Abstract
This paper considers \(\ell ^1\)-based regularized signal estimation that are often used in applications. The estimated signal is obtained as the solution of an optimization problem and the quality of the recovered signal directly depends on the quality of the solver. This paper describes a simple algorithm that computes an exact minimizer of \( \Vert D \cdot \Vert _1\) under the constraints \(A\mathbf {x}=\mathbf {y}\). A comparative evaluation of the algorithm is presented. An illustrative application to real signals of bacterial flagellar motor is also presented.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
References
Beck, A., Teboulle, M.: A fast iterative shrinkage-thresholding algorithm for linear inverse problems. SIAM J. Imaging Sci. 2(1), 183–202 (2009)
Blumensath, T., Davies, M.E.: Iterative hard thresholding for compressed sensing. Appl. Comput. Harmonic Anal. 27(3), 265–274 (2009)
Bonnans, J.F., Gilbert, J.C., Lemaréchal, C., Sagastizábal, C.A.: Numerical Optimization: Theoretical and Practical Aspects. Springer, Heidelberg (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-35447-5
Burger, M., Möller, M., Benning, M., Osher, S.: An adaptive inverse scale space method for compressed sensing. Math. Comput. 82(281), 269–299 (2013)
Cai, J.F., Osher, S., Shen, Z.: Linearized bregman iterations for compressed sensing. Math. Comput. 78(267), 1515–1536 (2009)
Candes, E.J., Tao, T.: Decoding by linear programming. IEEE Trans. Inform. Theory 51(12), 4203–4215 (2005)
Candes, E.J., Tao, T.: Near-optimal signal recovery from random projections: universal encoding strategies? IEEE Trans. Inform. Theory 52(12), 5406–5425 (2006)
Chen, S.S., Donoho, D.L., Saunders, M.A.: Atomic decomposition by basis pursuit. SIAM Rev. 43(1), 129–159 (2001)
Ciril, I., Darbon, J., Tendero, Y.: A simple and exact algorithm to solve l1 linear problems - application to the compressive sensing method. In: Proceedings of the 13th International Joint Conference on Computer Vision, Imaging and Computer Graphics Theory and Applications - Volume 4: VISAPP, pp. 54–62. INSTICC, SciTePress (2018)
Dai, W., Milenkovic, O.: Subspace pursuit for compressive sensing signal reconstruction. IEEE Trans. Inform. Theory 55(5), 2230–2249 (2009)
Donoho, D.L.: Compressed sensing. IEEE Trans. Inform. Theory 52(4), 1289–1306 (2006)
Donoho, D.L., Elad, M.: Optimally sparse representation in general (nonorthogonal) dictionaries via \(\ell 1\) minimization. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 100(5), 2197–2202 (2003)
Foucart, S.: Stability and robustness of weak orthogonal matching pursuits. In: Bilyk, D., De Carli, L., Petukhov, A., Stokolos, A., Wick, B. (eds.) Recent Advances in Harmonic Analysis and Applications, vol. 25, pp. 395–405. Springer, New York (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4614-4565-4_30
Grant, M.C., Boyd, S.P.: The CVX Users’ Guide, Release 2.1
Hale, E.T., Yin, W., Zhang, Y.: A fixed-point continuation method for l1-Regularized minimization with applications to compressed sensing. CAAM Technical Report TR07-07 (2007)
Hiriart-Urruty, J.B., Lemarechal, C.: Convex Analysis and Minimization Algorithms II: Advanced Theory and Bundle Methods. Grundlehren der mathematischen Wissenschaften. Springer, Heidelberg (1996)
Jain, P., Tewari, A., Dhillon, I.S.: Orthogonal matching pursuit with replacement. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, pp. 1215–1223 (2011)
Maleki, A.: Coherence analysis of iterative thresholding algorithms. In: 47th Annual Allerton Conference on Communication, Control, and Computing, Allerton, pp. 236–243. IEEE (2009)
Mallat, S., Zhang, Z.: Matching pursuits with time-frequency dictionaries. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 41(12), 3397–3415 (1993)
Moeller, M., Zhang, X.: Fast sparse reconstruction: greedy inverse scale space flows. Math. Comput. 85(297), 179–208 (2016)
Needell, D., Tropp, J.A.: CoSaMP: iterative signal recovery from incomplete and inaccurate samples. Appl. Comput. Harmonic Anal. 26(3), 301–321 (2009)
Needell, D., Vershynin, R.: Uniform uncertainty principle and signal recovery via regularized orthogonal matching pursuit. Found. Comput. Math. 9(3), 317–334 (2009)
