Summary
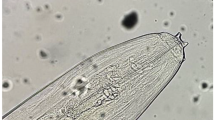
Based on morphometric findings and polymerase chain reaction amplification of internal transcribed spacer regions (ITSs), the worms and eggs retrieved from sloth bear (Melursus ursinus) kept at Mahendra Mohan Choudhury Zoological Park, Chhatbir (Punjab, India) were delineated as Baylisascaris transfuga. Therapeutic intervention with fenbendazole à 10 mg/kg body weight for three consecutive days, associated with complete disinfection of the enclosures, proved to be effective for the first few days with the reduction of eggs per gram (EPG) of faeces from 2800 (zero day) to 400 (14.28 %), 700 (25 %) and 800 (28.57 %) on days 1, 4 and 7 post treatments, respectively. The intensity of EPG increased to 2400 (85.71 %) on day 21 post treatment with respect to day zero. A modified schedule with fenbendazole à 15 mg/kg body weight for first three days followed by 10 mg/kg body weight for next three days proved to be effective thus indicating the development of resistance. The study places on record the molecular characterisation of B. transfuga from sloth bears and development of resistance against fenbendazole.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arizono, N., Yoshimura, Y., Tohzaka, N., Yamada, M., Tegoshi, T. (2010): Ascariasis in Japan: is pig- derived Ascaris infecting humans?. Japn. J. Infect. Dis., 63: 447–448
Bauer, C. (2013): Baylisascariosis — Infections of animals and humans with unusual roundworms. Vet. Parasitol., 193: 404–412. DOI: 10.1016/j.vetpar.2012.12.036
Baylis, H. A., Daubney, R. (1922): Report on the parasitic nematodes in the collection of the zoological survey of India. Mem. Indian Mus., 7: 263–347
Coles, G. C., Watson, C. L., Anziani, O. S. (2001): Ivermectin-resistant Cooperia in cattle. Vet. Rec., 148: 283–284
Couturier, M. (1954): L’Ours Brun. Cours Jean Jaures, Grenoble, France
Dangoudoubiyam, S., Vemulapalli, R., Kazakos, K. R. (2009): PCR assays for detection of 283 Baylisascaris procyonis eggs and larvae. J. Parasitol., 95: 571–577
de Ambrogi, M., Aghazadeh, M., Hermosilla, C., Huber, D., Majnaric, D. Reljic, S., Elson-Riggins, J. (2011): Occurrence of Baylisascaris transfuga in wild populations of European brown bears (Ursus arctos) as identified by a new PCR method. Vet. Parasitol., 179: 272–276. DOI: 10.1016/j.vetpar.2011.02.025
Foster, G. W., Cunningham, M. W., Kinsella, J. M., Forrester, D. J. (2004): Parasitic helminths in black bear cubs (Ursus americanus) from Florida. J. Parasitol., 90: 173–175. DOI: 10.1645/GE-1905.1
Franssen, F., Xie, K., Sprong, H., Van Der Geissen, J. (2013): Molecular analysis of Baylisascaris columnaris revealed molecular and nuclear polymorphisms. Parasit. Vectors, 6: 124. DOI: 10.1186/1756-3305-6-124
Galvan, N., Middleton, J. R., Nagy, D. W., Schultz, L. G., Schaeffer, J. W. (2012): Anthelmintic resistance in a herd of alpacas (Vicugna pacos). Can. Vet. J., 53: 1310–1313
Garretson, P. D., Hammond, E. E., Craig, T. M., Holman, P. J. (2009): Anthelmintic resistant Haemonchus contortus in a giraffe (Giraffa camelopardalis) in Florida. J. Zoo. Wildl. Med., 40: 131–139. DOI:10.1638/2007-0094.1
Gerwert, S., Failing, K., Bauer, C. (2002): Prevalence of levamisole and benzimidazole resistance in Oesophagostomum populations of pig-breeding farms in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. Parasitol Res., 88: 63–68. DOI: 10.1007/s004360100507
Islam, S., Nashiruddullah, N. (2000): Baylisascaris transfuga from a Himalayan black bear (Selenarctos thibetinus). J. Vet. Parasitol., 14: 81–82
Kazacos, K. R., Turek, J. J. (1983): Scanning electron microscopy of the eggs of Baylisascaris procyonis, Baylisascaris transfuga and Parascaris equorum, and their comparison with Toxocara canis and Ascaris suum. P. Helm. Soc.Washington, 50: 36–42
Matoff, K., Komandarev, S. (1965): Comparative studies on the migration of the larvae of Toxascaris leonina and Toxascaris transfuga. Z. Parasitenkd., 25: 538–555
Moudgil, A. D., Singla, L. D., Singh, M. P. (2014): In vitro study targeting on developmental embryonation pattern of eggs of ascarid species of wild animals. Appl. Biol. Res., 16: (In press)
