Abstract
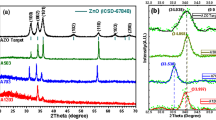
Hard transparent conducting oxide films of hex-element AlxCoCrCuFeNi were deposited by reactive direct current (dc) magnetron sputtering using homogeneous alloy targets. The composition–property relation was investigated by changing the aluminum molar ratio, x value, from 0.5 to 2. The films comprise only a cubic spinel phase without other accompanying crystalline oxide phases and exhibit a high hardness up to 22.2 GPa. A small, negative deviation from Vegard’s law was observed for the spinel phase, which indicated changes in cation distribution. The optical transmittance in both the visible and infrared region is increased with aluminum content, however, together with a loss of film conductivity. The Hall measurements reveal a p-type conducting behavior for the Al0.5CoCrCuFeNi oxide film with a conductivity of 40.1 Ω−1cm−1, a carrier density of 5.81 × 1018 cm−3, and a mobility as high as 43.2 cm2V−1s−1. Moreover, Hall measurements show metallic conduction behavior for the Al0.5CoCrCuFeNi oxide film and thermal activated semiconducting properties for the Al1CoCrCuFeNi and Al2CoCrCuFeNi oxide films. Combine the crystal field theory and the x-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) measurements, the decrease of film conductivity is explained by the decreases of available carriers and mobility due to the fact that increasing aluminum content reduces the number of conducting cations at octahedral sites and increases the activation energy for electrical conduction. XPS analyses also show lots of excess oxygen originated from anion-rich growth condition in the films deposited at high oxygen partial pressure that produce p-type carriers lowering the electrical resistivity. The amount of excess oxygen decreases with increasing Al content and also contributes to the variation of conductivity with x value.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
D.S. Ginley, C. Bright: Transparent conducting oxides. MRS Bull. 25, 15 2000
H. Kawazoe, H. Yanagi, K. Ueda, H. Hosono: Transparent p-type conducting oxides: Design and fabrication of p-n heterojunctions. MRS Bull. 25, 28 2000
T.J. Coutts, D.L. Young, X.N. Li: Characterization of transparent conducting oxides. MRS Bull. 25, 58 2000
H. Kawazoe, M. Yasukawa, H. Hyodo, M. Kurita, H. Yanagi, H. Hosono: P-type electrical conduction in transparent thin films of CuAlO2. Nature 389, 939 1997
K. Nomura, H. Ohta, A. Takagi, T. Kamiya, M. Hirano, H. Hosono: Room-temperature fabrication of transparent flexible thin-film transistors using amorphous oxide semiconductors. Nature 432, 488 2004
F.J. DiSalvo: Challenges and opportunities in solid-state chemistry. Pure Appl. Chem. 72, 1799 2000
T.K. Chen, T.T. Shun, J.W. Yeh, M.S. Wong: Nanostructured nitride films of multi-element high-entropy alloys by reactive DC sputtering. Surf. Coat. Technol. 188–89, 193 2004
T.K. Chen, M.S. Wong, T.T. Shun, J.W. Yeh: Nanostructured nitride films of multi-element high-entropy alloys by reactive DC sputtering. Surf. Coat. Technol. 200, 1361 2005
J.W. Yeh, S.K. Chen, S.J. Lin, J.Y. Gan, T.S. Chin, T.T. Shun, C.H. Tsau, S.Y. Chang: Nanostructured high-entropy alloys with multiple principal elements: Novel alloy design concepts and outcomes. Adv. Eng. Mater. 6, 299 2004
T.K. Chen, M.S. Wong: Structure and properties of reactively-sputtered AlxCoCrCuFeNi oxide films. Thin Solid Films 516, 141 2007
C.J. Tong, Y.L. Chen, S.K. Chen, J.W. Yeh, T.T. Shun, C.H. Tsau, S.J. Lin, S.Y. Chang: Microstructure characterization of AlxCoCrCuFeNi high-entropy alloy system with multiprincipal elements. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 36, 881 2005
J.M. Wu, S.J. Lin, J.W. Yeh, S.K. Chen, Y.S. Huang: Adhesive wear behavior of AlxCoCrCuFeNi high-entropy alloys as a function of aluminum content. Wear 261, 513 2006
J.I. Pankove: Optical Processes in Semiconductors Dover Publications Inc. New York 1971
P.L. Edwards: Magnetic properties of the manganese chromite-aluminates. Phys. Rev. 116, 294 1959
