Abstract
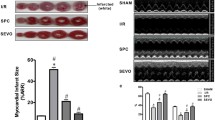
Sevoflurane postconditioning reduces myocardial infarct size. The objective of this study was to examine the role of the phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase (PI3K)/Akt pathway in anesthetic postconditioning and to determine whether PI3K/Akt signaling modulates the expression of pro- and antiapoptotic proteins in sevoflurane postconditioning. Isolated and perfused rat hearts were prepared first, and then randomly assigned to the following groups: Sham-operation (Sham), ischemia/reperfusion (Con), sevoflurane postconditioning (SPC), Sham plus 100 nmol/L wortmannin (Sham+Wort), Con+Wort, SPC+Wort, and Con+dimethylsulphoxide (DMSO). Sevoflurane postconditioning was induced by administration of sevoflurane (2.5%, v/v) for 10 min from the onset of reperfusion. Left ventricular developed pressure (LVDP), left ventricular end-diastolic pressure (LVEDP), maximum increase in rate of LVDP (+dP/dt), maximum decrease in rate of LVDP (−dP/dt), heart rate (HR), and coronary flow (CF) were measured at baseline, R30 min (30 min of reperfusion), R60 min, R90 min, and R120 min. Creatine kinase (CK) and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) were measured after 5 min and 10 min reperfusion. Infarct size was determined by triphenyltetrazolium chloride staining at the end of reperfusion. Total Akt and phosphorylated Akt (phospho-Akt), Bax, Bcl-2, Bad, and phospho-Bad were determined by Western blot analysis. Analysis of variance (ANOVA) and Student-Newman-Keuls’ test were used to investigate the significance of differences between groups. The LVDP, ±dP/dt, and CF were higher and LVEDP was lower in the SPC group than in the Con group at all points of reperfusion (P<0.05). The SPC group had significantly reduced CK and LDH release and decreased infarct size compared with the Con group [(22.9±8)% vs. (42.4±9.4)%, respectively; P<0.05]. The SPC group also had increased the expression of phospho-Akt, Bcl-2, and phospho-Bad, and decreased the expression of Bax. Wortmannin abolished the cardioprotection of sevoflurane postconditioning. Sevoflurane postconditioning may protect the isolated rat heart. Activation of PI3K and modulation of the expression of pro- and antiapoptotic proteins may play an important role in sevoflurane-induced myocardial protection.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams, J.M., Cory, S., 1998. The Bcl-2 protein family: arbiters of cell survival. Science, 281(5381):1322–1326. [doi: 10.1126/science.281.5381.1322]
Bartling, B., Holtz, J., Darmer, D., 1998. Contribution of myocyte apoptosis to myocardial infarction? Basic Res. Cardiol., 93(2):71–84. [doi:10.1007/s003950050065]
Cantley, L.C., 2002. The phosphoinositide 3-kinase pathway. Science, 296(5573):1655–1657. [doi:10.1126/science.296.5573.1655]
Cao, C.M., Xia, Q., Tu, J., Chen, M., Wu, S., Wong, T.M., 2004. Cardioprotection of interleukin-2 is mediated via kappa-opioid receptors. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther., 309(2): 560–567. [doi:10.1124/jpet.103.061135]
Chen, H.T., Yang, C.X., Li, H., Zhang, C.J., Wen, X.J., Zhou, J., Fan, Y.L., Huang, T., Zeng, Y.M., 2008. Cardioprotection of sevoflurane postconditioning by activating extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 in isolated rat hearts. Acta Pharmacol. Sin., 29(8):931–941. [doi:10.1111/j.1745-7254.2008.00824.x]
Chiari, P.C., Bienengraeber, M.W., Pagel, P.S., Krolikowski, J.G., Kersten, J.R., Warltier, D.C., 2005. Isoflurane protects against myocardial infarction during early reperfusion by activation of phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase signal transduction: evidence for anesthetic-induced postconditioning in rabbits. Anesthesiology, 102(1):102–109. [doi: 10.1097/00000542-200501000-00018]
Datta, S.R., Dudek, H., Tao, X., Masters, S., Fu, H., Gotoh, Y., Greenberg, M.E., 1997. Akt phosphorylation of Bad couples survival signals to the cell-intrinsic death machinery. Cell, 91(2):231–241. [doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(00)80405-5]
