Abstract
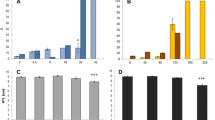
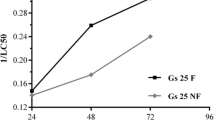
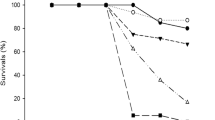
Water sources used as reproductive sites by crying frog, Physalaemus gracilis, are extensively associated with agroecosystems in which the herbicide atrazine is employed. To evaluate the lethal and sublethal effects of atrazine commercial formulation, acute and chronic toxicity tests were performed in the embryonic phase and the beginning of the larval phase of P. gracilis. Tests were started on stage 19 of Gosner (Herpetologica 16:183–190, 1960) and performed in 24-well cell culture plates. Acute tests had a duration of 96 h with embryo mortality monitoring every 24 h. Chronic assays contemplated the transition from the embryonic to larval stages and lasted 168 h. Every 24 h the embryos/larvae were observed for mortality, mobility, and malformations. The LC50 of atrazine determined for P. gracilis embryos was 229.34 mg L−1. The sublethal concentrations did not affect the development of the larvae but were observed effects on mobility and malformations, such as spasmodic contractions, reduced mobility, malformations in mouth and intestine, and edema arising. From 1 mg L−1 atrazine, the exposed larvae began to have changes in mobility and malformations. The atrazine commercial formulation has caused early life effects of P. gracilis that may compromise the survival of this species but at higher concentrations than recorded in the environment, so P. gracilis can be considered tolerant to this herbicide at environmentally relevant concentrations.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albuquerque AF, Ribeiro JS, Kummrow F, Nogueira AJA, Montagner CC, Umbuzeiro GA (2016) Pesticides in Brazilian freshwaters: a critical review. Environ Sci Process Impacts 18:779–787. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6EM00268D
Belanger RM, Peters TJ, Sabhapathy GS, Khan S, Katta J, Abraham NK (2015) Atrazine exposure affects the ability of crayfish (Orconectes rusticus) to localize a food odor source. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 68:636–645. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-015-0142-y
Belanger RM, Mooney LN, Nguyen HM, Abraham NK, Peters TJ, Kana MA, May LA (2016) Acute atrazine exposure has lasting effects on chemosensory responses to food odors in Crayfish (Orconectes virilis). Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 70:289–300. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-015-0234-8
Brazil (2008) Resolução Conama no. 396, de 3 de abril de 2008. http://www.mma.gov.br/port/conama/legiabre.cfm?codlegi=562. Accessed 19 Dec 2017
Brazil (2011) Portaria no. 2.914, de 12 de dezembro de 2011. http://bvsms.saude.gov.br/bvs/saudelegis/gm/2011/prt2914_12_12_2011.html. Accessed 19 Dec 2017
Bridges CM (2000) Long-term effects of pesticide exposure at various life stages of the southern leopard frog (Rana sphenocephala). Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 39:91–96. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002440010084
Brodeur JC, Svartz G, Perez-Coll CS, Marino DJG, Herkovits J (2009) Comparative susceptibility to atrazine of three developmental stages of Rhinella arenarum and influence on metamorphosis: non-monotonous acceleration of the time to climax and delayed tail resorption. Aquat Toxicol 91:161–170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2008.07.003
Casara KP, Vecchiato AB, Lourencetti C, Pinto AA, Dores EFGC (2012) Environmental dynamics of pesticides in the drainage area of the São Lourenço River Headwaters, Mato Grosso State, Brazil. J Braz Chem Soc 23:1719–1731
Cerejeira MJ, Viana P, Batista S, Pereira T, Silva E, Valerio MJ, Silva A, Ferreira M, Fernandes AM (2003) Pesticides in Portuguese surface and ground waters. Water Res 37:1055–1063. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1354(01)00462-6
Chicati ML, Nanni MR, Cézar E (2012) Chemical contamination of water in irrigated rice on Paraná State, Brazil. Semina Cienc Agrar 33:1455–1462
Christopher R, Kinney O, Fiori A, Congdon J (1996) Oral deformities in tadpoles (Rana catesbeiana) associated with coal ash deposition: effects on grazing ability and growth. Freshw Biol 36:723–730. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2427.1996.00123.x
Duellman WE, Trueb L (1994) Biology of amphibians. McGraw-Hill, New York
Ezemonye L, Tongo I (2009) Lethal and sublethal effects of atrazine to amphibian larvae. Jordan J Biol Sci 2:29–36