R.G. Kulkarni, B.S. Trivedi, H.H. Joshi, G.J. Baldha: Magnetic properties of copper ferrite aluminates. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 159, 375 1996
F.C. Romeijn: Physical and crystallographical properties of some spinels. Philips Res. Rep. 8, 304 1953
T. Kohara, H. Tamagaki, Y. Ikari, H. Fujii: Deposition of alpha-Al2O3 hard coatings by reactive magnetron sputtering. Surf. Coat. Technol. 185, 166 2004
P. Hones, F. Levy, N.X. Randall: Influence of deposition parameters on mechanical properties of sputter-deposited Cr2O3 thin films. J. Mater. Res. 14, 3623 1999
M. Jirout, J. Musil: Effect of addition of Cu into ZrOx film on its properties. Surf. Coat. Technol. 200, 6792 2006
F.M. Gao: Hardness estimation of complex oxide materials. Phys. Rev. B 69, 094113 2004
N. Nitani, T. Yamashita, T. Matsuda, S. Kobayashi, T. Ohmichi: Thermophysical properties of rock-like oxide fuel with spinel-yttria stabilized zirconia system. J. Nucl. Mater. 274, 15 1999
R.G. Gordon: Criteria for choosing transparent conductors. MRS Bull. 25, 52 2000
K.Y. Zeng, F.R. Zhu, J.Q. Hu, L. Shen, K. Zhang, H. Gong: Investigation of mechanical properties of transparent conducting oxide thin films. Thin Solid Films 443, 60 2003
S.K. Park, T. Ishikawa, Y. Tokura: Charge-gap formation upon the Verwey transition in Fe3O4. Phys. Rev. B 58, 3717 1998
V.N. Antonov, B.N. Harmon, V.P. Antropov, A.Y. Perlov, A.N. Yaresko: Electronic structure and magneto-optical Kerr effect of Fe3O4 and Mg2+- or Al3+-substituted Fe3O4. Phys. Rev. B 64, 134410 2001
Z. Szotek, W.M. Temmerman, D. Kodderitzsch, A. Svane, L. Petit, H. Winter: Electronic structures of normal and inverse spinel ferrites from first principles. Phys. Rev. B 74, 174431 2006
R.K. Selvan, C.O. Augustin, C. Sanjeeviraja, V.G. Pol, A. Gedanken: Optimization of sintering on the structural, electrical and dielectric properties of SnO2 coated CuFe2O4 nanoparticles. Mater. Chem. Phys. 99, 109 2006
J. Vanelp, J.L. Wieland, H. Eskes, P. Kuiper, G.A. Sawatzky, F.M.F. Degroot, T.S. Turner: Electronic-structure of CoO, Li-doped CoO, and LiCoO2. Phys. Rev. B 44, 6090 1991
B. Pejova, A. Isahi, M. Najdoski, I. Grozdanov: Fabrication and characterization of nanocrystalline cobalt oxide thin films. Mater. Res. Bull. 36, 161 2001
A.M. Goodman: Photoemission of holes and electrons from aluminum into aluminum oxide. J. Appl. Phys. 41, 2176 1970
S.D. Mo, W.Y. Ching: Electronic and optical properties of theta-Al2O3 and comparison to alpha-Al2O3. Phys. Rev. B 57, 15219 1998
G. Goodlet, S. Faty, S. Cardoso, P.P. Freitas, A.M.P. Simoes, M.G.S. Ferreira, M.D. Belo: The electronic properties of sputtered chromium and iron oxide films. Corros. Sci. 46, 1479 2004
J. Ghijsen, L.H. Tjeng, J. Vanelp, H. Eskes, J. Westerink, G.A. Sawatzky, M.T. Czyzyk: Electronic-structure of Cu2O and CuO. Phys. Rev. B 38, 11322 1988
H. Yanagi, S. Inoue, K. Ueda, H. Kawazoe, H. Hosono, N. Hamada: Electronic structure and optoelectronic properties of transparent p-type conducting CuAlO2. J. Appl. Phys. 88, 4159 2000
D.R. Lide: CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics CRC Press 2002
R.D. Shannon: Revised effective ionic-radii and systematic studies of interatomic distances in halides and chalcogenides. Acta Crystallogr., Sect. A 32, 751 1976
C.F. Windisch, G.J. Exarhos, K.F. Ferris, M.H. Engelhard, D.C. Stewart: Infrared transparent spinel films with p-type conductivity. Thin Solid Films 398, 45 2001
C.F. Windisch, K.F. Ferris, G.J. Exarhos: Synthesis and characterization of transparent conducting oxide cobalt-nickel spinel films. J. Vac. Sci. Technol., A 19, 1647 2001
N. Tsuda, K. Nasu, A. Fujimori, K. Siratori: Electronic Conduction in Oxides Springer Berlin 2000 54 168 199 268
P. Nkeng, G. Poillerat, J.F. Koenig, P. Chartier, B. Lefez, J. Lopitaux, M. Lenglet: Cobaltzation of spinel-type cobalt and nickel-oxide thin-films by x-ray near grazing diffraction, transmission and reflectance spectroscopies, and cyclic voltammetry. J. Electrochem. Soc. 142, 1777 1995
