Abstract
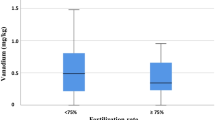
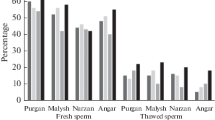
This paper reports differences observed in the elemental content of fertile and infertile human spermatozoa used in an in vitro fertilization (IVF) program. “Fertile” and “infertile” were designated by the successful penetration or failure to penetrate an oocyte in vitro. We report morphological and morphometric differences which, together with elemental changes, may be causes of infertility in apparently normal spermatozoa. There were significant differences (P<0.05) in sodium and chlorine concentrations between fertile and infertile samples and there was more chlorine than could be accounted for as sodium chloride. Many spermatozoa showed particles adhering to tails, with a higher incidence of “contamination” in the infertile spermatozoa. There were significant differences in both shapes of heads and lengths of tails between fertile and infertile spermatozoa.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sundström P, Nilsson O, Liederholm P: Cleavage rate and morphology of early embryos obtained after artificial fertilization and culture. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 1981;60:109–120
Lopata A, Kohlman DJ, Kellow GN: The fine structure of human blastocysts developed in culture. Prog Clin Biol Res 1982;85:69–85
Dvorak M, Tesarik J, Pilka L, Travnik P: Fine structure of human two cell ova fertilized and cleavedin vitro. Fertil Steril 1982;37:661–667
Mohr L, Trounson A: Comparative ultrastructure of hatched human, mouse and bovine blastocysts. J Reprod Fert 1982;66:499–504
Trounson A, Mohr L: Human pregnancy following cryopreservation, thawing and transfer after an eight cell embryo. Nature 1983;305:707–709
Chandler JA, Battersby S: X-ray microanalysis of ultrathin frozen and freeze dried sections of human sperm cells. J Microsc 1976;107:55
Faine-Maurel MA, Dadoune JP: Scanning electron microscopy X-ray. Microanalysis and distribution of elements within the head of human spermatozoa. Arch Androl 1979;3:1–11
Baccetti B, Burrini AG, Pallini V: Spermatozoa and cilia lacking axoneme in an infertile man. Andrologia 1980;12:525–532
Chandler JA: Application of X-ray microanalysis in reproductive physiology. Scan Electron Microsc 1980;Pt 2:475–484
Dadoune JP, Fain-Maurel MA, Guillaumin M, Guillaumin D: Scanning electron microscope morphometry of a discriminated population of elongated human spermatozoa. Int J Fertil 1980;25:18–27
Harrison RF, Sheppard BL, Kaliszerm M: Observation on the motility, ultrastructure and elemental composition of human spermatozoa incubated with caffeine. II. A time sequence study. Andrologia 1980;12:434–443
Muscato JJ, Haney AF, Weinberg JB: Sperm phagocytosis by human peritoneal macrophages: A possible cause of infertility in endometriosis. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1980;144:503–510
Shappard BL, Sheppard U, Harrison RF: The preparation of human spermatozoa for analytical and scanning electron microscopy. J Microsc 1980;119:241–247
Cheng CY, Rose RJ, Boettcher B: The binding of oestrodiol-17B to human spermatozoa—an electron microscope autoradiographic study. Int J Androl 1981;4:304–313
Langlais J, Zollinger M, Plante L, Chapdelaine A, Bleau G, Roberts KD: Localization of cholesterol sulfate in human spermatozoa in support of the hypothesis for the mechanism of capacitation. Proc Natl Acad Sci 1981;78:7266–7270
Mortimer D: The assessment of human sperm morphology in surface replica preparations for transmission electron microscopy. Gamete Res 1981;4:113–119
Perroti ME, Gariola A, Gioria M: Ultrastructural study of the decapitated sperm defect in infertile men. J Reprod Fert 1981;63:543–549
Söderström KO: An acrosomal abnormality in spermatids from infertile men. Arch Androl 1981;7:275–278
