Abstract
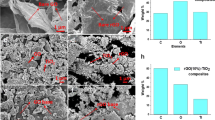
Graphene quantum dots (GQDs) of different sizes were synthesized by the top-down approach, using charcoal as the precursor material. Size and absorption characteristics of synthesized GQDs were analyzed using Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM), Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM), Photoluminescence Spectroscopy (PL), and UV-vis Spectroscopy. The results showed that GQDs with an average height of 8.5 nm, synthesized at a relatively lower temperature of 85°C, exhibited higher UV and visible light absorption. GQD concentration was varied to form 0.5, 1, 2.5, and 5 wt.% GQD-titania (TiO2) nano composites. Surface morphology of the composite was examined using Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM). Photocatalytic activity of the samples was assessed from methylene blue dye degradation in UV irradiation at 340nm. A distinguishable trend for pure TiO2 and composites at various concentrations were observed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Ni, M. K. H. Leung, D. Y. C. Leung, and K. Sumathy, “A review and recent developments in photocatalytic water-splitting using TiO2 for hydrogen production,” Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev., vol. 11, no. 3, pp. 401–425, 2007.
J. Lee, D. Kim, J. Park, Y. Cha, J. Y. Yoon, H. S. Jeon, B. K. Min, M. T. Swihart, S. Jin, S. S. Al-deyab, and S. S. Yoon, “Graphene – Titania Hybrid Photoanodes by Supersonic Kinetic Spraying for Solar Water Splitting,” vol. 3668, no. 34885, pp. 3660–3668, 2014.
P. Wang, Y. Ao, C. Wang, J. Hou, and J. Qian, “Enhanced photoelectrocatalytic activity for dye degradation by graphene - titania composite film electrodes,” J. Hazard. Mater., vol. 223–224, pp. 79–83, 2012.
K. T. Dembele, G. S. Selopal, C. Soldano, R. Nechache, J. C. Rimada, I. Concina, G. Sberveglieri, F. Rosei, and A. Vomiero, “Hybrid carbon nanotubes-TiO2 photoanodes for high efficiency dye-sensitized solar cells,” J. Phys. Chem. C, vol. 117, no. 28, pp. 14510– 14517, 2013.
A. Adán-Más and D. Wei, “Photoelectrochemical Properties of Graphene and Its Derivatives,” Nanomaterials, vol. 3, no. 3, pp. 325–356, 2013.
C. Chen, W. Cai, M. Long, B. Zhou, Y. Wu, D. Wu, and Y. Feng, “Synthesis of visible-light responsive graphene oxide/TiO2 composites with p/n heterojunction,” ACS Nano, vol. 4, no. 11, pp. 6425–6432, 2010.
D. Pan, J. Jiao, Z. Li, Y. Guo, C. Feng, Y. Liu, L. Wang, and M. Wu, “Efficient Separation of Electron-Hole Pairs in Graphene Quantum Dots by TiO2 Heterojunctions for Dye Degradation,” ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng., vol. 3, no. 10, pp. 2405–2413, 2015.
J. Lu, P. S. E. Yeo, C. K. Gan, P. Wu, and K. P. Loh, “Transforming C60 molecules into graphene quantum dots,” Nat Nano, vol. 6, no. 4, pp. 247–252, Apr. 2011.
G. Eda, Y. Y. Lin, C. Mattevi, H. Yamaguchi, H. A. Chen, I. S. Chen, C. W. Chen, and M. Chhowalla, “Blue photoluminescence from chemically derived graphene oxide,” Adv. Mater., vol. 22, no. 4, pp. 505–509, 2010.
L. Tapaszto, G. Dobrik, P. Lambin, and L. P. Biro, “Tailoring the atomic structure of graphene nanoribbons by scanning tunnelling microscope lithography,” Nat Nano, vol. 3, no. 7, pp. 397–401, Jul. 2008.
R. Ye, C. Xiang, J. Lin, Z. Peng, K. Huang, Z. Yan, N. P. Cook, E. L. G. Samuel, C. Hwang, G. Ruan, G. Ceriotti, A. O. Raji, J. M. Tour, and A. A. Martı, “Coal as an abundant source of graphene quantum dots,” Nature Communications., vol. 4, pp. 1–7, 2013.
J. Peng, W. Gao, B. K. Gupta, Z. Liu, R. Romero-Aburto, L. Ge, L. Song, L. B. Alemany, X. Zhan, G. Gao, S. A. Vithayathil, B. A. Kaipparettu, A. A. Marti, T. Hayashi, J. J. Zhu, and P. M. Ajayan, “Graphene quantum dots derived from carbon fibers,” Nano Lett., vol. 12, no. 2, pp. 844–849, 2012.
D. Tan, S. Zhou, and J. Qiu, “Comment on ‘Upconversion and Downconversion Fluorescent Graphene Quantum Dots: Ultrasonic Preparation and Photocatalysis,’” ACS Nano, vol. 6, no. 2, pp. 6530–6531, 2012.
X. Luan, M. T. Gutierrez, and Y. Wang, “Enhanced photocatalytic activity of graphene oxide / titania nanosheets composites for methylene blue degradation,” Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process., vol. 30, pp. 592–598, 2015.
S. Zhu, L. Wang, B. Li, Y. Song, X. Zhao, G. Zhang, S. Zhang, S. Lu, J. Zhang, H. Wang, H. Sun, and B. Yang, “Investigation of photoluminescence mechanism of graphene quantum dots and evaluation of their assembly into polymer dots,” Carbon N. Y., vol. 77, pp. 462–472, 2014.
H. Li, J. Xing, Z. Xia, and J. Chen, “Preparation of coaxial heterogeneous graphene quantum dots sensitized TiO2 nanotube arrays via linker molecules binding and electrophoretic,” Carbon N. Y., vol. 1, 2014.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chinnusamy Jayanthi, S., Kaur, R. & Erogbogbo, F. Graphene Quantum Dot - Titania Nanoparticle Composite for Photocatalytic Water Splitting. MRS Advances 1, 2071–2077 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1557/adv.2016.470
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/adv.2016.470