Z.G. Lu, J.H. Zhu, E.A. Payzant, M.P. Paranthaman: Electrical conductivity of the manganese chromite spinel solid solution. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 88, 1050 2005
C.F. Windisch, K.F. Ferris, G.J. Exarhos, S.K. Sharma: Conducting spinel oxide films with infrared transparency. Thin Solid Films 420, 89 2002
Y.D. Park, A.T. Hanbicki, S.C. Erwin, C.S. Hellberg, J.M. Sullivan, J.E. Mattson, T.F. Ambrose, A. Wilson, G. Spanos, B.T. Jonker: A group-IV ferromagnetic semiconductor: MnxGe1–x. Science 295, 651 2002
J.D. Dunitz, L.E. Orgel: Electronic properties of transition-metal oxides. 2. Cation distribution amongst octahedral and tetrahedral sites. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 3, 318 1957
A. Miller: Distribution of cations in spinels. J. Appl. Phys. 30, S24 1959
P.A. Miles, W.B. Westphal, A. Vonhippel: Dielectric spectroscopy of ferromagnetic semiconductors. Rev. Mod. Phys. 29, 279 1957
K.T. Jacob, C.B. Alcock: Activities and their relation to cation distribution in NiAl2O4–MgAl2O4 spinel solid-solutions. J. Solid State Chem. 20, 79 1977
K. Krezhov, P. Konstantinov: Cationic distributions in the binary oxide spinels MxCo3–xO4 (M = Mg,Cu,Zn,Ni). Physica B (Amsterdam) 234, 157 1997
J.T. Sampanthar, H.C. Zeng: Synthesis of CoIICoIII2−xAlx O4−Al2O3 nanocomposites via decomposition of CoII0.73 CoIII0.27(OH)2.00(NO3)0.23(CO3)0.02⋅0.5H2O in a sol-gel-derived γ-Al2O3 matrix. Chem. Mater. 13, 4722 2001
A.R. Naghash, T.H. Etsell, S. Xu: XRD and XPS study of Cu–Ni interactions on reduced copper-nickel-aluminum oxide solid solution catalysts. Chem. Mater. 18, 2480 2006
M.W. Nydegger, G. Couderc, M.A. Langell: Surface composition of CoxNi1–xO solid solutions by x-ray photoelectron and Auger spectroscopies. Appl. Surf. Sci. 147, 58 1999
J.G. Kim, D.L. Pugmire, D. Battaglia, M.A. Langell: Analysis of the NiCo2O4 spinel surface with Auger and x-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. Appl. Surf. Sci. 165, 70 2000
C.G. Fonstad, R.H. Rediker: Electrical properties of high-quality stannic oxide crystals. J. Appl. Phys. 42, 2911 1971
H. Kawazoe, K. Ueda: Transparent conducting oxides based on the spinel structure. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 82, 3330 1999
B.J. Ingram, T.O. Mason, R. Asahi, K.T. Park, A.J. Freeman: Electronic structure and small polaron hole transport of copper aluminate. Phys. Rev. B 64, 155114 2001
H. Kim, C.M. Gilmore, A. Pique, J.S. Horwitz, H. Mattoussi, H. Murata, Z.H. Kafafi, D.B. Chrisey: Electrical, optical, and structural properties of indium-tin-oxide thin films for organic light-emitting devices. J. Appl. Phys. 86, 6451 1999
A. Kudo, H. Yanagi, H. Hosono, H. Kawazoe: SrCu2O2: A p-type conductive oxide with wide band gap. Appl. Phys. Lett. 73, 220 1998
J.F. Moulder, W.F. Stickle, P.E. Sobol, K.D. Bomben: Handbook of X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy Perkin-Elmer Corporation Eden Prairie, MN 1992
M. Eriksson, J. Sainio, J. Lahtinen: Chromium deposition on ordered alumina films: An x-ray photoelectron spectroscopy study of the interaction with oxygen. J. Chem. Phys. 116, 3870 2002
J. Sloczynski, J. Janas, T. Machej, J. Rynkowski, J. Stoch: Catalytic activity of chromium spinels in SCR of NO with NH3. Appl. Catal. Environ. 24, 45 2000
K. Kawatsura, N. Takeshima, T. Imaoku, K. Takahiro, Y. Mokuno, Y. Horino, T. Sekioka, M. Terasawa: High-resolution x-ray spectroscopy for copper and copper oxides and a new WDX system using an ion microbeam. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res., Sect. B 193, 877 2002
B. Gillot, S. Buguet, E. Kester, C. Baubet, P. Tailhades: Cation valencies and distribution in the spinels CoxCuyMnz FeuO4+δ (δ ⩾ 0) thin films studied by x-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. Thin Solid Films 357, 223 1999
S. Asbrink, A. Waskowska, E. Talik: Distribution of metal ions and magnetic susceptibility in CuGaMnO4 spinel. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 60, 573 1999
