Abstract
The vast and fast-growing STEM literature makes it imperative to develop systems for automated math-semantics extraction from technical content, and for semantically-enabled processing of such content. Grammar-based techniques alone are inadequate for the task. We present a new project for using deep learning (DL) for that purpose. It will explore a number of DL and representation-learning models, which have shown superior performance in applications that involve sequences of data. As math and science involve sequences of text, symbols and equations, such as deep learning models are expected to deliver good performance in math-semantics extraction and processing.
The project has several goals: (1) to apply different DL models to math-semantics extraction and processing, designing more suitable models as needed, for such foundational tasks as accurate tagging and automated translation from  to semantically-resolved machine understandable forms such as cMathML; (2) to create and make available to the public labeled math-content datasets for model training and testing, and Word2Vec/Math2Vec representations derived from large math datasets; and (3) to conduct extensive comparative performance evaluations gaining insights into which DL models, data representations, and traditional machine learning models, are best for the above-stated goals.
to semantically-resolved machine understandable forms such as cMathML; (2) to create and make available to the public labeled math-content datasets for model training and testing, and Word2Vec/Math2Vec representations derived from large math datasets; and (3) to conduct extensive comparative performance evaluations gaining insights into which DL models, data representations, and traditional machine learning models, are best for the above-stated goals.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Notes
- 1.
arXiv.org, https://arxiv.org/.
- 2.
NIST Digital Library of Mathematical Functions (DLMF) https://dlmf.nist.gov/.
- 3.
(World) Digital Mathematics Library, https://www.math.unibielefeld.de/~rehmann/DML/dml_links.html.
- 4.
The European Digital Mathematics Library, https://eudml.org/.
- 5.
Göttinger Digitalisierungszentrum, http://gdz.sub.uni-goettingen.de/gdz/.
- 6.
The database MathSciNet, http://www.ams.org/mathscinet/.
- 7.
The database zbMATH, http://www.zentralblatt-math.org/zbmath/.
- 8.
- 9.
References
Altman, N.S.: An introduction to kernel and nearest-neighbor nonparametric regression. Am. Stat. 46(3), 175–185 (1992)
Bengio, Y.: Deep learning of representations: looking forward. In: Dediu, A.-H., Martín-Vide, C., Mitkov, R., Truthe, B. (eds.) SLSP 2013. LNCS (LNAI), vol. 7978, pp. 1–37. Springer, Heidelberg (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-39593-2_1
Bordes, A., Glorot, X., Weston, J., Bengio, Y.: Joint learning of words and meaning representations for open-text semantic parsing. In: AISTATS (2012)
Bengio, Y., LeCun, Y., Hinton, G.: Deep learning. Nature 521, 436–444 (2015)
Breiman, L.: Random forests. Mach. Learn. 45(1), 5–32 (2001)
Carette, J., Farmer, W.M.: A review of mathematical knowledge management. In: Carette, J., Dixon, L., Coen, C.S., Watt, S.M. (eds.) CICM 2009. LNCS (LNAI), vol. 5625, pp. 233–246. Springer, Heidelberg (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-02614-0_21
Chung, J., Gülçehre, Ç., Cho, K., Bengio, Y.: Gated feedback recurrent neural networks. In: ICML (2015)
Cho, K., Van Merriënboer, B., Bahdanau, D., Bengio, Y.: On the properties of neural machine translation: Encoder-decoder approaches. ArXiv e-prints, abs/1409.1259 (2014)
Cho, K., van Merriënboer, B., Gulcehre, C., Bougares, F., Schwenk, H., Bengio, Y.: Learning phrase representations using RNN encoder-decoder for statistical machine translation. In: The Empiricial Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP 2014) (2014)