Nirody, J.A., Sun, Y.R., Lo, C.J.: The biophysicist’s guide to the bacterial flagellar motor. Adv. Phys.: X 2(2), 324–343 (2017)
Osher, S., Burger, M., Goldfarb, D., Xu, J., Yin, W.: An iterative regularization method for total variation-based image restoration. Multiscale Model. Simul. 4(2), 460–489 (2005)
Osher, S., Mao, Y., Dong, B., Yin, W.: Fast linearized bregman iteration for compressive sensing and sparse denoising. arXiv preprint arXiv:1104.0262 (2011)
Pati, Y.C., Rezaiifar, R., Krishnaprasad, P.: Orthogonal matching pursuit: recursive function approximation with applications to wavelet decomposition. In: Conference Record of The Twenty-Seventh Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems and Computers, pp. 40–44. IEEE (1993)
Sowa, Y., et al.: Direct observation of steps in rotation of the bacterial flagellar motor. Nature 437(7060), 916 (2005)
Tropp, J.A., Gilbert, A.C.: Signal recovery from random measurements via orthogonal matching pursuit. IEEE Trans. Inform. Theory 53(12), 4655–4666 (2007)
Zhang, X., Burger, M., Osher, S.: A unified primal-dual algorithm framework based on bregman iteration. J. Sci. Comput. 46(1), 20–46 (2011)
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Y. Sowa for the flagellar motor data used in our experiments. We also would like to thank M. Möller for providing the implementation of the AISS and GISS algorithms.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Appendix
Appendix
1.1 A.1 Notations and Definitions
- (i) :
-
(n first integers)
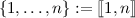
- (ii) :
-
(Vectors) Vectors of, e.g., \(\mathbb {R}^n\) are denoted in bold typeface, e.g., \(\mathbf {x}\). Other objects like scalars or functions are denoted in non-bold typeface. Entries of \(\mathbf {x}\) are denoted, e.g., \(x_i\)
- (iii) :
-
(Norms) \(\Vert \mathbf {x}\Vert _1:=\sum _i |x_i|\), \(\Vert \mathbf {x}\Vert _2:= \sqrt{ \sum _i |x_i|^2}\) and \(\Vert \mathbf {x}\Vert _\infty := \max _i|x_i|\)
- (iv) :
-
(Canonical basis) \( \mathbf {e}_i \) denotes the i-th canonical vector of \( \mathbb {R}^n,\) and \( \mathbf {\tilde{e}}_i \) denotes the i-th canonical vector of \( \mathbb {R}^{2n}\)
- (v) :
-
(Inner product) \(\langle \mathbf {x}, \mathbf {y}\rangle =\sum _i x_i y_i\)
- (vi) :
-
(Identity matrix) \( I_n \) denotes de identity matrix of size \( n \times n\)
- (vii) :
-
(Transpose operator) \(M^\dagger \) denotes the transpose of a matrix M
- (viii) :
-
(Column of matrix) col(M, i) denotes the i-th column of matrix M
- (ix) :
-
(Convex function) A function \(f :\mathbb {R}^n \rightarrow \mathbb {R}\cup \{+\infty \}\) is said to be convex if \(\forall (\mathbf {x},\mathbf {y}) \in \mathbb {R}^n \times \mathbb {R}^n\) and \(\forall \alpha \in (0,1)\)
 holds true (in \( \mathbb {R}\cup \{+\infty \}\))
holds true (in \( \mathbb {R}\cup \{+\infty \}\)) - (x) :
-
(Set \(\varGamma _0(\mathbb {R}^n)\)) The set of lower semi-continuous, convex functions with \(\text {dom~}f \ne \emptyset \) is denoted by \(\varGamma _0(\mathbb {R}^n)\)
- (xi) :
-
(Characteristic function of a set) \(\chi _{E}(\mathbf {x})=0\) if \(\mathbf {x}\in E\) and \(\chi _{E}(\mathbf {x})=+\infty \) otherwise
- (xii) :
-
(Convex conjugate) For any f convex that satisfies \(\text {dom~}f \ne \emptyset \), the function \(f^*\) defined by \(\mathbb {R}^n \ni \mathbf {s}\mapsto f^*(\mathbf {s}):=\sup _{\mathbf {x}\in \text {dom~}f}\left\{ \langle \mathbf {s},\mathbf {x}\rangle -f(\mathbf {x}) \right\} \). (See, e.g., [16, Def. 1.1.1, p. 37])
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2019 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Tendero, Y., Ciril, I., Darbon, J. (2019). A Simple and Exact Algorithm to Solve Linear Problems with \(\ell ^1\)-Based Regularizers. In: Bechmann, D., et al. Computer Vision, Imaging and Computer Graphics Theory and Applications. VISIGRAPP 2018. Communications in Computer and Information Science, vol 997. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-26756-8_12
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-26756-8_12
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-26755-1
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-26756-8
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)


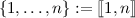
 holds true (in
holds true (in