Abstract
In sports medicine, chronic hip, groin and buttock pain is a common diagnostic problem. Because of the complex anatomy of this region and the many potential neurological causes for pain, few sports clinicians have a detailed understanding of this problem. This paper discusses the clinical aspects of nerve entrapment syndromes related to sport and takes a regional approach in order to provide a diagnostic framework for the general sports physician. The various neurological syndromes are discussed and the surgical management elaborated in detail.
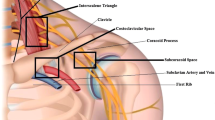
For some specific conditions, such as the so-called ‘piriformis syndrome’, the pathophysiological understanding has changed since the early descriptions and now this particular diagnosis is often ascribed to almost any cause of buttock and/or hamstring symptoms. We discuss the nature of the origin of local symptoms and note that the often described symptoms are more likely due to compression of structures other then the sciatic nerve. Furthermore, the role of piriformis hypertrophy or anatomical nerve variations in the genesis of this syndrome must be questioned. We suggest renaming this the ‘deep gluteal syndrome’ to account for all of the observed phenomena.
As sports medicine continues to develop a scientific basis, the role of nerve entrapments as the basis for chronic symptomatology is undergoing a new understanding and clinicians need to be aware of the diagnostic possibilities and be able to advise patients accordingly on the basis of scientific fact not anecdotal fiction.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brukner P, Khan KM. Clinical Sports Medicine. Sydney: McGraw-Hill, 1993
Baquie P, Brukner P. Injuries presenting to an Australian sports medicine centre. Clin J Sports Med 1997; 7: 28–32
Kannus P, Aho H, Jarvinen M, et al. Computerised recording of visits to an outpatient sports clinic. Am J Sports Med 1987; 15: 79–85
Galasko C, Monor T, Lenon G, et al. University of Manchester sports injury clinic. Br J Sports Med 1982; 16: 23–6
Witman P, Melvin M, Nicholas J. Common problems seen in a metropolitan sports injury clinic. Phys Sportsmed 1981; 9: 105–8
Fricker P, Taunton J, Ammann W. Osteitis pubis in athletes: infection, inflammation or injury? Sports Med 1991; 12 (4): 266–79
Bradshaw C, McCrory P, Bell S, et al. Obturator nerve entrapment: a cause of groin pain in athletes. Am J Sports Med 1997; 25: 402–8
Bradshaw C, McCrory P. Obturator nerve entrapment. Clin J Sports Med 1997; 7: 217–9
Stewart J. Focal peripheral neuropathies. 2nd ed. New York: Raven Press, 1993
Missoul C. Nerve Injuries. In: Dee R, editor. Principles of orthopaedic practice. New York: McGraw-Hill, 1989
Kopell HP, Thompson W. Peripheral nerve entrapments of the lower extremity. N Engl J Med 1962; 266: 16–9
Mumenthaler M, Schliack H. Peripheral nerve lesions: diagnosis and therapy. New York: Thieme, 1991
Sunderland S. Nerves and nerve injuries. 2nd ed. Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone, 1978
Stulz P, Pfeiffer KM. Peripheral nerve injuries resulting from common surgical procedures in the lower portion of the abdomen. Arch Surg 1982; 117: 324–7
Kopell H, Thompson W, Postel A. Entrapment neuropathy of the ilioinguinal nerve. N Engl J Med 1962; 266: 16–9
Knockaert D, D’Heygere FG, Bobbaers H. Ilio-inguinal nerve entrapment: a little known cause of iliac fossa pain. Postgrad Med J 1989; 65: 632–5