Pedersen H, Hammen R: Ultrastructure of human spermatozoa with complete subcellular derangement. Arch Androl 1982;9:251–259
Sauvalle AM, Prigent JR, Izard JY: A method of comparing spermatozoa with light and scanning electron microscopy. Acta Cytol 1982;26:371–375
Hall TA, Gupta BL: The localization and assay of chemical elements by microprobe methods. Q Rev Biophys 1983;16:279–339
Appleton TC: A cryostat approach to ultrathin “dry” frozen sections for electron microscopy: A morphological and X-ray analytical study. J Microsc 1974;100:49–74
Edwards RG, Anderson, Pickering, Purdy JM: Rapid assay of urinary LH in women using a simplified method of Hi-Gonavis.In Human Conceptionin Vitro, RG Edwards, JM Purdy (eds). London, Academic Press, 1982, pp 19–34
Brown JB, McLeod SG, MacNaughton C, Smith MA, Smyth B: A rapid method for estimating oestrogens in urine using a semi-automatic extractor. J Endocrinol 1968;42:5–15
Steptoe PC, Edwards RG, Purdy JM: Clinical aspects of pregnancies established with cleaving embryos grown in culture. Br J Obstet Gynecol 1980;87:737–756
Edwards RG: Test-tube babies. Nature 1981;293:253–256
Steptoe PC, Webster J: Laproscopy of normal and disordered ovary.In Human Conceptionin Vitro, RG Edwards, JM Purdy (eds). London, Academic Press, 1982, pp 97–103
Edwards RG, Purdy JM, Steptoe PC, Walters: The growth of human pre-implantation embryosin vitro. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1981;141:404–416
Purdy JM: Methods forin vitro fertilization and embryo culturein vitro.In Human Conceptionin Vitro, RG Edwards, JM Purdy (eds). London, Academic Press, 1982, pp 135–148
Edwards RG, Steptoe PC: Induction of follicular growth, ovulation and luteinization of the human ovary. J Reprod Fertil Suppl 1975;2:121–156
Edwards RG: Conception in the Human Female. London, Academic Press, 1980
Fishel S, Edwards RG: Essentials of fertilization.In Human Conceptionin Vitro, RG Edwards, JM Purdy (eds). London, Academic, Press, 1982, pp 157–179
Appleton TC: Cryo-ultramicrotomy, possible applications in cytochemistry.In Electron Microscopy and Cytochemistry, E Wisse, WTh Daems, I Molenaar, P van Dui (eds). Amsterdam, North-Holland, 1974, pp 229–242
Appleton TC: The contribution of cryo-ultramicrotomy to X-ray microanalysis in biology.In Electron Probe Microanalysis in Biology, DA Erasmus (ed). London, Chapman & Hall, 1978, pp 148–182
Appleton TC: The localization of diffusible substances: Experience in the electron microscope. J Histochem Cytochem 1979;27:1518–1519
Warley A, Stephen J, Hockaday A, Appleton TC: X-ray microanalysis of HeLa S3 Cells. I. Instrumental calibration and analysis of randomly growing cultures. J Cell Sci 1983;60:217–229
Swenson CE, O'Leary WM: Examination of human semen infected with Ureaplasma urealyticum by fluorescence microscopy. Arch Androl 1980;5:373–377
Chandler JA: X-ray microanalysis in the electron microscope.In Practical Methods in the Electron Microscope, AM Glauert (ed). Amsterdam, North-Holland, Vol 5, pp 503–505
Hyne RV, Higgison RE, Kohlman D, Lopata A: Sodium requirement for capacitation and membrane fusion during guinea pig sperm acrosome reaction. J Reprod Fert 1984;70:83–94
Baker JRJ, Appleton TC: A technique for electron microscopeautoradiography (and X-ray microanalysis) of diffusible substances using freeze-dried fresh frozen sections. J Microsc 1976;108:307–315
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Appleton, T.C., Fishel, S.B. Morphology and X-ray microprobe analysis of spermatozoa from fertile and infertile men in in vitro fertilization. J Assist Reprod Genet 1, 188–203 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01139213
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01139213