Deyhimy, D.I., Fleming, N.W., Brodkin, I.G., Liu, H., 2007. Anesthetic preconditioning combined with postconditioning offers no additional benefit over preconditioning or postconditioning alone. Anesth. Analg., 105(2):316–324. [doi:10.1213/01.ane.0000267524.71445.e7]
Feng, J., Lucchinetti, E., Ahuja, P., Pasch, T., Perriard, J.C., Zaugg, M., 2005. Isoflurane postconditioning prevents opening of the mitochondrial permeability transition pore through inhibition of glycogen synthase kinase 3beta. Anesthesiology, 103(5):987–995. [doi:10.1097/00000542-200511000-00013]
Freude, B., Masters, T.N., Kostin, S., Robicsek, F., Schaper, J., 1998. Cardiomyocyte apoptosis in acute and chronic conditions. Basic Res. Cardiol., 93(2):85–89. [doi:10.1007/s003950050066]
Freude, B., Masters, T.N., Robicsek, F., Fokin, A., Kostin, S., Zimmermann, R., Ullmann, C., Lorenz-Meyer, S., Schaper, J., 2000. Apoptosis is initiated by myocardial ischemia and executed during reperfusion. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol., 32(2):197–208. [doi:10.1006/jmcc.1999.1066]
Fujio, Y., Nguyen, T., Wencker, D., Kitsis, R.N., Walsh, K., 2000. Akt promotes survival of cardiomyocytes in vitro and protects against ischemia-reperfusion injury in mouse heart. Circulation, 101(6):660–667.
Haunstetter, A., Izumo, S., 1998. Apoptosis: basic mechanisms and implications for cardiovascular disease. Circ. Res., 82(11):1111–1129.
Hausenloy, D.J., Yellon, D.M., 2004. New directions for protecting the heart against ischaemia-reperfusion injury: targeting the reperfusion injury salvage kinase (RISK)-pathway. Cardiovasc. Res., 61(3):448–460. [doi:10.1016/j.cardiores.2003.09.024]
Hausenloy, D.J., Tsang, A., Mocanu, M.M., Yellon, D.M., 2005. Ischemic preconditioning protects by activating prosurvival kinases at reperfusion. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol., 288(2):H971–H976. [doi:10.1152/ajpheart.00374.2004]
He, W., Zhang, F.J., Wang, S.P., Chen, G., Chen, C.C., Yan, M., 2008. Postconditioning of sevoflurane and propofol is associated with mitochondrial permeability transition pore. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B, 9(2):100–108. [doi:10.1631/jzus.B0710586]
Inamura, Y., Miyamae, M., Sugioka, S., Domae, N., Kotani, J., 2010. Sevoflurane postconditioning prevents activation of caspase 3 and 9 through antiapoptotic signaling after myocardial ischemia-reperfusion. J. Anesth., 24(2): 215–224. [doi:10.1007/s00540-010-0877-6]
Kirshenbaum, L.A., de Moissac, D., 1997. The Bcl-2 gene product prevents programmed cell death of ventricular myocytes. Circulation, 96(5):1580–1585.
Krolikowski, J.G., Bienengraeber, M., Weihrauch, D., Warltier, D.C., Kersten, J.R., Pagel, P.S., 2005. Inhibition of mitochondrial permeability transition enhances isoflurane-induced cardioprotection during early reperfusion: the role of mitochondrial KATP channels. Anesth. Analg., 101(6): 1590–1596. [doi:10.1213/01.ANE.0000181288.13549.28]
Krolikowski, J.G., Weihrauch, D., Bienengraeber, M., Kersten, J.R., Warltier, D.C., Pagel, P.S., 2006. Role of Erk1/2, p70s6K, and eNOS in isoflurane-induced cardioprotection during early reperfusion in vivo. Can. J. Anaesth., 53(2):174–182. [doi:10.1007/BF03021824]
Li, D.Y., Zhang, Y.C., Philips, M.I., Sawamura, T., Mehta, J.L., 1999. Upregulation of endothelial receptor for oxidized low-density lipoprotein (LOX-1) in cultured human coronary artery endothelial cells by angiotensin II type 1 receptor activation. Circ. Res., 84(9):1043–1049. [doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1681.2008.04952.x]
Li, H., Wang, J.K., Zeng, Y.M., Yang, C.X., Chen, H.T., Wen, X.J., Shui, C.L., Liang, H., 2008. Sevoflurane postconditioning protects against myocardial reperfusion injury by activation of phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase signal transduction. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol., 35(9): 1043–1051.
