Abstract
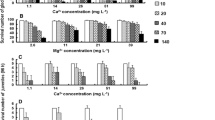
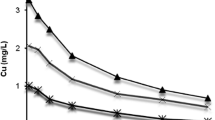
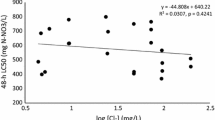
The possible interactive effect of the chlorides of copper and mercury on the euryhaline amphipod Gammarus duebeni in 100% sea water was examined using the following indices: (i) 96 h LC50 values, (ii) urine production rates and (iii) degree of mercury accumulation. Both (a) the interaction of the chlorides of mercury and copper together in solution and (b) the influence of cupric chloride pre-treatment of individuals prior to exposure to mercuric chloride were investigated. Presence of a sublethal level of cupric chloride protected G. duebeni against the toxic action of mercuric chloride. Cupric chloride pretreatment was not so effective. The nature of the interaction between mercury and copper is discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature Cited
Barnes, H. and F. A. Stanbury: The toxic action of copper and mercury salts both separately and when mixed on the harpacticid copepod, Nitocra spinipes (Boeck). J. exp. Biol. 25, 270–275 (1948)
Batley, G. E. and T. M. Florence: Determination of the chemical forms of dissolved cadmium, lead and copper in sea water. Mar. Chem. 4, 347–363 (1976)
Corner, E. D. S. and B. W. Sparrow: The modes of action of toxic agents. I. Observations on the poisoning of certain crustaceans by copper and mercury. J. mar. biol. Ass. U.K. 35, 531–548 (1956)
Foster, P. and A. W. Morris: The seasonal variation of dissolved ionic and organically associated copper in the Menai Straits. Deep Sea Research 18, 231–236 (1971)
Gray, J. S.: Synergistic effects of three heavy metals on growth rates of a marine ciliate protozoan. In: Pollution and physiology of marine organisms, pp 465–483. Ed. by F. J. Vernberg and W. B. Vernberg. New York and London: Academic Press 1974
Hunter, W. R.: The poisoning of Marinogammarus marinus by cupric sulphate and mercuric chloride. J. exp. Biol. 26, 113–124 (1949)
Kester, D. R., I. W. Duedeall, D. N. Connors and R. M. Pytkowick: Preparation of artificial sea water. Limnol. Oceanogr. 12, 176–179, (1967)
Lloyd, R. and L. D. Orr: The diuretic response by rainbow trout to sub-lethal concentrations of ammonia. Water Research 3, 335–344 (1969)
Lloyd, R. and D. J. Swift: Some physiological responses by fresh-water fish to low dissolved oxygen, high CO2, NH2 and phenol with particular reference to water balance. In: The effects of pollutants on aquatic organisms, p 47. Ed. by A. P. M. Lockwood. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press (1976)
Lockwood, A. P. M. and C. B. E. Inman,: Diuresis in the amphipod Gammarus duebeni induced by methylmercury, D. D. T., lindane fenithrothion. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 52C, 75–80 (1975)
Maddrell, S. H. P. and J. E. Casida: Mechanism of insecticideinduced diuresis in Rhodnius. Nature, Lond. 231, (5297), 55–56 (1971)
Millward, G. E. and J. D. Burton: Association of mercuric ions and humic acid in a sodium chloride solution. Mar. Sci. Comm. 1 (1), 15–26 (1975)
Moulder, S. M.: Effects of interactions between heavy metals and salinity on the physiological responses of the amphipod Gammarus duebeni, 174 pp. Ph. D. Thesis, University of Southampton. 1979
Murakami, T. H., M. Hayakawa, T. Fujii, T. Hara, Y. Itami, A. Kishida and I. Nisida: The effects of heavy metals on developing sea urchin eggs. J. Okayama Med. Soc. 88, 39–50 (1976)
Pineda, J. P.: Aspects of the organic chemistry of sea water. M. Phil. Thesis, Southampton University, 1973
Pyefinch, K. A. and J. C. Mott: The sensitivity of barnacles and their larvae to copper and mercury. J. exp. Biol. 25, 276–298 (1948)
Reeve, M. R., M. A. Walter, K. Darcy and T. Ikeda: Evaluation of potential indicators of sub-lethal toxic stress on marine zooplankton (feeding, fecundity, respiration and excretion): CEPEX. Bull. Mar. Sci. 27 (1), 105–113 (1977)
Tattersfield, F. and H. M. Morris: An apparatus for testing the toxic values of contact insecticides under controlled conditions. Bull. Entomol. Res. 14, 223–233 (1924)
Williams, P. M.: The association of copper with dissolved organic matter in sea water. Limnol. Oceanogr. 14, 156–158 (1969)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by J. Mauchline, Oban
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moulder, S.M. Combined effect of the chlorides of mercury and copper in sea water on the euryhaline amphipod Gammarus duebeni . Mar. Biol. 59, 193–200 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00404741
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00404741