Abstract
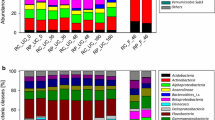
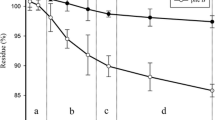
Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) are common contaminants in a municipal solid waste (MSW) composting site. Knowledge of changes in microbial structure is useful to identify particular PAH degraders. However, the microbial community in the MSW composting soil and its change associated with prolonged exposure to PAHs and subsequent biodegradation remain largely unknown. In this study, anthracene was selected as a model compound. The bacterial community structure was investigated using terminal restriction fragment length polymorphism (TRFLP) and 16S rRNA gene clone library analysis. The two bimolecular tools revealed a large shift of bacterial community structure after anthracene amendment and subsequent biodegradation. Genera Methylophilus, Mesorhizobium, and Terrimonas had potential links to anthracene biodegradation, suggesting a consortium playing an active role.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abed, R.M.M., Safi, N.M.D., Köster, J., de Beer, D., El-Nahhal, Y., Rullkötter, J., Garcia-Pichel, F., 2002. Microbial diversity of a heavily polluted microbial mat and its community changes following degradation of petroleum compounds. Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 68(4): 1674–1683. [doi:10.1128/AEM.68.4.1674-1683.2002]
Baun, A., Ledin, A., Reitzel, L.A., Bjerg, P.L., Christensen, T.H., 2004. Xenobiotic organic compounds in leachates from ten Danish MSW landfills-chemical analysis and toxicity tests. Water Res., 38(18):3845–3858. [doi:10. 1016/j.watres.2004.07.006]
Cébron, A., Beguiristain, T., Faure, P., Norini, M.P., Masfaraud, J.F., Leyval, C., 2009. Influence of vegetation on the in situ bacterial community and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon degraders in aged PAH-contaminated or thermal-desorption-treated soil. Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 75(19):6322–6330. [doi:10.1128/AEM.02862-08]
Chang, Y.T., Lee, J.F., Chao, H.P., 2007. Variability of communities and physiological characteristics between free-living bacteria and attached bacteria during the PAH biodegradation in a soil/water system. Eur. J. Soil. Biol., 43(5–6):283–296. [doi:10.1016/j.ejsobi.2007.02.012]
Chen, W.M., Zhu, W.F., Bontemps, C., Young, J.P.W., Wei, G.H., 2010. Mesorhizobium alhagi sp. nov. isolated from wild Alhagi sparsifolia in north-western China. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol., 60(4):958–962. [doi:10.1099/ijs.0.014043-0]
Clarke, K.R., Warwick, R.M., 2001. Change in Marine Communities: An Approach to Statistical Analysis and Interpretation, 2nd Ed. PRIMER-E, Plymouth Marine Laboratory, Plymouth, UK, p.172.
Cunliffe, M., Kertesz, M.A., 2006. Effect of Sphingobiumyanoikuyae B1 inoculation on bacterial community dynamics and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon degradation in aged and freshly PAH-contaminated soils. Environ. Pollut., 144(1):228–237. [doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2005.12.026]
Cupples, A.M., Sims, G.K., 2007. Identification of in situ 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid-degrading soil microorganisms using DNA-stable isotope probing. Soil Biol. Biochem., 39(1):232–238. [doi:10.1016/j.soilbio.2006.07.011]
Doronina, N.V., Trotsenko, Y.A., 1994. Methylophilus leisingerii sp. nov., a new species of restricted facultatively methylotrophic bacteria. Mikrobiologiya, 63(3):529–536.
Dunbar, J.M., Ticknor, L.O., Kuske, C.R., 2000. Assessment of microbial diversity in four southwestern United States soils by 16S rRNA gene terminal restriction fragment analysis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 66(7):2943–2950. [doi:10.1128/AEM.66.7.2943-2950.2000]
Dunbar, J.M., Ticknor, L.O., Kuske, C.R., 2001. Phylogenetic specificity and reproducibility and new method for analysis of terminal restriction fragment profiles of 16S rRNA genes from bacterial communities. Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 67(1):190–197. [doi:10.1128/AEM.67.1.190-197.2001]
Falk, M.W., Song, K.G., Matiasek, M.G., Wuertz, S., 2009. Microbial community dynamics in replicate membrane bioreactors—natural reproducible fluctuations. Water Res., 43(3):842–852. [doi:10.1016/j.watres.2008.11.021]
Feng, Y.S., Lee, C.M., 2009. The potential of the acetonitrile biodegradation by Mesorhizobium sp. F28. J. Hazard. Mater., 164(2–3):646–650. [doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008. 08.039]
Feng, Y.S., Lee, C.M., Wang, C.C., 2008. Methods for increasing nitrile biotransformation into amides using Mesorhizobium sp. Appl. Biochem. Microbiol., 44(3): 271–275. [doi:10.1134/S0003683808030071]
Gandolfi, I., Sicolo, M., Franzetti, A., Fontanarosa, E., Santagostino, A., Bestetti, G., 2010. Influence of compost amendment on microbial community and ecotoxicity of hydrocarbon-contaminated soils. Bioresource Technol., 101(2):568–575. [doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2009.08.095]
Ghosh, W., Roy, P., 2006. Mesorhizobium thiogangeticum sp. nov. a novel sulfur-oxidizing chemolithoautotroph from rhizosphere soil of an Indian tropical leguminous plant. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol., 56(1):91–97. [doi:10.1099/ijs.0.63967-0]
Goyal, A.K., Zylstra, G.J., 1996. Molecular cloning of novel genes for polycyclic hydrocarbon degradation from Comamonastestosteroni GZ39. Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 62(1):230–236.