Hahn L. Clinical findings and results of operative treatment in ilio-inguinal nerve entrapment syndrome. Br J Obstet Gynaecol 1989; 96: 1080–3
Bohm E, Fiorillo A, Pellettieri L. Ilio-inguinal neuralgia: a forgotten disease. Acta Neurol Scand 1979; 34: 33–8
Smith C, DeLee J, Ramamurthy S. Ilioinguinal neuralgia following iliac bone grafting: report of two cases and review of the literature. J Bone Joint Surg 1984; 66A: 1306–8
Dawson D, Hallett M, Millender L. Entrapment Neuropathies. Boston: Little Brown and Co., 1963
Nakano K. The entrapment neuropathies. Muscle Nerve 1978; 1: 264–79
Starling J, Harms BA, Schroeder M, et al. Diagnosis and treatment of genitofemoral and ilioinguinal entrapment neuralgia. Surgery 1987; 102: 581–6
Winer JB, Harrison M. Iatrogenic nerve injuries. Postgrad Med J 1982; 58: 142–5
Komar J. Das Ilioinguinalis Syndrom. Nervenarzt 1971; 42: 637–40
Lichtenstein I, Schulman A, Amid P, et al. Cause and prevention of postherniorraphy neuralgia: a proposed protocol for treatment. Am J Surg 1988; 155: 786–90
Purves J, Miller J. Inguinal neuralgia: a review of 50 patients. Can J Surg 1986; 29: 43–5
Sippo W, Gomez A. Nerve entrapment syndromes from lower abdominal surgery. J Fam Pract 1987; 25: 585–7
Miyazaki F, Shook G. Ilioinguinal nerve entrapment during needle suspension for stress incontinence. Obstet Gynaecol 1992; 80: 246–8
Starling J, Harms B. Diagnosis and treatment of genitofemoral and ilioinguinal neuralgia. World J Surg 1989; 13: 586–91
McGee R. Genitofemoral causalgia (a new syndrome). Can Med Assoc J 1942; 46: 326–9
Lyon E. Genitofemoral causalgia. Can Med Assoc J 1945; 53: 213–6
Laha R, Rao S, Pidgeon C. Genitofemoral neuralgia. Surg Neurol 1977; 8: 280–2
O’Brien M. Genito-femoral neuropathy. BMJ 1979; 1: 1052
Romanes GJ. Cunningham’s manual of practical anatomy. Vol. 1. London: Oxford University Press, 1976
Clark JM. Obstetrical palsy. J Bone Joint Surg 1956; 47B: 806
Silski J, Scott R. Obturator nerve palsy resulting from intrapelvic extrusion of cement during total hip arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg 1985; 67A: 1225–30
Weber E, Daube J, Coventry M. Peripheral neuropathies associated with total hip arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg 1976; 58A: 66–73
Sowell A, Ljungdahl I, Spanger L. Thigh neuralgia as a symptom of obturator hernia. Acta Chir Scand 1976; 142: 457–9
Kozlowski JM, Beck JM. Obturator hernia: an elusive diagnosis. Arch Surg 1977; 112: 1001–2
Williams P, Trzil K. Management of meralgia paraesthetica. J Neurosurg 1991; 74: 76–80
Stookey B. Meralgia parasthetica: etiology and surgical treatment. JAMA 1928; 90: 1705–7
Stevens H. Meralgia paraesthetica. Arch Neurol Psychiatr 1957; 77: 557–74
Jefferson D, Eames R. Subclinical entrapment of the lateral femoral cutaneous nerve: an autopsy study. Muscle Nerve 1979; 2: 145–54
McGregor J, Moncur J. Meralgia paraesthetica: a sport lesion in girl gymnasts. Br J Sports Med 1977; 11: 16–7
Ecker A, Woltman H. Meralgia paraesthetica: a report of 150 cases. JAMA 1938; 110: 1650–2
Fulton J. Harvey Cushing: a biography. Springfield (IL): Charles C Thomas, 1946
van Eerten F, Polder T, Broere C. Operative treatment of meralgia paraesthetica: transection versus neurolysis. Neurosurg 1995; 37: 63–5