Matsui, T., Tao, J., del Monte, F., Lee, K.H., Li, L., Picard, M., Force, T.L., Franke, T.F., Hajjar, R.J., Rosenzweig, A., 2001. Akt activation preserves cardiac function and prevents injury after transient cardiac ischemia in vivo. Circulation, 104(3):330–335.
Misao, J., Hayakawa, Y., Ohno, M., Kato, S., Fujiwara, T., Fujiwara, H., 1996. Expression of Bcl-2 protein, an inhibitor of apoptosis, and Bax, an accelerator of apoptosis, in ventricular myocytes of human hearts with myocardial infarction. Circulation, 94(7):1506–1512.
Nakamura, M., Wang, N.P., Zhao, Z.Q., Wilcox, J.N., Thourani, V., Guyton, R.A., Vinten-Johansen, J., 2000. Preconditioning decreases Bax expression, PMN accumulation and apoptosis in reperfused rat heart. Cardiovasc. Res., 45(3):661–670. [doi:10.1016/S0008-6363(99)00393-4]
Obal, D., Preckel, B., Scharbatke, H., Müllenheim, J., Höterkes, F., Thämer, V., Schlack, W., 2001. One MAC of sevoflurane provides protection against reperfusion injury in the rat heart in vivo. Br. J. Anaesth., 87(6): 905–911. [doi:10.1093/bja/87.6.905]
Obal, D., Dettwiler, S., Favoccia, C., Scharbatke, H., Precke, B., Schlack, W., 2005. The influence of mitochondrial KATP-channels in the cardioprotection of preconditioning and postconditioning by sevoflurane in the rat in vivo. Anesth. Analg., 101(5):1252–1260. [doi:10.1213/01.ANE.0000181336.96511.32]
Pagel, P.S., Krolikowski, J.G., Neff, D.A., Weihrauch, D., Bienengraeber, M., Kersten, J.R., Warltier, D.C., 2006. Inhibition of glycogen synthase kinase enhances isoflurane-induced protection against myocardial infarction during early reperfusion in vivo. Anesth. Analg., 102(5): 1348–1354. [doi:10.1213/01.ane.0000202379.61338.37]
Preckel, B., Schlack, W., Comfère, T., Obal, D., Barthel, H., Thämer, V., 1998. Effects of enflurane, isoflurane, sevoflurane and desflurane on reperfusion injury after regional myocardial ischaemia in the rabbit heart in vivo. Br. J. Anaesth., 81(6):905–912.
Preckel, B., Thamer, V., Schlack, W., 1999. Beneficial effects of sevoflurane and desflurane against myocardial reperfusion injury after cardioplegic arrest. Can. J. Anaesth., 46(11):1076–1081. [doi:10.1007/BF03013206]
Raphael, J., Abedat, S., Rivo, J., Meir, K., Beeri, R., Pugatsch, T., Zuo, Z., Gozal, Y., 2006. Volatile anesthetic preconditioning attenuates myocardial apoptosis in rabbits after regional ischemia and reperfusion via Akt signaling and modulation of Bcl-2 family proteins. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther., 318(1):186–194. [doi:10.1124/jpet.105.100537]
Schlack, W., Preckel, B., Stunneck, D., Thämer, V., 1998. Effects of halothane, enflurane, isoflurane, sevoflurane and desflurane on myocardial reperfusion injury in the isolated rat heart. Br. J. Anaesth., 81(6):913–919.
Steenbergen, C., Afshari, C.A., Petranka, J.G., Collins, J., Martin, K., Bennett, L., Haugen, A., Bushel, P., Murphy, E., 2003. Alterations in apoptotic signaling in human idiopathic cardiomyopathic hearts in failure. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol., 284(1):H268–H276.