Grant, R.J., Muckian, L.M., Clipson, N.J.W., Doyle, E.M., 2007. Microbial community changes during the bioremediation of creosote-contaminated soil. Lett. Appl. Microbiol., 44(3):293–300. [doi:10.1111/j.1472-765X.2006.02066.x]
Guo, C., Sun, J.B., Harsh, J.B., Ogram, A., 1997. Hybridization analysis of microbial DNA from fuel oil-contaminated and noncontaminated soil. Microb. Ecol., 34(3):178–187. [doi:10.1007/s002489900047]
Han, X.J., Li, L.Q., Pan, G.X., Hu, Z.L., 2009. Pollution characteristics of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in soils from farmland around the domestic refuse dump. Ecol. Environ. Sci., 18(4):1251–1255 (in Chinese).
Huang, A.H., Teplitski, M., Rathinasabapathi, B., Ma, L.N., 2010. Characterization of arsenic-resistant bacteria from the rhizosphere of arsenic hyperaccumulator Pterisvittata. Can. J. Microbiol., 56(3):236–246. [doi:10.1139/W10-005]
Huang, Y., Zhang, S.Y., Lv, M.J., Xie, S.G., 2010. Biosorption characteristics of ectomycorrhizal fungal mycelium for anthracene. Biomed. Environ. Sci., 23(5):378–383. [doi: 10.1016/S0895-3988(10)60079-7]
Hutalle-Schmelzer, K.M.L., Zwirnmann, E., Kruger, A., Grossart, H.P., 2010. Enrichment and cultivation of pelagic bacteria from a humic lake using phenol and humic matter additions. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol., 72(1):58–73. [doi:10.1111/j.1574-6941.2009.00831.x]
Jacques, R.J.S., Santos, E.C., Bento, F.M., Peralba, M., Selbach, P.A., Flá, S., Camargo, F.A.O., 2005. Anthracene biodegradation by Pseudomonas sp. isolated from a petrochemical sludge landfarming site. Int. Biodeter. Biodegr., 56(3):143–150. [doi:10.1016/j.ibiod.2005.06.005]
Jenkins, O., Byrom, D., Jones, D., 1987. Methylophilus: a new genus of methanol-utilizing bacteria. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol., 37(4):446–448. [doi:10.1099/00207713-37-4-446]
Juhasz, A.L., Britz, M.L., Stanley, G.A., 1997. Degradation of fluoranthene, pyrene, benz[a]anthracene and dibenz[a,h] anthracene by Burkholderia cepacia. J. Appl. Microbiol., 83(2):189–198. [doi:10.1046/j.1365-2672.1997.00220.x]
Krivobok, S., Miriouchkine, E., Seigle-Murandi, F., Benoit-Guyod, J.L., 1998. Biodegradation of anthracene by soil fungi. Chemosphere, 37(3):523–530. [doi:10.1016/S00 45-6535(98)00067-8]
Large, P.J., Haywood, G.W., 1981. Methylophilus methylotrophus grows on methylated amines. FEMS Microbiol. Lett., 11(2–3):207–209. [doi:10.1111/j.1574-6968.1981. tb06964.x]
Lin, D.X., Chen, W.F., Wang, F.Q., Hu, D., Wang, E.T., Sui, X.H., Chen, W.X., 2009. Rhizobium mesosinicum sp. nov. isolated from root nodules of three different legumes. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol., 59(8):1919–1923. [doi:10. 1099/ijs.0.006387-0]
Liu, H.Z., Yan, J.P., Wang, Q., Karlson, U., Zou, G., Yuan, Z.M., 2009. Biodegradation of methyl tert-butyl ether by enriched bacterial culture. Curr. Microbiol., 59(1):30–34. [doi:10.1007/s00284-009-9391-1]
Luo, C.L., Xie, S.G., Sun, W.M., Li, X.D., Cupples, A.M., 2009. Identification of a novel toluene-degrading bacterium from the candidate phylum TM7, as determined by DNA stable isotope probing. Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 75(13):4644–4647. [doi:10.1128/AEM. 00283-09]
Luo, Y.L., 2008. Study on the Degradation Characteristics and Pathway of PAH-Degrading Bacteria. PhD Thesis, Xiamen University, China (in Chinese).