Nahabedian M, Dellon A. Meralgia paraesthetica: aetiology, diagnosis and outcome of surgical decompression. Ann Plast Surg 1995; 25: 590–4
Aldrich E, van den Heever C. Suprainguinal ligament approach for the surgical treatment of meralgia paraesthetica. J Neurosurg 1989; 70: 492–4
Fraser D, Campbell I, Ewing D. Mononeuropathy in diabetes mellitus. Diabetes 1979; 28: 96–101
Goodman J. Femoral neuropathy in relation to diabetes mellitus. Diabetes 1954; 3: 266–73
Coppack S, Watkins P. The natural history of diabetic femoral neuropathy. Q J Med 1991; 79: 307–13
Allen R, Hosker G, Smith A, et al. Pelvic floor damage and childbirth: a neurophysiological study. Br J Obstet Gynaecol 1990; 97: 770–9
Hofmann A, Jones R, Schoenvogel R. Pudendal nerve neuropraxia as a result of traction on the fracture table. J Bone Joint Surg 1982; 64A: 136–8
Goodson J. Pudendal neuritis from biking [letter]. N Engl J Med 1981; 304: 365
Desai K, Gingell J. The hazards of long distance cycling. BMJ 1989; 298: 1072–3
Hinman F. Atlas or uro-surgical anatomy. Philadelphia (PA): WB Saunders & Co., 1993
Arnoldussen W, Korten J. Pressure neuropathy of the posterior femoral cutaneous nerve. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 1982; 82: 57–60
Muller-Vahl H. Isolated complete paralysis of the tensor fascia latae muscle. Eur Neurol 1985; 2: 289–91
Rask M. Superior gluteal nerve entrapment syndrome. Muscle Nerve 1980; 3: 304–7
Pecina M, Krmpotic-Nemanic J, Markiewitz A. Tunnel syndromes: peripheral nerve compression syndromes. 2nd ed. Boca Raton (FL): CRC Press, 1997
Pecina M. Contribution to the etiological explanation of the piriformis syndrome. Acta Anat 1979; 105: 181–7
LaBan M, Meerschaert J, Taylor R. Electromyographic evidence of inferior gluteal nerve compromise; an early representation of recurrent colo-rectal carcinoma. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 1982; 63: 33–5
Stohr M. Traumatic and postoperative lesions of the lumbosacral plexus. Arch Neurol 1978; 35: 757–60
Puranen J, Orava S. The hamstring syndrome. A new diagnosis of gluteal sciatic pain. Am J Sports Med 1988; 16: 517–21
Yeoman W. The relationship of arthritis of the sacro-iliac joint to sciatica. Lancet 1928; II: 1119–22
Freiburg A, Vinkle T. Sciatica and the sacro-iliac joint. J Bone Joint Surg 1934; 16: 126–36
Fishman L, Zybert P. Electrophysiologic evidence of piriformis syndrome. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 1992; 73: 359–64
Synek V. Short latency somatosensory evoked potentials in patients with painful dysaesthesias in peripheral nerve lesions. Pain 1987; 29: 49–58
Vandertop W, Bosma N. The piriformis syndrome. J Bone Joint Surg 1991; 73A: 1095–7
Durrani Z, Winnie A. The piriformis muscle syndrome: an under diagnosed cause of sciatica. J Pain Symptom Manage 1991; 6: 374–9
Solheim L, Siewers P, Paus B. The piriformis muscle syndrome. Acta Orthop Scand 1981; 52: 73–5
Binnie C, Cooper R, Fowler C, et al. Clinical neurophysiology. Oxford: Butterworth-Heinemann, 1995
Kimura J. Electrodiagnosis in diseases of nerve and muscles: principles and practice. 2nd ed. Philadelphia: FA Davis, 1989
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
McCrory, P., Bell, S. Nerve Entrapment Syndromes as a Cause of Pain in the Hip, Groin and Buttock. Sports Med 27, 261–274 (1999). https://doi.org/10.2165/00007256-199927040-00005
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2165/00007256-199927040-00005