Cortes, C., Vapnik, V.: Support-vector networks. Mach. Learn. 20(3), 273–297 (1995)
Cohl, H.S., et al.: Semantic preserving bijective mappings of mathematical formulae between document preparation systems and computer algebra systems. In: Geuvers, H., England, M., Hasan, O., Rabe, F., Teschke, O. (eds.) CICM 2017. LNCS (LNAI), vol. 10383, pp. 115–131. Springer, Cham (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-62075-6_9
Devlin, J., Zbib, R., Huang, Z., Lamar, T., Schwartz, R., Makhoul, J.: Fast and robust neural network joint models for statistical machine translation. In: Proceedings of the ACL 2014 (2014)
Goodfellow, I., Bengio, Y., Courville, A.: Deep Learning. MIT Press, Cambridge (2016)
Garcia, S., Derrac, J., Cano, J., Herrera, F.: Prototype selection for nearest neighbor classification: taxonomy and empirical study. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 34(3), 417–435 (2012)
Ginev, D., Jucovschi, C., Anca, S., Grigore, M., David, C., Kohlhase, M.: An architecture for linguistic and semantic analysis on the arXMLiv corpus. In: Applications of Semantic Technologies (AST) Workshop at Informatik (2009)
Gao, L., et al.: Preliminary exploration of formula embedding for mathematical information retrieval: can mathematical formulae be embedded like a natural language? arXiv:1707.05154 (2017)
Graves, A.: Supervised Sequence Labelling with Recurrent Neural Networks. SCI. Springer, Heidelberg (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-24797-2
Guidi, F., Sacerdoti Coen, C.: A survey on retrieval of mathematical knowledge. In: Kerber, M., Carette, J., Kaliszyk, C., Rabe, F., Sorge, V. (eds.) CICM 2015. LNCS (LNAI), vol. 9150, pp. 296–315. Springer, Cham (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-20615-8_20
Hastie, T.: The Elements of Statistical Learning: Data Mining, Inference, and Prediction, 2nd edn. Springer, New York (2013)
Lau, J.H., Baldwin, T.: An empirical evaluation of doc2vec with practical insights into document embedding generation. In: 1st Workshop on Representation Learning for NLP (2016)
Hochreiter, S., Schmidhuber, J.: Long short-term memory. Neural Comput. 9(8), 1735–1780 (1997)
Jurafsky, D., Martin, J.H.: Speech and Language Processing. Pearson Education, London (2009)
Kim, Y.: Convolutional neural networks for sentence classification. In: Conference on Empirical Methods in NLP, October 2014, Doha, Qatar, pp. 1746–1751 (2014)
Kohlhase, M.: Semantic markup for mathematical statements. v1.2 (2016)
Kottwitz, S.:
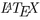 Beginner’s Guide. PACKT Publishing, Birmingham (2001)
Beginner’s Guide. PACKT Publishing, Birmingham (2001)Kstovski, K., Blei, D.M.: Equation Embeddings, March 2018. https://arxiv.org/abs/1803.09123
LeCun, Y., Kavukcuoglu, K., Farabet, C.: Convolutional networks and applications in vision. In: 2010 IEEE Internatioanl Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS), pp. 253–256 (2010)
Lai, S., Liu, K., He, S., Zhao, J.: How to generate a good word embedding. IEEE Intell. Syst. 31(6), 5–14 (2016)
Le, Q., Mikolov, T.: Distributed representations of sentences and documents. In: International Conference on Machine Learning, pp. 1188–1196, January 2014
Mikolov, T., Chen, K., Corrado, G., Dean, J.: Efficient estimation of word representations in vector space. In: International Conference on Learning Representations: Workshops Track (2013)
Miller, B.:
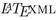 : A
: A 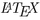 to XML/HTML/MathML Converter. http://dlmf.nist.gov/LaTeXML/
to XML/HTML/MathML Converter. http://dlmf.nist.gov/LaTeXML/Mikolov, T., Sutskever, I., Chen, K., Corrado, G.S., Dean, J.: Distributed representations of words and phrases and their compositionality. In: NIPS, pp. 3111–3119 (2013)