Freitas CM, Porto MFS, Pivetta F, Moreira JC, Machado JMH (2001) Poluição química ambiental: um problema de todos, que afeta uns mais que os outros. http://www6.ensp.fiocruz.br/repositorio/resource/353526. Accessed 3 July 2017
Frost DR (2017) Amphibian species of the world: an online reference. Version 6.0 5.5. http://research.amnh.org/herpetology/amphibia/index.html. Accessed 7 Aug 2017
GHS (2011) Globally harmonized system of classification and labelling of chemicals. United Nations, New York
Gonçalves MW, Carvalho WF, Pereira RR, Silva DM, Bastos RP, Cruz AD (2014) Avaliação de danos genômicos em anfíbios anuros do cerrado goiano. Estudos 41:89–104
Gosner KL (1960) A simplified table for staging anuran embryos and larvae with notes on identification. Herpetologica 16:183–190
Graymore M, Stagnitti F, Allinson G (2001) Impacts of atrazine in aquatic ecosystems. Environ Int 26:483–495. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0160-4120(01)00031-9
Hayes TB, Collins A, Lee M, Mendonza M, Noriega N, Stuart AA, Vonk A (2002) Hermaphroditic, demasculinized frogs after exposure to the herbicide atrazine at low ecologically relevant doses. PNAS 99:5476–5480. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.082121499
Herkovits J, Ponce B, Olabe J (1980) Efecto de la prostaglandina F2 alfa sobre la proliferación celular y el transporte de Na, K, Ca y Mg en células epiteliales embrionarias. Medicina 40:858–859
IBAMA (2014) Brazilian Institute of Environment and Renewable Natural Resources Pesticides and related products marketed in 2014 in Brazil. http://www.ibama.gov.br/agrotoxicos/relatorios-de-comercializacao-de-agrotoxicos. Accessed 1 Aug 2017
Knapp RA, Morgan AT (2006) Tadpole mouthpart depigmentation as an accurate indicator of chytridiomycosis, an emerging disease of amphibians. Copeia 2:188–197
Knutson MG, Richardson WB, Reineke DM, Gray BR, Parmelee JR, Weick SE (2004) Agricultural ponds support amphibian populations. Ecol Appl 14:669–684
Lajmanovich RC, Sandoval MT, Peltzer PM (2003) Induction of mortality and malformation in Scinax nasicus larvae exposed to glyphosate formulations. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 70:612–618. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-003-0029-x
Larson DL, McDonald S, Fivizzani AJ, Newton WE, Hamilton SJ (1998) Effects of the herbicide atrazine on Ambystoma tigrinum metamorphosis: duration, larval growth, and hormonal response. Physiol Zool 71:671–679
Lavilla E, Kwet A, Segalla MV, Langone J, Baldo D (2010) Physalaemus gracilis. In the IUCN red list of threatened species. The IUCN red list of threatened species. Version 2017-1. www.Iucnredlist.org. Accessed 7 Aug 2017
Lenkowski JR, Reed MJ, Deininger L, Mclaughlin KA (2008) Perturbation of organogenesis by the herbicide atrazine in the amphibian Xenopus laevis. Environ Health Perspect 116:223–230. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.10742
Lingnau R (2009) Distribuição temporal, atividade reprodutiva e vocalizações em uma assembleia de anfíbios anuros de uma floresta ombrófila mista em Santa Catarina, sul do Brasil. Tesis, Pontifícia Universidade Católica do Rio Grande do Sul
McDiarmid RW, Altig R (1999) Tadpoles: the biology of anuran larvae. The University of Chicago Press, Chicago
McMahon TA, Romansic JM, Rohr JR (2013) Non-monotonic and monotonic effects of pesticides on the pathogenic fungus Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis in culture and on larvae. Environ Sci Technol 47:7958–7964. https://doi.org/10.1021/es401725s
Miltner RJ, Baker DB, Speth TF (1989) Treatment of seasonal pesticides in surface water. J Am Water Works Assoc 81:43–52
Montagner CC, Vidal C, Acayaba RD, Jardim WF, Jardim ICSF, Umbuzeiro G (2014) Trace analysis of pesticides and an assessment of their occurrence in surface and drinking waters from the State of São Paulo (Brazil). Anal Methods 6:6668–6677
Moreira JC, Peres F, Simões AC, Pignati WA, Dores EC, Vieira SN, Strüssmann C, Mott T (2012) Contaminação de águas superficiais e de chuva por agrotóxicos em uma região do estado do Mato Grosso. Ciência e Saúde Coletiva 17:1557–1568. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1413-81232012000600019
Morgan MK, Scheuerman PR, Bishop CS, Pyles RA (1996) Teratogenic potential of atrazine and 2,4-D using FETAX. J Toxicol Environ Health 48:151–168
Newman MC, Unger MA (2003) Fundamentals of ecotoxicology. Lewis Publishers, Boca Raton
Nieves-Puigdoller K, Björnsson BT, McCormick SD (2007) Effects of hexazinone and atrazine on the physiology and endocrinology of smolt development in Atlantic salmon. Aquat Toxicol 84:27–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2007.05.011