Nashiruddullah, N., Chakraborty, A. (2001): Parasites of captive wild carnivores of Assam State Zoo. Intas Polivet, 2: 173–81
Owen, J., Slocombe, D., Coté, J. F., de Gannes, R. V. G. (2008): The persistence of benzimidazole-resistant cyathostomes on horse farms in Ontario over 10 years and the effectiveness of ivermectin and moxidectin against these resistant strains. Can. Vet. J., 49: 56–60
Papini, R., Cavicchio, P., Casarosa, L. (1990): Baylisascaris transfuga found in captive polar bears (Thalarctos maritimus) in Italy. Ann. Fac. Med. Vet. Univ. Pisa, 43: 151–155
Papini, R., Cavicchio, P., Casarosa, L. (1993): Experimental infection in chickens with larvae of Baylisascaris transfuga (Nematoda: Ascaridoidea). Folia Parasitol., 40: 141–143
Papini, R., Cavicchio, P., Casarosa, L. (1994a): In vivo ovicidal effect of mebendazole on Baylisascaris transfuga eggs. Recl. Med. Vet., 1: 55–57
Papini, R., Malloggi, M., Cavicchio, P., Casarosa, L. (1994b): Observations on the development of Baylisascaris transfuga eggs. Helminthologia, 31: 5–7
Papini, R., Renzoni, G., Malloggi, M., Casarosa, L. (1994c): Visceral larva migrans in mice experimentally infected with Baylisascaris transfuga (Ascarididae: Nematoda). Parasitologia, 36: 321–329
Papini, R., Renzoni, G., Lo Piccolo, S., Casarosa, L. (1996): Ocular larva migrans and histopathological lesions in mice experimentally infected with Baylisascaris transfuga embryonated eggs. Vet. Parasitol., 61: 315–320. DOI: 10.1016/0304-4017(95)00825-X
Rogers, L. L., Rogers, S. M. (1976): Parasites of bears: a review. Int. Conf. Bear Res. Manage., 3: 411–430
Sato, H., Matsuo, K., Osanai, A., Kamiya, H., Akao, N., Owaki, S., Furuoka, H. (2004): Larva migrans by Baylisascaris transfuga: fatal neurological diseases in Mongolian jirds, but not in mice. J. Parasitol., 90: 774–781. DOI: 10.1645/GE-3330
Sato, H., Une, Y., Kawakami, S., Saito, E., Kamiya, H., Akao, N., Furuoka, H. (2005): Fatal Baylisascaris larva migrans in a colony of Japanese macaques kept by a safaristyle zoo in Japan. J. Parasitol., 91: 716–719. DOI: 10.1645/GE-3374RN
Singh, P., Gupta, M. P., Singla, L. D., Singh, N., Sharma, D. R. (2009): Prevalence and chemotherapy of gastrointestinal helminthic infections in wild carnivores of Mahendra Choudhury Zoological Park, Punjab. J. Vet. Parasitol., 20: 17–23
Soulsby, E. J. L. (1982): Helminths, Arthropods and Protozoa of Domesticated Animals. 7th Edition, Bailliére-Tindall, London
Sprent, J. F. A. (1968): Notes on Ascaris and Toxascaris with a definition of Baylisascaris gen. nov. Parasitology, 58: 185–198
Sutherland, I. A., Leathwick, D. M. (2011): Anthelmintic resistance in nematode parasites of cattle: a global issue?. Trends Parasitol., 27: 176–181. DOI: 10.1016/j.pt.2010.11.008
Sutherland, I. A., Lee, D. L., Lewis, D. (1988): Detection of benzimidazole resistance in trichostrongylid nematodes. Trends Parasitol., 4: 22–24. DOI: 10.1016/0169-4758(88)90055-5
Tamura, K., Peterson, D., Peterson, N., Stecher, G., Nei, M., Kumar, S. (2011): MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol. Biol. Evol., 28: 2731–2739. DOI: 10.1093/molbev/msr121
Testini, G., Papini, R., Lia, R. P., Parisi, A., Dantastorres, F., Traversa, D., Otranto, D. (2011): New insights into the morphology, molecular characterization and identification of Baylisascaris transfuga (Ascaridida, Ascarididae). Vet. Parasitol., 175: 97–102. DOI: 10.1016/j.vetpar.2010.09.017
Traversa, D., Giangaspero, A., Iorio, R., Otranto, D., Paoletti, B., Gasser, R. B. (2004): Semi-nested PCR for the specific detection of Habronema microstoma or Habronema muscae DNA in horse faeces. Parasitology, 129: 733–739
Zajac, A. M. (1994): Fecal examination in the diagnosis of parasitism. In: Sloss, M. W., Kemp, R. L., Zajac, A. M. (Eds.), Veterinary Clinical Parasitology. Iowa State University Press, Ames, IA, pp. 3–88
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Moudgil, A.D., Singla, L.D. & Singh, M.P. First report on molecular identification and fenbendazole resistance against Baylisascaris transfuga infection in Melursus ursinus (sloth bear). Helminthologia 51, 262–268 (2014). https://doi.org/10.2478/s11687-014-0239-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2478/s11687-014-0239-2