Takatani, T., Takahashi, K., Uozumi, Y., Matsuda, T., Ito, T., Schaffer, S.W., Fujio, Y., Azuma, J., 2004. Taurine prevents the ischemia-induced apoptosis in cultured neonatal rat cardiomyocytes through Akt/caspase-9 pathway. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 316(2):484–489. [doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2004.02.066]
Tsang, A., Hausenloy, D.J., Mocanu, M.M., Yellon, D.M., 2004. Postconditioning: a form of “modified reperfusion” protects the myocardium by activating the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-Akt pathway. Circ. Res., 95(3):230–232. [doi:10.1161/01.RES.0000138303.76488.fe]
Tsutsumi, Y.M., Yokoyama, T., Horikawa, Y., Roth, D.M., Patel, H.H., 2007. Reactive oxygen species trigger ischemic and pharmacological postconditioning: in vivo and in vitro characterization. Life Sci., 81(15):1223–1227. [doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2007.08.031]
Uchiyama, T., Engelman, R.M., Maulik, N., Das, D.K., 2004. Role of Akt signaling in mitochondrial survival pathway triggered by hypoxic preconditioning. Circulation, 109(24): 3042–3049. [doi:10.1161/01.CIR.0000130647.29030.90]
van Heerde, W.L., Robert-Offerman, S., Dumont, E., Hofstra, L., Doevendans, P.A., Smits, J.F., Daemen, M.J., Reutelingsperger, C.P., 2000. Markers of apoptosis in cardiovascular tissues: focus on annexin V. Cardiovasc. Res., 45(3):549–959. [doi:10.1016/S0008-6363(99)00396-X]
Venkatapuram, S., Wang, C., Krolikowski, J.G., Weihrauch, D., Kersten, J.R., Warltier, D.C., Pratt, P.F.Jr., Pagel, P.S., 2006. Inhibition of apoptotic protein p53 lowers the threshold of isoflurane-induced cardioprotection during early reperfusion in rabbits. Anesth. Analg., 103(6):1400–1405. [doi:10.1213/01.ane.0000240903.63832.d8e]
Wang, C., Neff, D.A., Krolikowski, J.G., Weihrauch, D., Bienengraeber, M., Warltier, D.C., Kersten, J.R., Pagel, P.S., 2006. The influence of B-cell lymphoma 2 protein, an antiapoptotic regulator of mitochondrial permeability transition, on isoflurane-induced and ischemic postconditioning in rabbits. Anesth. Analg., 102(5):1355–1360. [doi:10.1213/01.ane.0000202463.28618.64]
Weihrauch, D., Krolikowski, J.G., Bienengraeber, M., Kersten, J.R., Warltier, D.C., Pagel, P.S., 2005. Morphine enhances isoflurane-induced postconditioning against myocardial infarction: the role of phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase and opioid receptors in rabbits. Anesth. Analg., 101(4):942–949. [doi:10.1213/01.ane.0000171931.08371.a2]
Yao, Y.T., Li, L.H., Chen, L., Wang, W.P., Li, L.B., Gao, C.Q., 2010. Sevoflurane postconditioning protects isolated rat hearts against ischemia-reperfusion injury: the role of radical oxygen species, extracellular signal-related kinases 1/2 and mitochondrial permeability transition pore. Mol. Biol. Rep., 37(5):2439–2446. [doi:10.1007/s11033-009-9755-4]
Zha, J., Harada, H., Yang, E., Jockel, J., Korsmeyer, S.J., 1996. Serine phosphorylation of death agonist BAD in response to survival factor results in binding to 14-3-3 not BCL-X(L). Cell, 87(4):619–628. [doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(00)81382-3]
Zha, J., Harada, H., Osipov, K., Jockel, J., Waksman, G., Korsmeyer, S.J., 1997. BH3 domain of BAD is required for heterodimerization with BCL-XL and pro-apoptotic activity. J. Biol. Chem., 272(39):24101–24104. [doi:10.1074/jbc.272.39.24101]
Zhao, Z.Q., Nakamura, M., Wang, N.P., Wilcox, J.N., Shearer, S., Ronson, R.S., Guyton, R.A., Vinten-Johansen, J., 2000. Reperfusion induces myocardial apoptotic cell death. Cardiovasc. Res, 45(3):651–660. [doi:10.1016/S0008-6363(99)00354-5]
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Project supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 30772090), the Natural Science Foundation of Zhejiang Province (Nos. Y204141 and R2090259), the Foundation from Science and Technology Department of Zhejiang Province (No. 2007R10034), and the Foundation from the Health Bureau of Zhejiang Province (No. 2007QN007), China
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, Ln., Yu, J., Zhang, Fj. et al. Sevoflurane postconditioning reduces myocardial reperfusion injury in rat isolated hearts via activation of PI3K/Akt signaling and modulation of Bcl-2 family proteins. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 11, 661–672 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B1000155
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B1000155