Abstract.
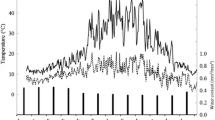
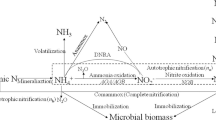
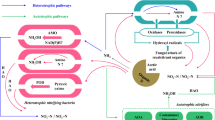
Laboratory incubation experiments were conducted to study the influence of easily oxidizable C (glucose) and mineral N (NH4 + and NO3 –) on N2O emission, evolution of CO2 and consumption of O2. A flush of N2O was always observed during the first few hours after the start of soil incubation, which was significantly higher with NH4 + compared to NO3 – applications. The increase in N2O emission was attributed mainly to enhanced soil respiration and subsequent O2 limitation at the microsite level. Application of NH4 + helped to develop denitrifying populations since subsequent additions of NO3 – and a C source significantly enhanced N2O emissions. In soils treated with NH4 +, N2O emissions declined rapidly, which was related to decreasing concentrations of easily oxidizable C. Addition of glucose in different amounts and pre-incubation of soil for different lengths of time (to create variation in the amount of easily oxidizable C) changed the pattern of N2O emissions, which was ascribed to changes in soil respiration.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Azam, .F., Müller, .C., Weiske, .A. et al. Nitrification and denitrification as sources of atmospheric nitrous oxide – role of oxidizable carbon and applied nitrogen. Biol Fertil Soils 35, 54–61 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-001-0441-5
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-001-0441-5