Murphy, K.P.: Machine Learning: A Probabilistic Perspective. MIT Press, Cambridge (2012)
Malon, C.D., Uchida, S., Suzuki, M.: Mathematical symbol recognition with support vector machines. Pattern Recogn. Lett. 29, 1326–1332 (2008)
Navigli, R.: Word sense disambiguation: a survey. ACM Comput. Surv. 41(2), 1–69 (2009)
Neumaier, A., Schodl, P.: A framework for representing and processing arbitrary mathematics. In: International Conference on Knowledge Engineering and Ontology Development, pp. 476–479 (2010)
Nickel, M., Kiela, D.: Poincare enbeddings for learning hierarchical representations. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (2017)
Nghiem, M.-Q., Yokoi, K., Matsubayashi, Y., Aizawa, A.: Mining coreference relations between formulas and text using Wikipedia. In: 2nd Workshop on NLP Challenges in the Information Explosion Era, Beijing, pp. 69–74 (2010)
Olver, F.W.J., Olde Daalhuis, A.B., Lozier, D.W., Schneider, B.I., Boisvert, R.F., Clark, C.W., Miller, B.R., Saunders, B.V., (eds.): NIST Digital Library of Mathematical Functions. https://dlmf.nist.gov/, Release 1.0.18 of 27 Mar 2018
Piotr, B., Grave, E., Joulin, A., Mikolov, T.: Enriching word vectors with subword information. Trans. Assoc. Comput. Linguist. 5, 135–146 (2017)
Pennington, J., Socher, R., Manning, C.D.: GloVe: global vectors for word representation. In: The 2014 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP), 25–29 October 2014, pp. 1532–1543 (2014)
Rudolph, M., Ruiz, F., Athey, S., Blei, D.M.: Structured embedding models for grouped data. In: NIPS, pp. 250–260 (2017)
Schoneberg, U., Sperber, W.: POS tagging and its applications for mathematics. In: CICM 2014, Coimbra, Portugal, pp. 213–223 (2014)
Schubotz, M., Grigorev, A., Leich, M., Cohl, H.S., Meuschke, N., Gippx, B., Youssef, A., Markl, V.: Semantification of identifiers in mathematics for better math information retrieval. In: The 39th Annual ACM SIGIR Conference (SIGIR 2016), Pisa, Italy, pp. 135–144, July 2016
Sutskever, I., Vinyals, O., Le, Q.V.: Sequence to sequence learning with neural networks. In: NIPS (2014)
Watt, S.M.: Exploiting implicit mathematical semantics in conversion between TEX and MathML. TUGBoat 23(1), 108 (2002)
Wolska, M., Grigore, M., Kohlhase, M.: Using discourse context to interpret object-denoting mathematical expressions. In: Towards Digital Mathematics Library, DML workshop, pp. 85–101. Masaryk University, Brno (2011)
Youssef, A.: Part-of-math tagging and applications. In: Geuvers, H., England, M., Hasan, O., Rabe, F., Teschke, O. (eds.) CICM 2017. LNCS (LNAI), vol. 10383, pp. 356–374. Springer, Cham (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-62075-6_25
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2018 This is a U.S. government work and its text is not subject to copyright protection in the United States; however, its text may be subject to foreign copyright protection
About this paper
Cite this paper
Youssef, A., Miller, B.R. (2018). Deep Learning for Math Knowledge Processing. In: Rabe, F., Farmer, W., Passmore, G., Youssef, A. (eds) Intelligent Computer Mathematics. CICM 2018. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 11006. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-96812-4_23
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-96812-4_23
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-96811-7
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-96812-4
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)


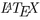 Beginner’s Guide. PACKT Publishing, Birmingham (2001)
Beginner’s Guide. PACKT Publishing, Birmingham (2001)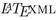 : A
: A 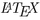 to XML/HTML/MathML Converter.
to XML/HTML/MathML Converter.