Abstract
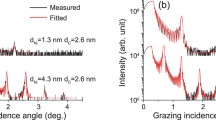
Microstructure evolution in amorphous Ge/Si multilayers grown by dual-target dc magnetron sputtering was investigated by cross-sectional transmission electron microscopy, x-ray diffraction, and growth simulations. In films grown under low intensity ion-irradiation conditions, the structure is columnar with low-density regions along column boundaries where layer intermixing was observed. By increasing the low-irradiation intensity (controlled by an applied negative substrate-bias), structures with smooth and well-defined layers could be grown. This was achieved at bias voltages between 80 and 140 V, depending on the sputtering gas pressure. As the ion-irradiation intensity is further increased, ion-induced intermixing degrades the layer interfaces and finally an amorphous Si1–xGex alloy forms. The combination of x-ray diffraction measurements and reflectivity calculations reveals an asymmetry between the Ge/Si and Si/Ge interface widths due, primarily, to a corresponding asymmetry in incident particle energies during the growth of alternate layers.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
An alternative term for superlattice is multilayer but not necessarily vice versa. Since the samples in this study cannot be considered as superlattices, the term multilayer is used throughout the text.
W. Deubner, Annin. Phys. 5, 261 (1930).
J. W. M. Dumond and J.P. Youtz, Phys. Rev. 48, 703 (1935).
L. Esaki and R. Tsu, IBM J. Res. Develop. 14, 61 (1970).
H. Munekata and H. Kukimoto, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 22, L544 (1983).
B. Abeles and T. Tiedje, Phys. Rev. Lett. 51, 2003 (1983).
J. P. Conde, V. Chu, D. S. Chen, and S. Wagner, J. Appl. Phys. 75, 1638 (1994).
I. Barzen, M. Edinger, J. Scherer, S. Ulrich, K. Jung, and H. Ehrhardt, Surf. Coatings Technol. 60, 454 (1993).
G. H. Döhler, J. Non-Cryst. Solids 77&78, 1041 (1985).
Y. Kuwano, H. Tarui, T. Takahama, M. Nishikuni, Y. Hishikawa, N. Nakamura, S. Tsuda, S. Nakano, and M. Ohnishi, J. Non-Cryst. Solids 97&98, 289 (1987).
M. Tsukude, S. Hata, Y. Kohda, S. Miyazaki, and M. Hirose, J. Non-Cryst. Solids 97&98, 317 (1987).
E. Majkova, S. Luby, M. Jergel, R. Senderak, B. George, M. Vaezzadeh, and J. Ghanbaja, Thin Solid Films 238, 295 (1992); J. M. Slaughter, D. W. Schultze, C. R. Hills, A. Mirone, R. Stalio, R. N. Watts, C. Tarrio, T. B. Lucatorto, M. Krumrey, P. Mueller, and C. M. Falco, J. Apply. Phys. 76, 2144 (1994).
B. Abeles, Superlattices and Microstructures 5, 473 (1989).
E. L. Z. Velasquez, M. C. A. Fantini, M. N. P. Carreño, I. Pereyra, H. Takahashi, and R. Landers, J. Appl. Phys. 75, 543 (1994).
S. Miyazaki, Y. Ihara, and M. Hirose, J. Non-Cryst. Solids 97&98, 887 (1987).
I. Honma, H. Komiyama, and K. Tanaka, J. Appl. Phys. 66, 1170 (1989).
S. M. Prokes and F. Spaepen, Appl. Phys. Lett. 47, 234 (1985).
Zs. Czigany, G. Radnóczi, K. Järrendahl, and J-E. Sundgren, J. Mater. Res. (1997, in press).
D. J. Miller, K. E. Gray, R. T. Kampwirth, and J. M. Murduck, Europhys. Lett. 19, 27 (1992).
I. Petrov, V. Orlinov, I. Ivanov, and J. Kourtev, Contrib. Plasma Phys. 28, 157 (1988).
I. Petrov, V. Orlinov, I. Ivanov, and J. Kourtev, Contrib. Plasma Phys. 30, 233 (1990).
G. Radnóczi and A´ . Barna, Surf. Coating Technol. 80, 89 (1996); Á. Barna, Specimen Preparation for Transmission Electron Microscopy of Materials III, edited by R. Anderson, B. Tracy, and J. Bravman (Mater. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. 254, Pittsburgh, PA, 1991), pp. 3–22.
D. K. G. de Boer, Phys. Rev. B 44, 498 (1991).
J. M. Cowley, Diffraction Physics (North-Holland/American Elsevier, Amsterdam, 1975).
S. Müller-Pfeiffer, H-J. Anklam, and W. Haubenreisser, Phys. Status Solidi 160, 491 (1990); S. Müller-Pfeiffer, H. van Kranenburg, and J. C. Lodder, Thin Solid Films 213, 143 (1992).
W. D. Westwood, J. Vac. Sci. Technol. 15, 1 (1978).
I. Ivanov, P. Kazansky, L. Hultman, I. Petrov, and J-E. Sundgren, J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A 12, 314 (1994).
R. Messier and J. E. Yehoda, J. Appl. Phys. 58, 3739 (1985).
M. Kardar, G. Parisi, and Y-C. Zhang, Phys. Rev. Lett. 56, 889 (1986).
G. S. Bales, R. Bruinsma, E. A. Eklund, R, O. U. Karunasiri, J. Rudnick, and A. Zangwill, Science 249, 264 (1990).
G. S. Bales and A. Zangwill, J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A 9, 145 (1991).
C. Tang, S. Alexander, and R. Bruinsma, Phys. Rev. Lett. 64, 772 (1990).
Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, 73rd ed. (CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL, 1992–93), pp. 9–131, 132.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
WWW home page: http://www.ifm.liu.se/Thinfilm
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Järrendahl, K., Ivanov, I., Sundgren, JE. et al. Microstructure evolution in amorphous Ge/Si multilayers grown by magnetron sputter deposition. Journal of Materials Research 12, 1806–1815 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1557/JMR.1997.0249
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/JMR.1997.0249