MacNaughton, S.J., Stephen, J.R., Venosa, A.D., Davis, G.A., Chang, Y.J., White, D.C., 1999. Microbial population changes during bioremediation of an experimental oil spill. Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 65(8):3566–3574.
Mills, D.K., Fitzgeralda, K., Litchfielda, C.D., Gillevetb, P.M., 2003. A comparison of DNA profiling techniques for monitoring nutrient impact on microbial community composition during bioremediation of petroleum-contaminated soils. J. Microbiol. Methods, 54(1):57–74. [doi:10.1016/S0167-7012(03)00007-1]
Mu, D.Y., Scow, K.M., 1994. Effect of trichloroethylene (TCE) and toluene concentrations on TCE and toluene biodegradation and the population density of TCE and toluene degraders in soil. Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 60(7): 2661–2665.
Muckian, L.M., Grant, R.J., Clipson, N.J.W., Doyle, E.M., 2009. Bacterial community dynamics during bioremediation of phenanthrene- and fluoranthene-amended soil. Int. Biodeter. Biodegr., 63(1):52–56. [doi:10.1016/j.ibiod. 2008.04.005]
Müncnerová, D., Augustin, J., 1994. Fungal metabolism and detoxification of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons: a review. Bioresource Technol., 48(2):97–106. [doi:10. 1016/0960-8524(94)90195-3]
Nikolausz, M., Nijenhuis, I., Ziller, K., Richnow, H.H., Kasner, M., 2006. Stable carbon isotope fractionation during degradation of dichloromethane by methylotrophic bacteria. Environ. Microbiol., 8(1):156–164. [doi:10.1111/j.1462-2920.2005.00878.x]
Osborn, R.K., Haydock, P.P.J., Edwards, S.G., 2010. Isolation and identification of oxamyl-degrading bacteria from UK agricultural soils. Soil Biol. Biochem., 42(6):998–1000. [doi:10.1016/j.soilbio.2010.01.016]
Pinyakong, O., Habe, H., Supaka, N., Pinpanichkarn, P., Juntongjin, K., Yoshida, T., Furihata, K., Nojiri, H., Yamane, H., Omori, T., 2000. Identification of novel metabolites in the degradation of phenanthrene by Sphingomonas sp. strain P2. FEMS Microbiol. Lett., 191(1):115–121. [doi:10.1111/j.1574-6968.2000.tb09327.x]
Pinyakong, O., Habe, H., Omori, T., 2003. The unique aromatic catabolic genes in sphingomonads degrading polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs). J. Gen. Appl. Microbiol., 49(1):l–19. [doi:10.2323/jgam.49.1]
Piskonen, R., Nyyssönen, M., Rajamäki, T., Itävaara, M., 2005. Monitoring of accelerated naphthalene biodegradation in a bioaugmented soil slurry. Biodegradation, 16(2): 127–134. [doi:10.1007/s10532-004-4893-9]
Rees, G.N., Baldwin, D.S., Watson, G.O., Perryman, S., Nielsen, D.L., 2004. Ordination and significance testing of microbial community composition derived from terminal restriction fragment length polymorphisms: application of multivariate statistics. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek, 86(4):339–347. [doi:10.1007/s10482-005-0498-5]
Röling, W.F.M., van Breukelen, B.M., Braster, M., Goeltom, M.T., Groen, J., van Verseveld, H.W., 2000. Analysis of microbial communities in a landfill leachate polluted aquifer using a new method for anaerobic physiological profiling and 16S rDNA based fingerprinting. Microb. Ecol., 40(3):177–188. [doi:10.1007/s002480000033]
Röling, W.F.M., van Breukelen, B.M., Braster, M., Lin, B., van Verseveld, H.W., 2001. Relationships between microbial community structure and hydrochemistry in a landfill leachate-polluted aquifer. Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 67(10):4619–4629. [doi:10.1128/AEM.67.10.4619-4629.2001]
Santos, E.C., Jacques, R.J.S., Bento, F.M., do Carmo, R., Peralba, M., Selbach, P.A., Flá, S., Camargo, F.A.O., 2008. Anthracene biodegradation and surface activity by an iron-stimulated Pseudomonas sp. Bioresource Technol., 99(7):2644–2649. [doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2007.04.050]
Singh, B.K., Munro, S., Reid, E., Ord, B., Potts, J.M., Paterson, E., Millard, P., 2006. Investigating microbial community structure in soils by physiological biochemical and molecular fingerprinting methods. Eur. J. Soil Sci., 57(1):72–82. [doi:10.1111/j.1365-2389.2005.00781.x]