F. Severino, J.L. Brito, J. Laine, J.L.G. Fierro, A.L. Agudo: Nature of copper active sites in the carbon monoxide oxidation on CuAl2O4 and CuCr2O4 spinel type catalysts. J. Catal. 177, 82 1998
F. Li, L.H. Zhang, D.G. Evans, X. Duan: Structure and surface chemistry of manganese-doped copper-based mixed metal oxides derived from layered double hydroxides. Colloids Surf., A 244, 169 2004
P.W. Park, J.S. Ledford: Characterization and CO oxidation activity of Cu/Cr/Al2O3 catalysts. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 37, 887 1998
J.L. Endrino, G.S. Fox-Rabinovich, A. Reiter, S.V. Veldhuis, R.E. Galindo, J.M. Albella, J.F. Marco: Oxidation tuning in AlCrN coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 201, 4505 2007
I. Pollini, A. Mosser, J.C. Parlebas: Electronic, spectroscopic and elastic properties of early transition metal compounds. Phys. Rep.-Rev. Sec. Phys. Lett. 355, 1 2001
R. Molina, G. Poncelet: Alpha-alumina-supported nickel catalysts prepared with nickel acetylacetonate. 2. A study of the thermolysis of the metal precursor. J. Phys. Chem. B 103, 11290 1999
J. Sloczynski, J. Ziolkowski, B. Grzybowska, R. Grabowski, D. Jachewicz, K. Wcislo, L. Gengembre: Oxidative dehydrogenation of propane on NixMg1–xAl2O4 and NiCr2O4 spinels. J. Catal. 187, 410 1999
Y.E. Roginskaya, O.V. Morozova, E.N. Lubnin, Y.E. Ulitina, G.V. Lopukhova, S. Trasatti: Characterization of bulk and surface composition of CoxNi1–xOy mixed oxides for electrocatalysis. Langmuir 13, 4621 1997
D. Emin: Small polarons. Phys. Today 35, 34 1982
A.J. Bosman, H.J. Vandaal: Small-polaron versus band conduction in some transition-metal oxides. Adv. Phys. 19, 1 1970
L. Degiorgi, P. Wachter, D. Ihle: Small-polaron conductivity in magnetite. Phys. Rev. B 35, 9259 1987
E.J. Verwey, P.W. Haayman, F.C. Romeijn: Physical properties and cation arrangement of oxides with spinel structures. 2. Electronic conductivity. J. Chem. Phys. 15, 181 1947
M.K. Fayek, S.S. Ata-Allah: 57Fe Mössbauer and electrical studies of the (NiO)–(Cr2O3)x–(Fe2O3)2–x system. Phys. Status Solidi A 198, 457 2003
W.J. King, A.C.C. Tseung: The reduction of oxygen on nickel-cobalt oxides—II. Correlation between crystal structure and activity of Co2NiO4 and related oxides. Electrochim. Acta 19, 493 1974
A. Zunger: Practical doping principles. Appl. Phys. Lett. 83, 57 2003
G. Xiong, J. Wilkinson, B. Mischuck, S. Tuzemen, K.B. Ucer, R.T. Williams: Control of p- and n-type conductivity in sputter deposition of undoped ZnO. Appl. Phys. Lett. 80, 1195 2002
T.K. Chen: Preparation, structure, and properties of AlCoCrCuFeNi multi-element nitride and oxide films by reactive sputtering. Ph.D. Thesis, National Dong Hwa University, Hualien, Taiwan, 2008
N. Duan, A.W. Sleight, M.K. Jayaraj, J. Tate: Transparent p-type conducting CuScO2 + x films. Appl. Phys. Lett. 77, 1325 2000
A. La Rosa-Toro, R. Berenguer, C. Quijada, F. Montilla, E. Morallon, J.L. Vazquez: Preparation and characterization of copper-doped cobalt oxide electrodes. J. Phys. Chem. B 110, 24021 2006
F.M. Pan, P.C. Stair, T.H. Fleisch: Chemisorption of pyridine and pyrrole on iron oxide surfaces studied by XPS. Surf. Sci. 177, 1 1986
S.E. Dorris, T.O. Mason: Electrical-properties and cation valencies in Mn3O4. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 71, 379 1988
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the National Science Council under Grant No. 95-2120-M-259-001 in Taiwan. The use of core facility of Nanotechnology Center in Eastern Taiwan is acknowledged. The alloy targets were provided by Prof. J.W. Yeh, National Tsing Hua University in Taiwan. We also thank Prof. C.H. Ho, National Dong Hwa University, for the electrical and Hall measurements and fruitful discussions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, TK., Wong, MS. Hard transparent conducting hex-element complex oxide films by reactive sputtering. Journal of Materials Research 23, 3075–3089 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1557/JMR.2008.0371
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/JMR.2008.0371