OECD (2013) Test No. 236: Fish Embryo Acute Toxicity (FET) test. OECD guidelines for the testing of chemicals, Section 2. OECD Publishing, Paris
Ortiz-Santaliestra ME, Marco A, Fernández MJ, Lizana M (2006) Influence of developmental stage on sensitivity to ammonium nitrate of aquatic stages of amphibians. Environ Toxicol Chem 25:105–111. https://doi.org/10.1897/05-023R.1
Peltzer PM, Junges CM, Attademo AM, Bassó A, Grenón P, Lajmanovich RC (2013) Cholinesterase activities and behavioral changes in Hypsiboas pulchellus (Anura: Hylidae) larvae exposed to glufosinate ammonium herbicide. Ecotoxicology 22:1165–1173. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-013-1103-8
Pérez-Iglesias JM, Soloneski S, Nikoloff N, Natale GS, Larramendy ML (2015) Toxic and genotoxic effects of the imazethapyr-based herbicide formulation Pivot H® on Montevideo tree frog Hypsiboas pulchellus larvae (Anura, Hylidae). Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 119:15–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2015.04.045
Rao DG, Senthilkumar R, Byrne JA, Feroz S (2013) Waste water treatment: advanced processes and technologies. CRC, New York
Rohr JR, McCoy KA (2010) A qualitative meta-analysis reveals consistent effects of atrazine on freshwater fish and amphibians. Environ Health Perspect 118:20–32. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.0901164
Rohr JR, Elskus AA, Shepherd BS, Crowley PH, McCarthy TM, Niedzwiecki JH, Sager T, Sih A, Palmer BD (2003) Lethal and sublethal effects of atrazine, carbaryl, endosulfan, and octylphenol on the streamside salamander (Ambystoma barbouri). Environ Toxicol Chem 22:2385–2392. https://doi.org/10.1897/02-528
Sass JB, Colangelo A (2006) European Union bans Atrazine, while the United States negotiates continued use. Int J Occup Environ Health 12:260–267. https://doi.org/10.1179/oeh.2006.12.3.260
Schiesari L, Grillittsch B, Grillittsch H (2007) Biogeographic biases in research and their consequences for linking amphibian declines to pollution. Conserv Biol 21:465–471
Semlitsch RD (ed) (2003) Introduction: general threats to amphibians. In: Amphibian conservation. Smithsonian books, Washington, London, pp 1–7
Simon E, Puky M, Braun M, Tóthmérész B (2012) Assessment of the effects of urbanization on trace elements of toe bones. Environ Monit Assess 184:5749. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-011-2378-y
Sousa AS, Duaví WC, Cavalcante RM, Milhome MA, Nascimento RF (2016) Estimated levels of environmental contamination and health risk assessment for herbicides and insecticides in surface water of Ceará, Brazil. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 96:90
Svartz GV, Herkovits J, Pérez-Coll CS (2012) Sublethal effects of Atrazine on embyo-larval development of Rhinella arenarum (Anura: Bufonidae). Ecotoxicology 21:1251–1259. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-012-0880-9
USEPA (United States Environmental Protection Agency) (2014) Atrazine ecological exposure monitoring program data Document ID: EPA-HQ-OPP-2003-0367-0303
Venesky MD, Parris MJ, Storfer A (2010) Impacts of Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis infection on tadpole foraging performance. EcoHealth 6:565–575. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10393-009-0272-7
Zhang JJ, Lu YC, Zhang JJ, Tan LR, Yang H (2014) Accumulation and toxicological response of atrazine in rice crops. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 102:105–112
Acknowledgements
Valuable help in laboratorial work was provided by Jessica Herek, Jéssica G. Slaviero, and Gregori B. Bieniek. The authors are grateful to the Federal University of Fronteira Sul—UFFS for providing logistical support. Camila Rutkoski, Natani Macagnan, and Cassiane Kolcenti were supported by fellowship from Fundação de Amparo a Pesquisa do Estado do Rio Grande do Sul—FAPERGS.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This study was licensed by IBAMA (50398-1) and authorized by the Ethics Committee for Animal Use of the Federal University of Fronteira Sul.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rutkoski, C.F., Macagnan, N., Kolcenti, C. et al. Lethal and Sublethal Effects of the Herbicide Atrazine in the Early Stages of Development of Physalaemus gracilis (Anura: Leptodactylidae). Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 74, 587–593 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-017-0501-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-017-0501-y