Tamura, K., Dudley, J., Nei, M., Kumar, S., 2007. MEGA4, molecular evolutionary genetics analysis, MEGA software version 4.0. Mol. Biol. Evol., 24(8):1596–1599. [doi:10.1093/molbev/msm092]
Teng, Y., Luo, Y.M., Sun, M.M., Liu, Z.J., Li, Z.G., Christie, P., 2010. Effect of bioaugmentation by Paracoccus sp. strain HPD-2 on the soil microbial community and removal of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons from an aged contaminated soil. Bioresource Technol., 101(10):3437–3443. [doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2009.12.088]
Tian, Y.J., Yang, H., Wu, X.J., Li, D.T., 2005. Molecular analysis of microbial community in a groundwater sample polluted by landfill leachate and seawater. J. Zhejiang Univ.-Sci. B, 6(3):165–170. [doi:10.1631/jzus.2005.B0165]
Uhlik, O., Jecna, K., Mackova, M., Vlcek, C., Hroudova, M., Demnerova, K., Paces, V., Macek, T., 2009. Biphenyl-metabolizing bacteria in the rhizosphere of horseradish and bulk soil contaminated by polychlorinated biphenyls as revealed by stable isotope probing. Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 75(20):6471–6477. [doi:10.1128/AEM.00466-09]
Vinas, M., Sabate, J., Espuny, M.J., Solanas, A.M., 2005. Bacterial community dynamics and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon degradation during bioremediation of heavily creosote-contaminated soil. Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 71(11):7008–7018. [doi:10.1128/AEM.71.11.7008-7018.2005]
Wang, Q., Garrity, G.M., Tiedje, J.M., Cole, J.R., 2007. Naïve Bayesian classifier for rapid assignment of rRNA sequences into the new bacterial taxonomy. Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 73(16):5261–5267. [doi:10.1128/AEM.00062-07]
Wani, P.A., Zaidi, A., Khan, M.S., 2009. Chromium reducing and plant growth promoting potential of Mesorhizobium species under chromium stress. Bioremediation J., 13(3):121–129. [doi:10.1080/10889860903124289]
Xu, Y.P., Zhou, Y.Q., Wang, D.H., Chen, S.H., Liu, J.X., Wang, Z.J., 2008. Occurrence and removal of organic micropollutants in the treatment of landfill leachate by combined anaerobic-membrane bioreactor technology. J. Environ. Sci., 20(11):1281–1287. [doi:10.1016/S1001-0742(08)62222-6]
Yousefi Kebria, D., Khodadadi, A., Ganjidoust, H., Badkoubi, A., Amoozegar, M.A., 2009. Isolation and characterization of a novel native Bacillus strain capable of degrading diesel fuel. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Tech., 6(3):435–442.
Yu, R., Gan, P., MacKay, A.A., Zhang, S.L., Barth, F., Smets, B.F., 2010. Presence distribution and diversity of iron-oxidizing bacteria at a landfill leachate-impacted groundwater surface water interface. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol., 71(2):260–271. [doi:10.1111/j.1574-6941.2009. 00797.x]
Yuan, S.Y., Chang, J.S., Yen, J.H., Chang, B.V., 2001. Biodegradation of phenanthrene in river sediment. Chemosphere, 43(3):273–278. [doi:10.1016/S0045-6535(00)00139-9]
Zhang, G.Y., Ling, J.Y., Sun, H.B., Luo, J., Fan, Y.Y., Cui, Z.J., 2009. Isolation and characterization of a newly isolated polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons-degrading Janibacter anophelis strain JY11. J. Hazard Mater., 172(2/3):580–586. [doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.07.037]
Zhang, S.Y., Wang, Q.F., Xie, S.G., 2011. Microbial community changes in contaminated soils in response to phenanthrene amendment. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Tech., 8(2):321–330.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Project (No. 50979002) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Sy., Wang, Qf., Wan, R. et al. Changes in bacterial community of anthracene bioremediation in municipal solid waste composting soil. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 12, 760–768 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B1000440
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B1000440