Abstract
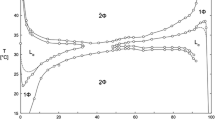
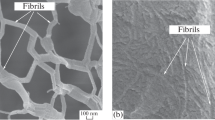
In this work, the effect of octane concentration on the phase behavior of CTAB/water/1-butanol system was studied by using pulsed field gradient spin-echo NMR measurements and freeze fracture electron microscopy (Cryo-TEM and FFEM). When the octane concentration increases, the liquid crystalline phase is destabilized and a continuous single-phase microemulsion region from the water apex to the oil apex is formed. The conductivity behavior has a distinct percolative phenomenon, which indicates that the single-phase microemulsion is changed continuously from oil-in-water (o/w) structure via a bicontinuous structure to water-in-oil (w/o) structure. This result is consistent with those of the PGSE-NMR, Cryo-TEM, and FFEM. In the w/o region, the self-diffusion coefficient of water is relatively high ((1–6)×10−10 m · s−1) due to the higher solubility of water in the continuous phase consisting of octane (10% by weight) and 1-butanol. The penetration of a large amount of octane molecules between surfactant chains results in the much lower self-diffusion coefficient of octane.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Eicke, H.-F., Topic in Current Chemistry: Micelles, Berlin: Springer-Verlag, 1980, 85–135.
Lindman, B., Stilbs, P., Microemulsion System (eds. Rosana, H. L., Clausse, M.), Surfactant Science Series, Vol. 24, New York: Marcel Dekker, 1987, 125–168.
Jahn, W., Strey, R., Microstructure of microemulsions by freeze fracture electron microscopy, J. Phys. Chem., 1988, 92: 2294.
Yinson, P. K., Bellare, J. R., Davis, H. T. et al., Direct imaging of surfactant micelles, vesicles, discs, and ripple phase structures by Cryo-transmission Electron Microscopy, J. Colloid and Interface Science, 1991, 142(1): 74.
Gustafsson, J., Nylander, T., Almgren, M. et al., Phase behavior and aggregate structure in aqueous mixtures of sodium chelate and glycerol monooleate, J. Colloid and Interface Science, 1999, 211: 326.
Beck, R., Gradzielski, M., Horbaschek, K. et al., Phase behavior, structure, and physical properties of the quarternary system teradecylamine oxide, HC1, 1-hexanol, and water, J. Colloid and Interface Science, 2000, 221: 200.
Regev, O., Ezrahi, S., Aserin, A. et al., A study of the microstructure of a four-component nonionic microemulsion by Cryo-TEM, NMR, SAXS, and SANS, Langmuir, 1996, 12: 668.
Hao Jingcheng, Wang Hanqing, Li Guozuo et al., Phase behavior and microstructures of microemulsions (1), Science in China, Ser. B, 1997, 40: 225.
Bolzinger-Thevenin, M. A., Grossiord, J. L., Poelman, M. C., Characterization of a sucrose ester microemulsion by Freeze Fracture Electron Micrograph and SANS experiments, Langmuir, 1999, 15: 2307.
Olsson, U., Shinoda, K., Lindman, B., Change of the structure of microemulsions with the hydrophile-lipophile balance of nonionic surfactant as revealed by NMR self-diffusion studies, J. Phys. Chem., 1986, 90: 4083.
Nisson, P. G., Lindman, B., Water self-diffusion on nonionic surfactant solutions, Hydration and obstruction effects, J. Phys. Chem., 1983, 87: 4756.
Ceglie, A., Das, K. P., Lindman, B., Effect of oil on the microscopic structure in four-component cosurfactant microemulsions, J. Colloid. and Inter. Sci., 1987, 115: 115.
Eicke, H. F., Denss, A., Solution Chemistry of Surfactants (ed. Mitta, K. L.), New York: Plenum Press, 1979, 699–745.
Stubenrauch, C., Findenegg, G. H., Microemulsions supported by octyl monoglucoside and geraniol (2): An NMR self-diffusion study of the microstructure, Langmuir, 1998, 14: 6005.
Corswant, C., Olsson, C., Soderman, O., Microemulsions based on soybean phosphatidylcholine and isopropylmyristate—Effect of addition of hydrophilic surfactants, Langmuir, 1998, 14: 6864.
Geiger, S., Eicke, H. F., The macrofluid concept versus the molecular mixture: A Spin-Echo-NMR study of the water/aerosol OT/oil system, J Colloid and Inter. Sci., 1986, 110: 181.
Jonstromer, M., Olsson, U., Parker, W. O., A self-diffusion study of microemulsion structure using a polar solvent mixture, Langmuir, 1995, 11: 61.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, J., Li, G., Zhai, L. et al. A study of the microstructure of CTAB/1-butanol/octane/ water system by PGSE-NMR and Cryo-TEM. Chin. Sci. Bull. 46, 1272–1276 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03184323
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03184323