a useful technique to guide axillary surgery, with a high identification rate.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Krag D, Weaver D, Ashikaga T, et al. The sentinel node in breast cancer—a multicenter validation study. N Engl J Med. 1998;339(14):941–6.
Veronesi U, Paganelli G, Galimberti V, et al. Sentinel-node biopsy to avoid axillary dissection in breast cancer with clinically negative lymph-nodes. Lancet. 1997;349(9069):1864–7.
Lucci A, McCall LM, Beitsch PD, et al. Surgical complications associated with sentinel lymph node dissection (SLND) plus axillary lymph node dissection compared with SLND alone in the American College of Surgeons Oncology Group Trial Z0011. J Clin Oncol. 2007;25(24):3657–63.
Kuerer HM, Sahin AA, Hunt KK, et al. Incidence and impact of documented eradication of breast cancer axillary lymph node metastases before surgery in patients treated with neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Ann Surg. 1999;230(1):72–8.
Hennessy BT, Hortobagyi GN, Rouzier R, et al. Outcome after pathologic complete eradication of cytologically proven breast cancer axillary node metastases following primary chemotherapy. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23(36):9304–11.
Dominici LS, Negron Gonzalez VM, Buzdar AU, et al. Cytologically proven axillary lymph node metastases are eradicated in patients receiving preoperative chemotherapy with concurrent trastuzumab for HER2-positive breast cancer. Cancer. 2010;116(12):2884–9.
Boughey JC, Suman VJ, Mittendorf EA, et al. Sentinel lymph node surgery after neoadjuvant chemotherapy in patients with node-positive breast cancer: the ACOSOG Z1071 (Alliance) clinical trial. JAMA. 2013;310(14):1455–61.
Kuehn T, Bauerfeind I, Fehm T, et al. Sentinel-lymph-node biopsy in patients with breast cancer before and after neoadjuvant chemotherapy (SENTINA): a prospective, multicentre cohort study. Lancet Oncol. 2013;14(7):609–18.
Xing Y, Foy M, Cox DD, Kuerer HM, Hunt KK, Cormier JN. Meta-analysis of sentinel lymph node biopsy after preoperative chemotherapy in patients with breast cancer. Br J Surg. 2006;93(5):539–46.
Fu JF, Chen HL, Yang J, Yi CH, Zheng S. Feasibility and accuracy of sentinel lymph node biopsy in clinically node-positive breast cancer after neoadjuvant chemotherapy: a meta-analysis. PLoS ONE. 2014;9(9):e105316.
Mamounas EP, Brown A, Anderson S, et al. Sentinel node biopsy after neoadjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer: results from National Surgical Adjuvant Breast and Bowel Project Protocol B-27. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23(12):2694–702.
Boileau JF, Poirier B, Basik M, et al. Sentinel node biopsy after neoadjuvant chemotherapy in biopsy-proven node-positive breast cancer: the SN FNAC study. J Clin Oncol. 2015;33(3):258–64.
Caudle AS, Yang WT, Krishnamurthy S, et al. Improved axillary evaluation following neoadjuvant therapy for patients with node-positive breast cancer using selective evaluation of clipped nodes: implementation of targeted axillary dissection. J Clin Oncol. 2016;34(10):1072–8.
Donker M, Straver ME, Wesseling J, et al. Marking axillary lymph nodes with radioactive iodine seeds for axillary staging after neoadjuvant systemic treatment in breast cancer patients: the MARI procedure. Ann Surg. 2015;261(2):378–82.
Caudle AS, Yang WT, Mittendorf EA, et al. Selective surgical localization of axillary lymph nodes containing metastases in patients with breast cancer: a prospective feasibility trial. JAMA Surg. 2015;150(2):137–43.
Allred DC, Harvey JM, Berardo M, Clark GM. Prognostic and predictive factors in breast cancer by immunohistochemical analysis. Mod Pathol. 1998;11(2):155–68.
Wolff AC, Hammond ME, Hicks DG, et al. Recommendations for human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 testing in breast cancer: American Society of Clinical Oncology/College of American Pathologists clinical practice guideline update. J Clin Oncol. 2013;31(31):3997–4013.
Shin K, Caudle AS, Kuerer HM, et al. Radiologic mapping for targeted axillary dissection: needle biopsy to excision. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2016;207(6):1372–79.
Choy N, Lipson J, Porter C, et al. Initial results with preoperative tattooing of biopsied axillary lymph nodes and correlation to sentinel lymph nodes in breast cancer patients. Ann Surg Oncol. 2015;22(2):377–82.
Nieweg OE, Estourgie SH. What is a sentinel node and what is a false-negative sentinel node? Ann Surg Oncol. 2004;11(3 Suppl):169S–73S.
Kuehn T, Bembenek A, Decker T, et al. A concept for the clinical implementation of sentinel lymph node biopsy in patients with breast carcinoma with special regard to quality assurance. Cancer. 2005;103(3):451–61.
Cho N, Moon WK, Han W, Park IA, Cho J, Noh DY. Preoperative sonographic classification of axillary lymph nodes in patients with breast cancer: node-to-node correlation with surgical histology and sentinel node biopsy results. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2009;193(6):1731–7.
Moss HA, Barter SJ, Nayagam M, Lawrence D, Pittam M. The use of carbon suspension as an adjunct to wire localisation of impalpable breast lesions. Clin Radiol. 2002;57(10):937–44.
Rose A, Collins JP, Neerhut P, Bishop CV, Mann GB. Carbon localisation of impalpable breast lesions. Breast. 2003;12(4):264–9.
Acknowledgement
This research was supported by the Korea Breast Cancer Foundation (KBCF-2016R005).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosure
Won Hwa Kim, Hye Jung Kim, Jin Hyang Jung, Ho Yong Park, Jeeyeon Lee, Wan Wook Kim, Ji Young Park, Yee Soo Chae, and Soo Jung Lee have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Electronic Supplementary Material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, W.H., Kim, H.J., Jung, J.H. et al. Ultrasound-Guided Restaging and Localization of Axillary Lymph Nodes After Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy for Guidance of Axillary Surgery in Breast Cancer Patients: Experience with Activated Charcoal. Ann Surg Oncol 25, 494–500 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-017-6250-3
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-017-6250-3